인프런 김영한님의 스프링 MVC 1편 강의 내용을 바탕으로 작성한 글입니다.
1. 서블릿 등록하기
package hello.servlet;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletComponentScan;
@ServletComponentScan // 서블릿 자동 등록
@SpringBootApplication
public class ServletApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ServletApplication.class, args);
}
}@ServletComponentScan: 스프링 부트에서 서블릿을 직접 등록해서 사용할 수 있도록 지원하는 어노테이션
@WebServlet(name = "exampleServlet", urlPatterns = "/example")
public class ExampleServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
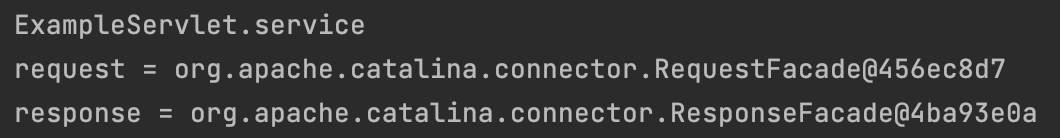
System.out.println("ExampleServlet.service");
System.out.println("request = " + request);
System.out.println("response = " + response);
}
}@WebServlet: 해당 클래스를 서블릿으로 등록하는 어노테이션name: 서블릿의 이름을 설정할 수 있음urlPatterns: 서블릿과 매핑할 URL을 설정할 수 있음
- 서블릿과 매핑된 URL이 호출되면, 서블릿 컨테이너는 해당 서블릿의
service()메서드를 실행- 위의 경우는
/exampleURL로 요청이 오면,ExampleServlet의service()가 호출된다. - 브라우저 주소창에
localhost:8080/example을 입력한 뒤 콘솔창을 확인해보자.
- 위의 경우는
2. HttpServletRequest
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
printRequestInfo(request);
}
private void printRequestInfo(HttpServletRequest request) {
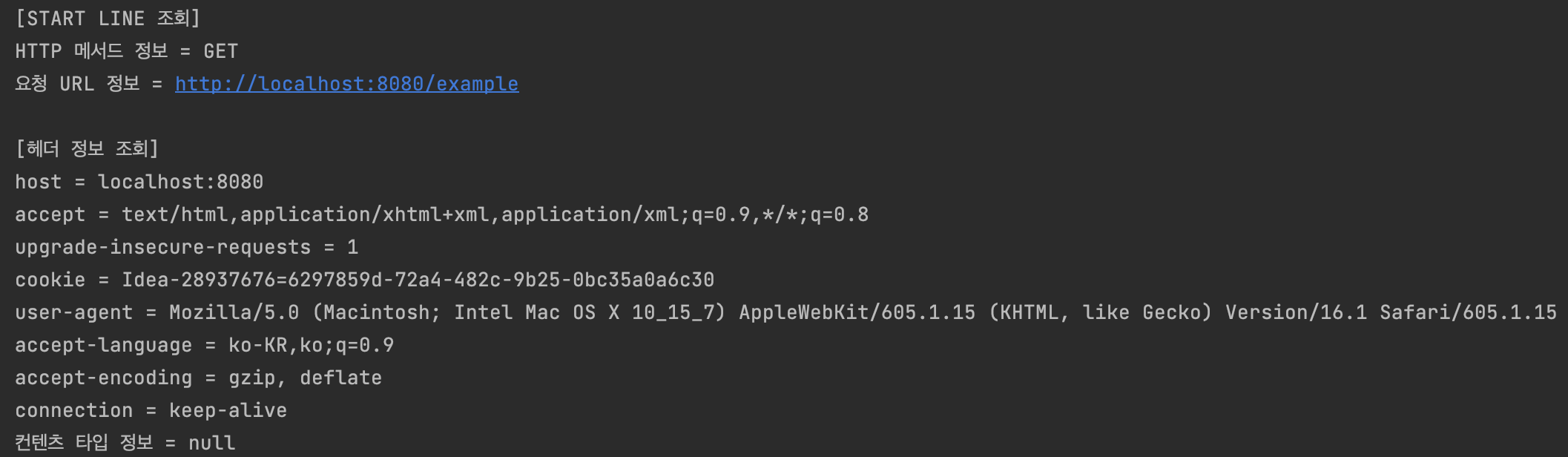
System.out.println("[START LINE 조회]");
System.out.println("HTTP 메서드 정보 = " + request.getMethod());
System.out.println("요청 URL 정보 = " + request.getRequestURL());
System.out.println();
System.out.println("[헤더 정보 조회]");
request.getHeaderNames().asIterator()
.forEachRemaining(headerName -> System.out.println(headerName + " = " + request.getHeader(headerName)));
System.out.println("컨텐츠 타입 정보 = " + request.getContentType());
}HttpServletRequest: HTTP 요청 메세지를 파싱한 결과가 담기는 클래스- 개발자는
HttpServletRequest를 통해 HTTP 요청 메세지를 편리하게 사용할 수 있다.
