🚀 확장 함수(Extension Functions) 이해하기
Kotlin에서 확장 함수는 기존 클래스에 새로운 메서드를 '추가'하는 강력한 기능을 제공합니다. 확장 함수를 사용하면 기존 클래스를 수정하거나 상속받지 않고도 새로운 기능을 추가할 수 있습니다.
🌟 예시 코드
class CustomUtil {
fun message() = println("first message")
}
fun CustomUtil.hello() = println("hello")
fun CustomUtil.yourName(name: String) = println("hello $name")
fun main() {
val customUtil = CustomUtil()
customUtil.hello()
customUtil.yourName("kotlin")
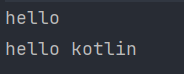
}🖨 출력 결과
🔍 디컴파일된 코드 분석
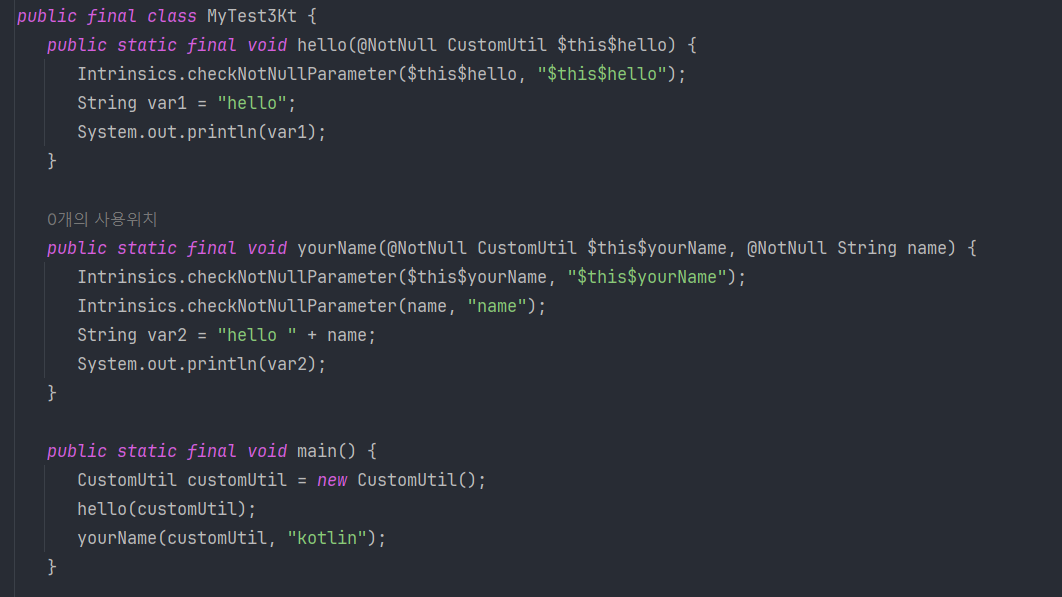
디컴파일된 코드를 살펴보면, 확장 함수들이 static final 메서드로 변환된 것을 볼 수 있습니다. 이들은 첫 번째 매개변수로 $this$메소드명을 가지고 있는데, 이는 확장 함수가 호출된 수신 객체를 나타냅니다.
🚨 주의사항: 메서드 오버라이딩
확장 함수는 클래스 내부의 멤버 메서드보다 낮은 우선순위를 갖습니다. 따라서, 메서드 시그니처가 같은 경우 클래스 멤버가 우선시됩니다.
⚙️ 코드 예시
class CustomUtil {
fun message() = println("first message")
}
fun CustomUtil.message() = print("second message")
fun main() {
val customUtil = CustomUtil()
customUtil.message()
}🖨 출력 결과
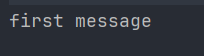
여기서는 클래스 내부의 message() 메서드가 확장 함수보다 우선적으로 호출됩니다.
🌐 Kotlin의 확장 함수: 널 가능 타입 확장
Kotlin에서 확장 함수는 널 가능한 타입(Nullable Type)에도 사용될 수 있습니다. 이를 통해 널 가능한 객체에 대한 처리를 구현할 수 있습니다.
🎯 예시 코드: 널 가능 타입을 위한 확장 함수
fun CustomUtil?.printIfNull() {
if (this == null)
println("null입니다.")
else
println("null이 아닙니다.")
}
fun main() {
var customUtil : CustomUtil? = null
customUtil.printIfNull()
customUtil = CustomUtil()
customUtil.printIfNull()
}이 예시에서는 CustomUtil 클래스의 객체가 널일 수 있는 경우를 고려하여 확장 함수를 정의하고 있습니다. 이 확장 함수는 CustomUtil 객체가 널인지 아닌지를 확인하고, 상응하는 메시지를 출력합니다.
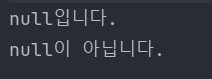
🖨 출력 결과
이 코드를 실행하면, customUtil 변수의 널 상태에 따라 다음과 같은 결과를 얻을 수 있습니다:
💡 확장 함수의 유용성
확장 함수는 기존 클래스에 메서드를 추가할 때 유용합니다. 특히, 소스 코드에 접근할 수 없거나 수정하고 싶지 않은 클래스에 대해 사용됩니다. 예를 들어, 표준 라이브러리 클래스에 추가 기능을 제공하고 싶을 때 활용할 수 있습니다.
📚 확장 함수의 사용 범위
- 기존 클래스 수정 없이 기능 추가: 기존 클래스의 코드를 변경하지 않고도 새로운 기능을 추가할 수 있습니다.
- 코드 재사용성 증가: 공통된 로직을 확장 함수로 구현하여 다양한 클래스에서 재사용할 수 있습니다.
- 클린 코드 유지: 기존 클래스를 수정하거나 상속을 사용하지 않으므로, 코드의 깔끔함과 유지 보수성이 향상됩니다.
