예제 7-1 프렌드 함수 만들기
두 Rect 객체를 비교하는 bool equals(Rect r, Rect s)를 Rect 클래스에 프렌드 함수로 작성하라.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Rect {
private:
int width;
int height;
public:
Rect(int w=1, int h=1);
void setWidth(int w) { this->width = w; }
void setHeight(int h) { this->height = h; }
friend bool equals(Rect r, Rect s);
};
Rect::Rect(int w, int h) {
width = w;
height = h;
}
bool equals(Rect r, Rect s) {
if (r.width == s.width && r.height == s.height)
return true;
else return false;
}
int main() {
Rect r, s;
r.setWidth(2); //임의의 값
r.setHeight(3); //임의의 값
s.setWidth(3); //임의의 값
s.setHeight(4); //임의의 값
if(equals(r, s))
//if(equals(r, s) == 1) //equals의 return타입이 boolean. if() 안이 1이면 참임.
cout << "equal" << endl;
else cout << "not equal" << endl;
return 0;
}답안 보고 고친 것
int main() {
Rect r, s;
r.set(2, 3); //임의의 값
s.set(3, 4); //임의의 값
if(equals(r, s))
cout << "equal" << endl;
else cout << "not equal" << endl;
return 0;
}class Rect {
private:
int width;
int height;
public:
Rect(int w, int h);
void set(int w, int h) {this->widht = w; this height = h;}
friend bool equals(Rect r, Rect s);
};최종