- 개발자는
- HttpServletRequest가 제공하는 기능
- START LINE 조회
- HTTP 메서드 정보:
request.getMethod() - 요청URL:
request.getRequestURI() - 그 외 쿼리 스트링, 스키마, 프로토콜 정보 등 조회 가능
- HTTP 메서드 정보:
- 헤더 조회
- 모든 헤더 정보 조회:
request.getHeaderNames() - 특정 헤더 정보만 조회:
request.getHeader(headerName) - HTTP 요청 메세지의 컨텐츠 타입 조회:
request.getContentType() - 그 외 다양한 헤더 정보 조회 가능
- 모든 헤더 정보 조회:
- 바디 조회: form 파라미터 형식 조회, 메세지 바디 데이터 직접 조회 가능
- 임시 저장소 기능
- 저장:
request.setAttribute(name, value) - 조회:
request.getAttribute(name)
- 저장:
- 세션 관리 기능
request.getSession(create: true)
- START LINE 조회
- 실행 결과
3. HTTP 요청 데이터 전송
HTTP 요청 메세지를 통해 클라이언트에서 서버로 데이터를 전송하는 방법은 크게 3가지가 있다.
(1) GET - 쿼리 파라미터 이용
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("username = " + request.getParameter("username"));
System.out.println("age = " + request.getParameter("age"));
}- 메세지 바디 없이 URL의 쿼리 파라미터를 사용해서 데이터 전달
- 그대로 노출되는 영역이므로, 외부에 보여져도 상관없는 데이터를 전달할 때 사용
?로 시작, 각 파라미터들을&로 구분- 실행:
http://localhost:8080/example?username=kim&age=20

(2) POST - HTML Form 이용
- HTML Form을 통해 데이터를 전송하는 방법
- content-type이
