이 글은 블로그주인장이 여태 공부했던 알고리즘 독학 및 강의들의 내용을 정리하는 포스팅입니다.
클래스(Class)란?
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct student { //C 방식 구조체
string name;
int score;
};
int main(void) {
struct student a;
a.name = "아무개";
a.score = 100;
cout << a.name << ":" << a.score << "\n";
system("pause");
}C언어의 구조체는 일반적으로 변수등만 사용가능 하지만 이 구조체 안에 메소드(함수)와 생성자 개념이 추가되면?
클래스(class)의 정의
-
현실 세계의 사물 인 객체(Object) 를 프로그램 내에서 구현
-
클래스는 분류. 집합. 같은 속성과 기능을 가진 객체를 총칭하는 개념
-
추상화(abstract), 캡슐화(Encapsulation), 상속성(Inheritance), 정보 은닉(Data Hiding), 다형성(Polymorphism)
-
맴버(Member) (C++ / Python)
class Student {
private: //접근 한정자 내부에서만 활용 가능
string name; //멤버변수를 속성 or Property라 함
int score;
public: //접근 한정자 내부,외부 상관없이 어떤 곳에서도 접근할 수있음
Student (string n , int s ) { name n ; score = s; }
void show() { cout << name << " : " score << "점\n";} #클래스 내 함수를 메소드라 함
};class Person:
#생성자
def __init__(self, param_name): #객체를 생성할 때 내부적으로 원하는 행동을 실행
print("hihihi", self)
self.name = param_name
def talk(self): #클래스 내부의 함수를 메소드(method)
print("저는", self.name, "입니다")- 인스턴스(Instance)
int main(void) {
Student a = Student("우하랄",100); //클래스를 활용해 만든 변수를 인스턴스라 함
a.show();
}- this 포인터 (C++/Python)
Student(string name , int englishScore , int mathScore )
this->name name ; // 자기 자신의 멤버 변수에 접근
this->englishScore = englishScore
this->mathScore = mathScore
//C++에서 this 포인터는 포인터 자료형으로 상수 라는 점에서 값을 변경불가능class Person:
def __init__(self, param_name):
print("hihihi", self)
self.name = param_name배열과 연결리스트
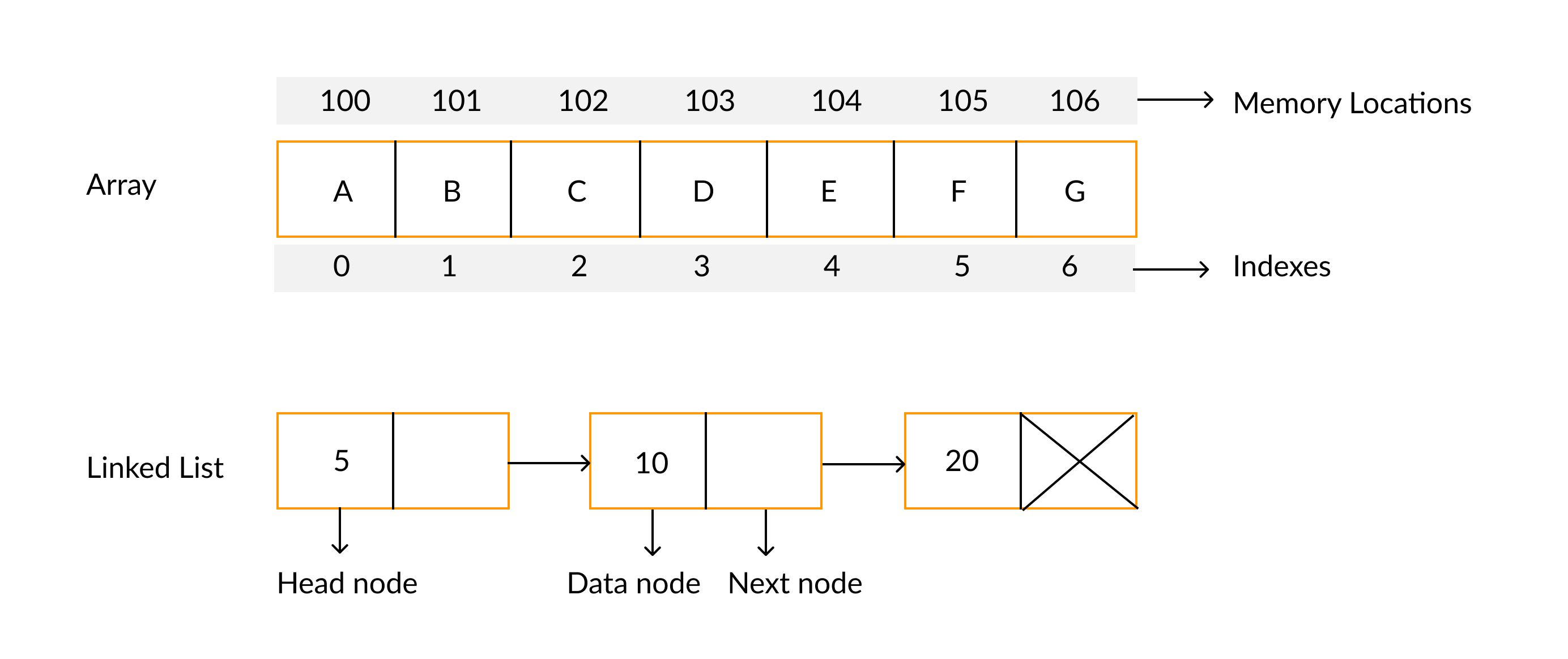
- 배열은 특정 사이즈를 생성하여 그 사이즈 안에 데이터를 사용
- 연결리스트는 연결고리(Node)를 이용하여 새로운 데이터를 추가/삭제해서 사용하기 용이
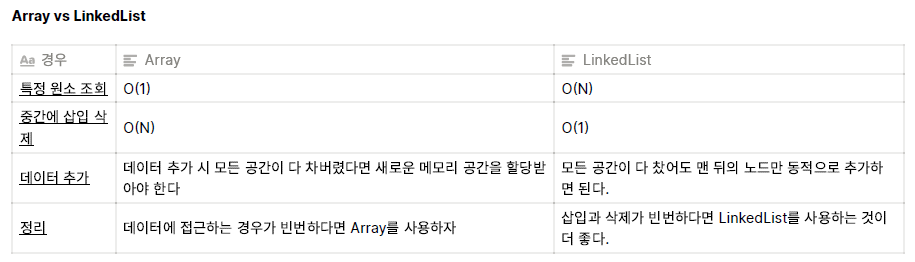
- 배열은 데이터 순회에 용이
- 링크드리스트는 수정에 용이
클래스/구조체를 이용하여 링크드리스트 구현
노드 선언
- 노드가 필요
- 현재 데이터와 그 다음 데이터
#data -> next
class Node:
def __init__(self,data):
self.data=data # head 에 시작하는 Node 를 연결