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Rect;
bool equals(Rect r, Rect s);
class Rect {
private:
int width;
int height;
public:
Rect(int width, int height);
void set(int w, int h) { this->width = w; this->height = h; }
friend bool equals(Rect r, Rect s);
};
Rect::Rect(int width, int height) {
this->width = width;
this->height = height;
}
bool equals(Rect r, Rect s) {
if(r.width == s.width && r.height == s.height) return true;
else return false;
}
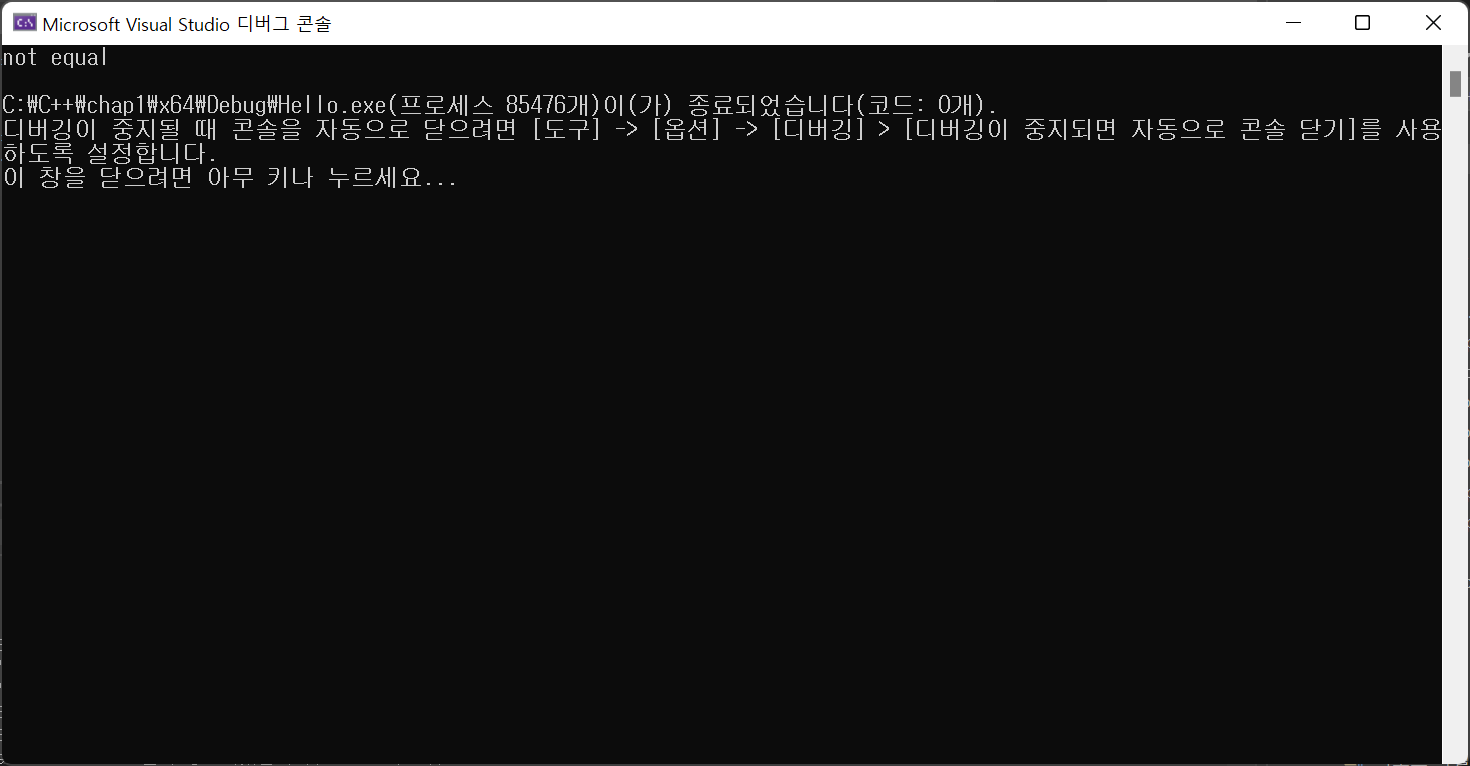
int main() {
Rect a(2,3), b(3,4);
if(equals(a, b)) cout<< "equal" << endl;
else cout << "not equal" << endl;
return 0;
}
예제 7-2 다른 클래스의 멤버 함수를 프렌드 함수로 선언
RectManager 클래스의 equals() 멤버 함수를 Rect 클래스의 프렌드로 선언한 사례를 보인다.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Rect;
class RectManager {
public:
bool equals(Rect r, Rect s);
};
class Rect {
private:
int width;
int height;
public:
Rect(int width, int height) { this->width = width; this->height = height; }
friend bool RectManager::equals(Rect r, Rect s);
};
bool RectManager::equals(Rect r, Rect s) {
if (r.width = s.width && r.height = s.height)
return true;
else return false;