application/x-www-form-urlencoded가 됨 - 메세지 바디에 쿼리 파라미터 형식으로 데이터가 들어감
username=kim&age=20
- 형식이 동일하므로 쿼리 파라미터 조회 메서드와 같은 방법으로 조회 가능
💡 쿼리 파라미터 형식으로 데이터를 전송할 때는, HTTP 메세지 바디에 데이터가 들어가지 않기 때문에 content-type이
null이었다. 하지만 HTML Form을 이용해 데이터를 전송하면, HTTP 메세지 바디에 데이터가 들어가기 때문에 content-type이application/x-www-form-urlencoded가 된다.
포스트맨을 이용해 간단하게 테스트해보자.
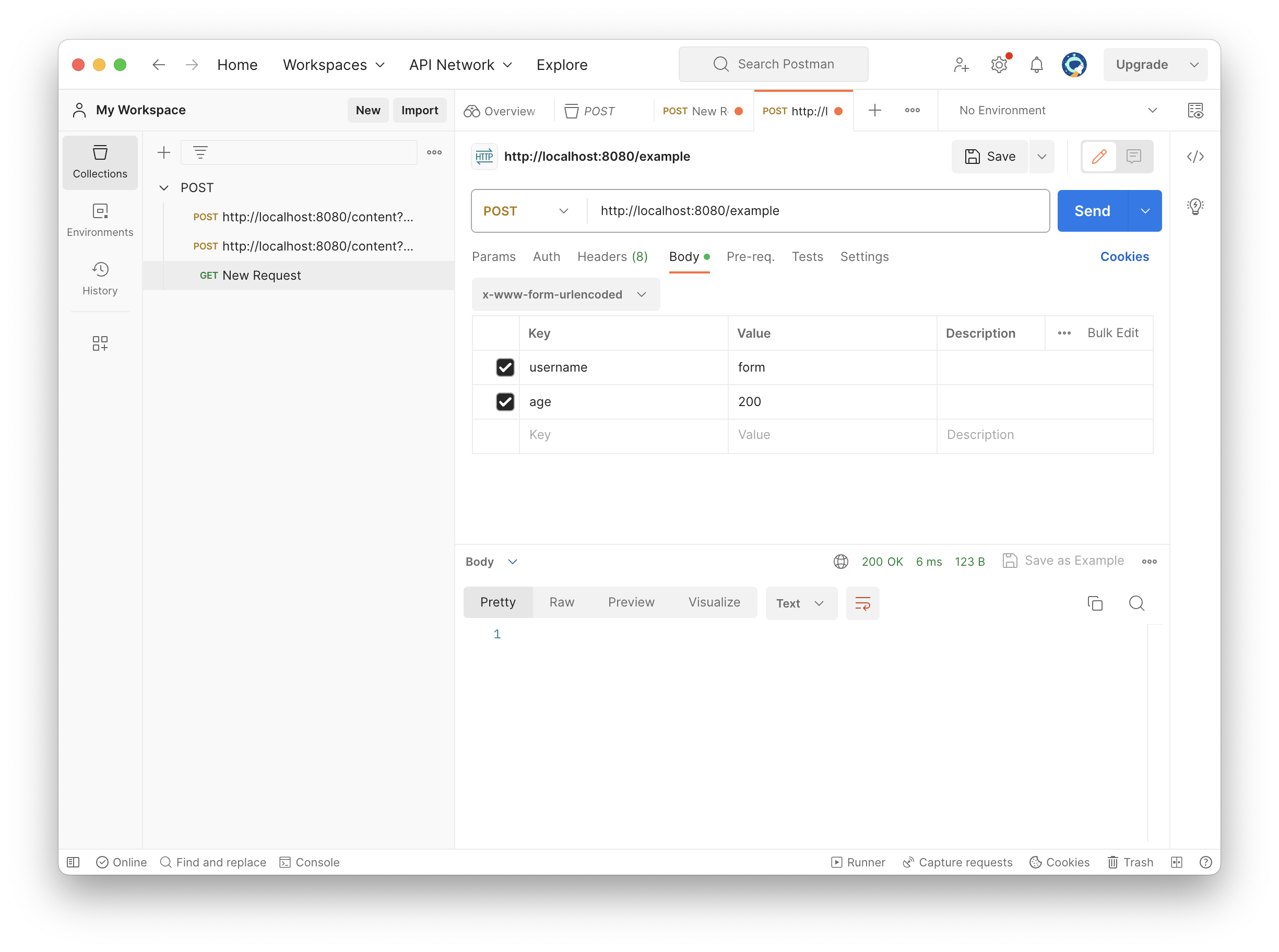
콘솔창을 확인하면 실행 결과가 제대로 찍히는 것을 확인할 수 있다.

(3) HTTP 메세지 바디에 직접 담아 전송
- HTTP 메세지 바디에 데이터를 직접 담아서 전송하는 방법
- HTTP API에서 주로 사용하는 방식
- 데이터 형식은 주로 JSON 사용
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletInputStream inputStream = request.getInputStream();
String data = StreamUtils.copyToString(inputStream, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("message body = " + data);
response.getWriter().write("ok!");
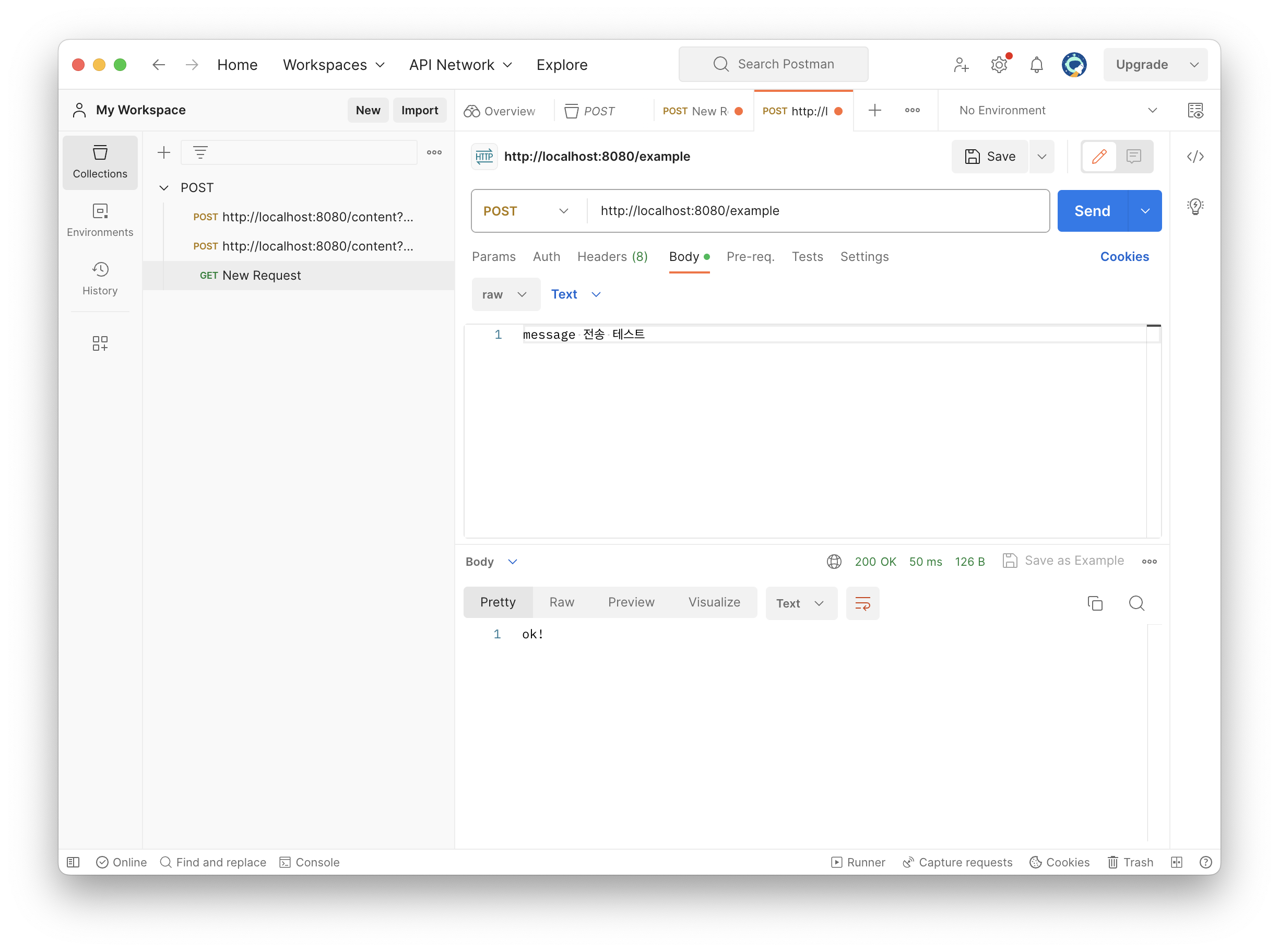
}- 텍스트 형식 데이터 전송
- content-type: text/plain
- 메세지 바디에 담기는 내용:
message 전송 테스트 request.getInputStream(): HTTP 메세지 바디 내용을 스트림으로 꺼내옴inputStream은 byte코드를 반환하므로, 우리가 읽을 수 있는 문자로 변환하기 위해 인코딩 형식을 UTF-8로 지정
포스트맨을 이용해 간단하게 테스트해보자.

- JSON 형식 데이터 전송
- HTTP API에서 주로 사용하는 방식이다.
- content-type: application/json
- 메세지 바디에 담기는 내용:
{"username": "kim", "age": 20}
테스트 진행 전, 들어오는 JSON 형식의 데이터를 객체로 변환할 수 있도록 동일 패키지에 ExampleData 클래스를 하나 추가한다.
@Getter
@Setter
public class ExampleData {
private String username;
private int age;
}JSON 데이터를 객체로 파싱하려면, JSON 변환 라이브러리를 추가해야 한다. 여기서는 Jackson 라이브러리의 ObjectMapper를 이용하여 파싱하였다.
@WebServlet(name = "exampleServlet", urlPatterns = "/example")
public class ExampleServlet extends HttpServlet {
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletInputStream inputStream = request.getInputStream();
String data = StreamUtils.copyToString(inputStream, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("message body = " + data);
ExampleData exampleData = objectMapper.readValue(data, ExampleData.class);
System.out.println("exampleData.username = " + exampleData.getUsername());
System.out.println("exampleData.age = " + exampleData.getAge());
response.getWriter().write("ok!");
}이제 포스트맨을 이용해 간단하게 테스트해보자.