self.next=Nonetypedef struct {
int data;
struct Node* next;
} Node; //data와 다음 노드의 주소값을 갖는 구조체 선언링크드 리스트
#data -> next
class Node:
def __init__(self,data):
self.data=data # head 에 시작하는 Node 를 연결
self.next=None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self, value):
self.head = Node(value) # head 에 시작하는 Node 를 연결typedef struct {
int data;
struct Node* next;
} Node; //data와 다음 노드의 주소값을 갖는 구조체 선언
Node* head; //헤드 선언뒤에서 삽입, 특정 위치 삽입, 삭제, 특정 인덱스 조회, 전체 조회
- python
#data -> next
class Node:
def __init__(self,data):
self.data=data # head 에 시작하는 Node 를 연결
self.next=None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self, value):
self.head = Node(value)
def append(self, value):
cur = self.head
while cur.next is not None:
cur = cur.next
cur.next = Node(value)
def print_all(self):
cur = self.head
while cur is not None:
print(cur.data)
cur = cur.next
def get_node(self, index):
node=self.head
count=0
while count < index:
node = node.next
count += 1
return node
def add_node(self,index,value):
new_node = Node(value) # 새 노드 생성
node = self.get_node(index-1) # 원하는 위치 노드의 이전 노드 생성
next_node = node.next # 기존 원하는 위치의 노드를 다음 노드에 저장
node.next = new_node # 원하는 위치의 이전 노드의 다음 노드에 새 노드 저장
new_node.next = next_node # 새 노드의 다음 노드를 이전에 저장해둔 노드에 연결
def delete_node(self,index):
if index == 0:
self.head=self.head.next #현재 head 의 다음 노드를 head 로 만들기만 하면 됨
return
node=self.get_node(index-1)
node.next=node.next.next- C
**** 생성함수(모든걸 초기화) => Create ****/
void Create(List* plist)
{
Node* head = NULL; // NULL 포인터 초기화, 리스트 머리를 가르키는 포인터변수
Node* tail = NULL; // NULL 포인터 초기화, 리스트 꼬리를 가르키는 포인터변수
Node* cur = NULL; // NULL 포인터 초기화, 저장된 데이터의 조회하는 포인터변수
plist->numOfData = 0; // 데이터 수
}
/***추가함수(데이터 추가)*****/
void Add(List* plist, int pdata)
{
Node* newNode = NULL; // NULL 포인터 초기화, 추가되는 노트의 포인터변수
newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
newNode->data = pdata;
newNode->next = NULL;
if (plist->head == NULL && plist->tail == NULL) //머리 꼬리가 비어있을 경우
plist->head = plist->tail = newNode;
else
{
plist->tail->next = newNode;
plist->tail = newNode;
}
(plist->numOfData)++;
}
/**** 삽입함수 => Insert ****/
void Insert(List* plist, int pdata, int pos)
{
//추가할 노드 만들기
Node* newNode = NULL; // NULL 포인터 초기화, 추가되는 노트의 포인터변수
newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
newNode->data = pdata;
newNode->next = NULL;
if (pos > 1 && pos <= plist->numOfData + 1)
{
Node* tmp = plist->head;
for (int j = 1; j < pos - 1; j++)
{
tmp = tmp->next;
}
newNode->next = tmp->next;
tmp->next = newNode;
plist->tail = newNode;
}
else if (pos == 1)
{
newNode->next = plist->head;
plist->head = newNode;
}
else
{
printf("해당위치에 삽입할 수 없습니다.\n");
}
(plist->numOfData)++;
}
/**** 탐색함수 => Search ****/
void Search(Node* Head, int data)
{
Node* temp = Head->next;
int n = 1;
while (temp != NULL)
{
Node* next = temp->next;
if (data == (int)temp->data)
{
printf("%d번째 시도만에 인덱스 %d에 있다는 것을 확인. \n", n, n - 1);
}
n++;
temp = next;
}
}
/**** 제거함수 => Remove ****/
void Remove(List* plist, int pos)
{
if (pos < 1 && pos <= plist->numOfData + 1)
{
printf("해당 위치에 삭제할 값이 없습니다.\n");
return;
}
else
{
Node* tmp = plist->head;
Node* remNode = plist->head;
if (pos == 1)
{
plist->head = plist->head->next;
}
else
{
for (int k = 1; k < pos - 1; k++)
{
tmp = tmp->next;
}
remNode = tmp->next;
tmp->next = tmp->next->next;
}
free(remNode);
(plist->numOfData)--;
}
}
참고
- 자료구조(열혈강의) -학부생때 강의
- 컴퓨터공학 전공 올인원 패키지 (SW기본) -패스트 캠퍼스
- 알고보면 알기 쉬운 알기쉬운 알고리즘 -스파르타 코딩클럽
- 소스코드
(Python)
https://github.com/BOLTB0X/Sparta-Algorithm/tree/main/week_2
(C)
https://github.com/BOLTB0X/DataStructure_Argolithm/tree/main/CRUD%20with%20LinkedList