}
int main() {
Rect a(3,4), b(3,4);
RectManager man;
if(man.equals(Rect a, Rect b)) cout << "equal" << endl;
else cout << "not equal" << endl;
}고친 것
int main() {
Rect a(3,4), b(3,4);
RectManager man;
if(man.equals(a, b)) cout << "equals" << endl; // man.equals() 안에 객체가 들어가야 함.
else cout << "not equal" << endl;
}
bool RectManager::equals(Rect r, Rect s) {
if (r.width == s.width && r.height == s.height)
//if (r.width = s.width && r.height = s.height)
return true;
else return false;
}최종
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Rect;
class RectManager {
public:
bool equals(Rect r, Rect s);
};
class Rect {
private:
int width, height;
public:
Rect(int width, int height) { this->width = width; this->height = height;}
friend bool RectManager::equals(Rect r, Rect s);
};
bool RectManager::equals(Rect r, Rect s) {
if (r.width == s.width && r.height == s.height) return true;
else return false;
}
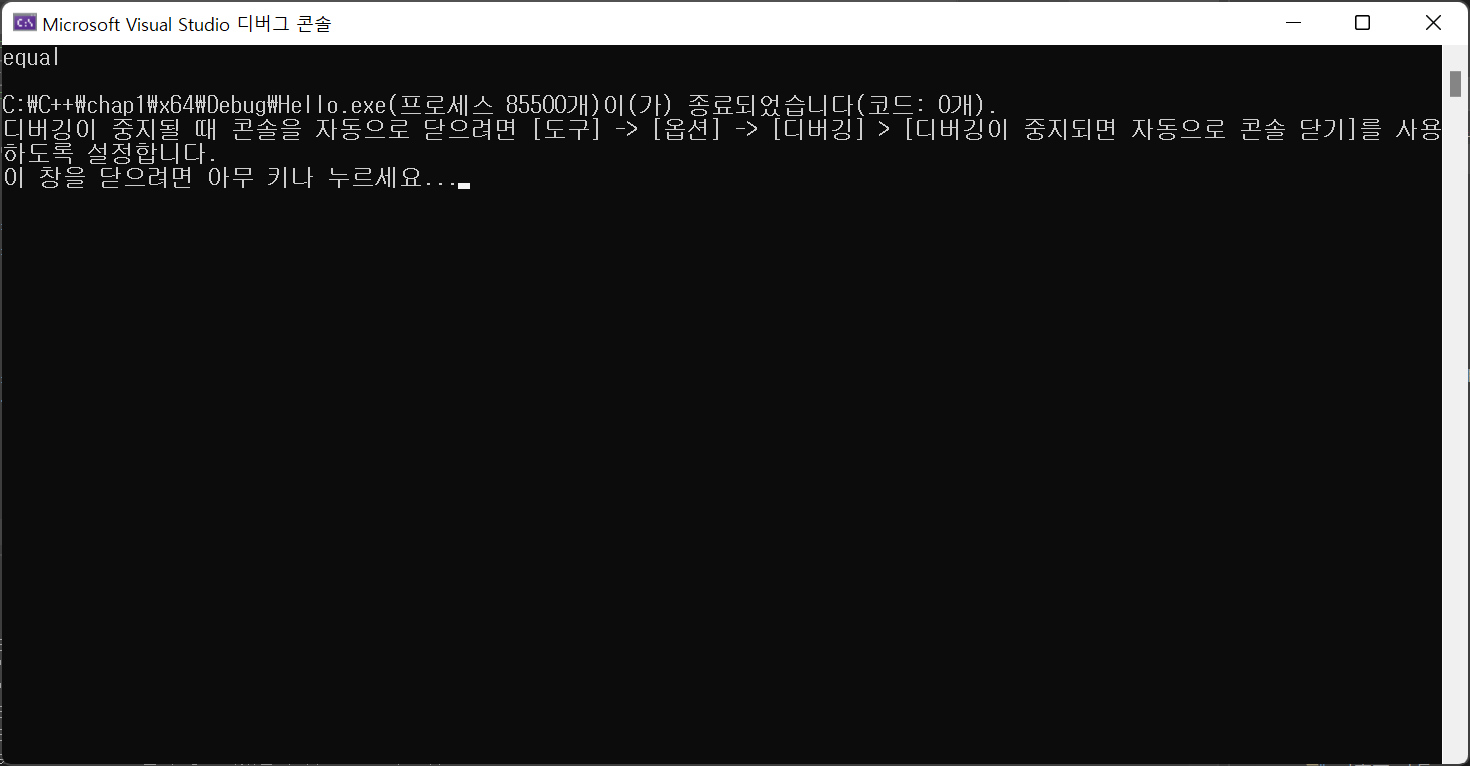
int main() {
Rect a(3,4), b(3,4);
RectManager man;
if (man.equals(a, b)) cout << "equal" << endl;
else cout << "not equal" << endl;
}
예제 7-3 다른 클래스 전체를 프렌드로 선언