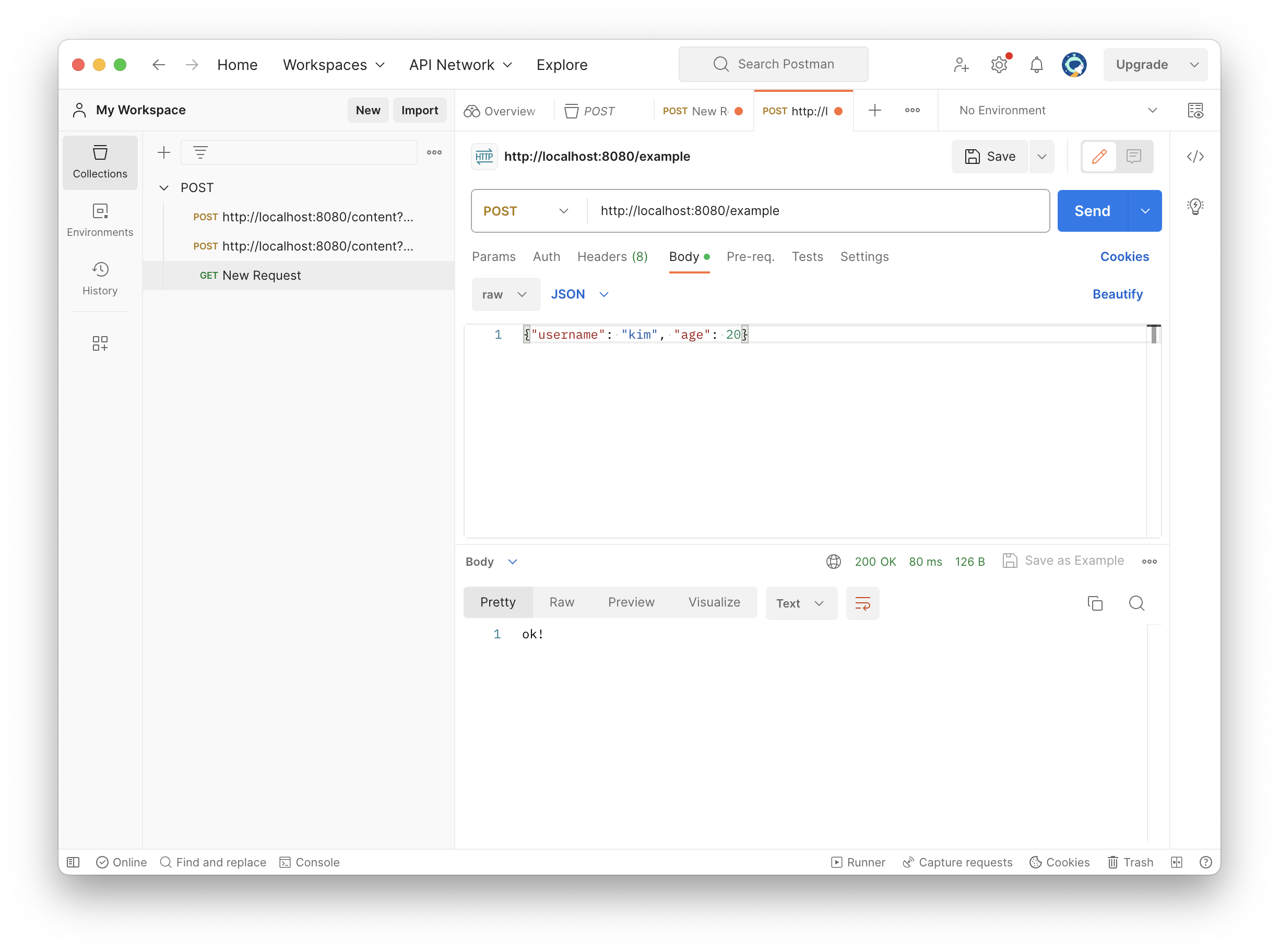
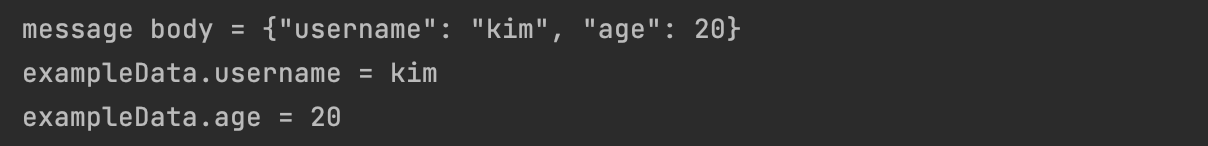
정상적으로 실행되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