RectManager 클래스 전체를 Rect 클래스의 프렌드로 선언하는 사례를 보인다. RectManager 클래스에는 두 개의 멤버 함수가 있으며, 이들은 모두 Rect 클래스의 private 멤버를 자유롭게 접근한다.
Rect 클래스 - 멤버 변수: int width, height/ 생성자: Rect()
RectManager 클래스 - 멤버 함수: copy(), equals(), friend
int main() 함수 - Rect 클래스 타입 객체 2개, RectManager 클래스 타입 객체 1개, if문 cout
생성자 Rect::Rect(int width, int height)
멤버함수 void RectManager::copy(Rect s, Rect r)
멤버함수 bool RectManager::equals(Rect r, Rect s)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Rect;
class RectManager {
public:
void copy(Rect r, Rect s);
bool equals(Rect r, Rect s);
};
class Rect {
private:
int width, height;
public:
Rect(int width, int height) { this->width = width; this->height = height;}
friend RectManager;
};
bool RectManager::equals(Rect r, Rect s) {
if(r.width==s.width && r.height==s.height)
return true;
else return false;
}
void RectManager::copy(Rect r, Rect s) {
r.width = s.width;
r.height = s.height;
}
int main() {
Rect a(3,4), b(4,5);
RectManager man;
man.copy(b, a)
if(man.equals(a, b)) cout << "equal" << endl;
else cout << "not equal" << endl;
}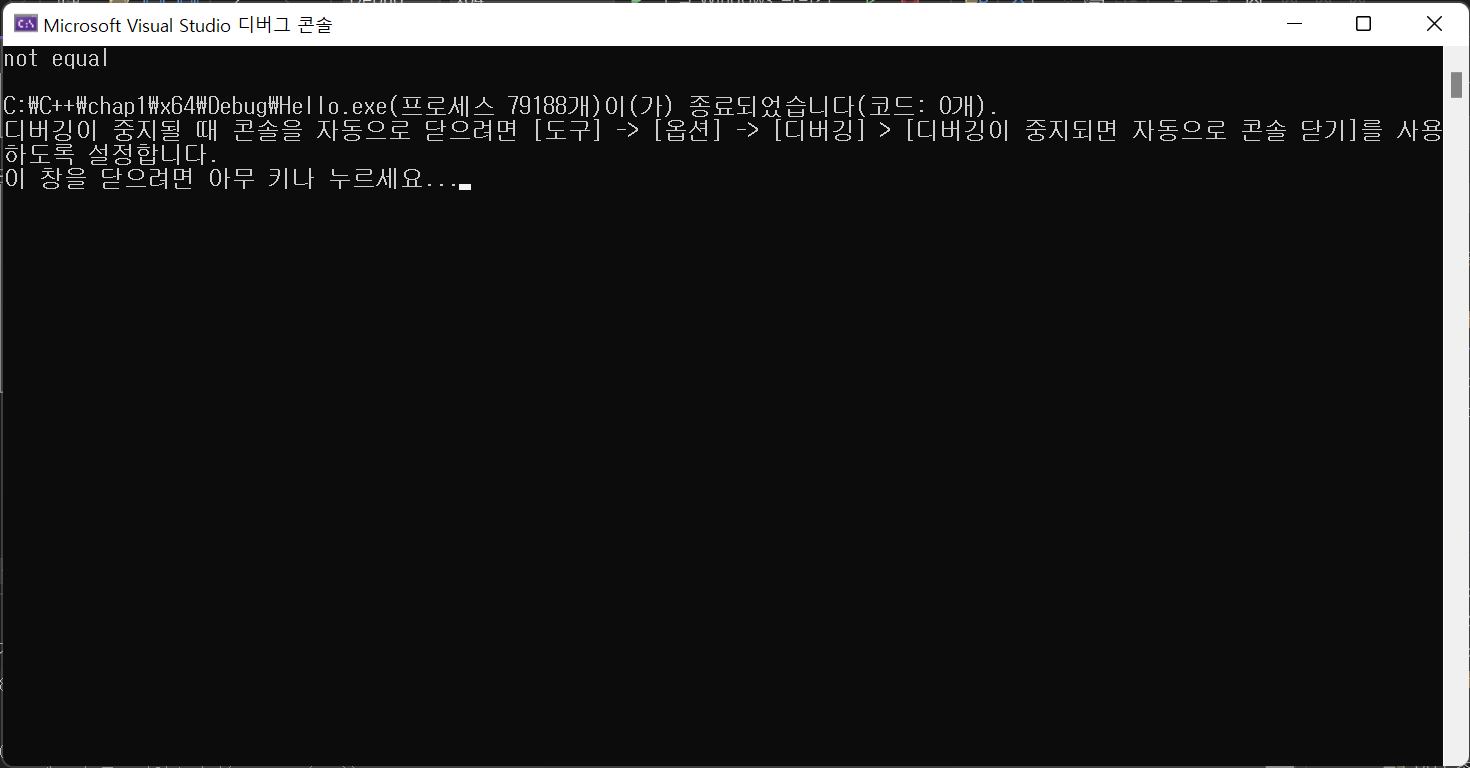
--> equal이 나와야 함. 코드가 틀린거임.
틀린 것
class RectManager {
public:
void copy(Rect r, Rect s);
bool equals(Rect r, Rect s);
};void RectManager::copy(Rect r, Rect s) {
r.width = s.width;
r.height = s.height;
}답안 보고 고치기
class RectManager {
public:
bool equals(Rect r, Rect s);
void copy(Rect& dest, Rect& src);
};
void RectManager::copy(Rect& dest, Rect& src) {
dest.width = src.width;
dest.height = src.height;
}팁
: c 복사할 때 사용하는 변수 이름 dest, src
- dest == destination (목적지)
- src == source (원본)
최종
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Rect;
class RectManager {
public:
bool equals(Rect r, Rect s);
void copy(Rect& dest, Rect& src);
};
class Rect {
private:
int width, height;
public:
Rect(int width, int height) { this->width = width; this->height = height; }
friend RectManager;
};
bool RectManager::equals(Rect r, Rect s) {
if(r.width==s.width && r.height==s.height)
return true;
else return false;
}
void RectManager::copy(Rect& dest, Rect& src) {
dest.width = src.width;
dest.heigth = src.height;
}
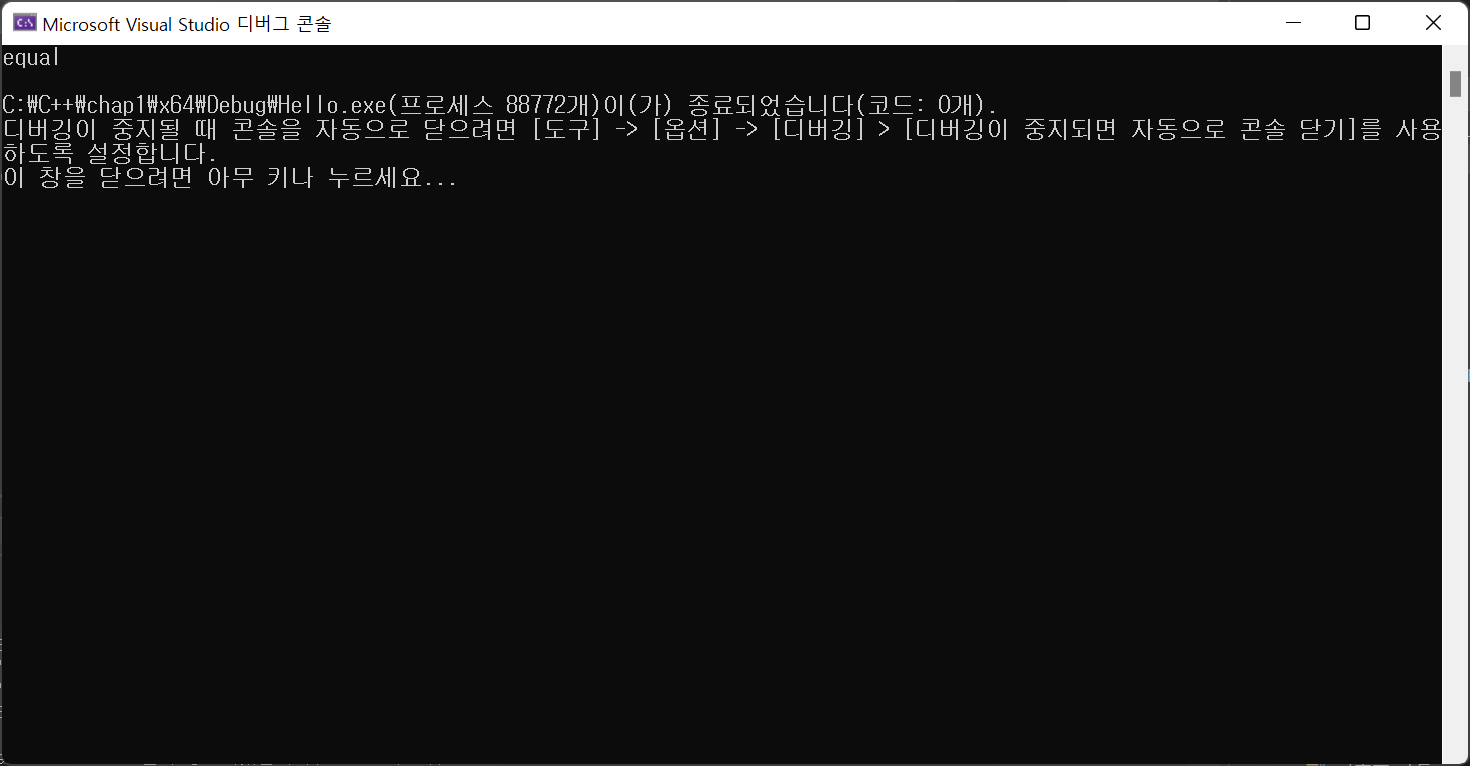
int main() {
Rect a(3,4), b(5,6);
RectManager man;
man.copy(b,a);
if(man.equals(a,b)) cout << "equal" << endl;
else cout << "not equal" << endl;
}
예제 7-4 두 개의 Power 객체를 더하는 + 연산자 작성
두 Power 객체를 더하는 + 연산자를 Power 클래스의 operator+() 멤버 함수로 작성하라.
[실행 결과]
kick=3, punch=5
kick=4, punch=6
kick=7, punch=11
int main() {
Power a(3,5), b(4,6), c;
c = a + b; //이게 연산자 중복해서 사용한 거겠지
a.show();
b.show();
c.show();
}
class Power {
public:
Power(int kick, int punch) {}
};