코틀린에서 static 다루기
코틀린(Kotlin)은 자바(Java)와는 다르게 static 키워드를 직접 사용하지 않지만, 비슷한 기능을 제공하는 여러 방법이 있습니다. 또한 코틀린의 톱레벨 함수는 전역적으로 사용할 수 있는 유용한 기능을 제공합니다. 🌍
1. 동반 객체(Companion Object)를 사용한 Static 유사 기능 구현 🏭
companion object를 사용하면 static 기능을 구현할 수 있습니다. 클래스와 함께 존재하는 단일 인스턴스 객체로, 클래스 이름으로 직접 접근할 수 있습니다.
class CustomUtils {
companion object Factory : Log {
private const val NAME = "kotlin"
private var num = 1
@JvmStatic
fun newString(customValue: String) = customValue + " ${num++} " + NAME
override fun log() {
println("Log 출력")
}
}
}
interface Log {
fun log()
}동반 객체는 인터페이스나 추상 클래스를 상속받아 구현할 수 있습니다. @JvmStatic 어노테이션을 사용하면 자바 코드에서 static 메소드처럼 사용할 수 있습니다.
2. 객체 선언(Object Declaration)을 통한 Static 유사 기능 구현 🌟
object를 사용하면 싱글톤 객체를 쉽게 만들 수 있습니다. 자바의 static과 유사한 효과를 내며, 클래스 내 모든 멤버가 공유되고 전역적으로 하나의 인스턴스만 존재합니다.
object CustomUtils2 : Log {
private const val NAME = "kotlin2"
private var num = 1
fun newString(customValue: String) = customValue + " ${num++} " + NAME
override fun log() {
println("Log2 출력")
}
}3. 톱레벨 함수(Top-Level Functions)와 프로퍼티 🔝
코틀린의 톱레벨 함수는 클래스나 객체에 속하지 않고, 파일 최상단에 선언됩니다.
private const val NAME = "kotlin3"
private var num = 1
fun newString(customValue: String) = customValue + " ${num++} " + NAME
fun log() {
println("Log3 출력")
}클래스 없이 메소드를 사용할 수 있으며, 필요한 곳에서 쉽게 import하여 사용할 수 있습니다.
출력 🖨️
출력 코드
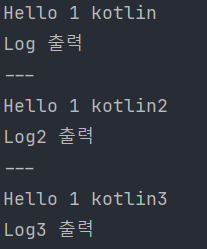
fun main() {
println(CustomUtils.newString("Hello"))
println(CustomUtils.Factory.newString("Hello"))
CustomUtils.log()
println("---")
println(CustomUtils2.newString("Hello"))
CustomUtils2.log()
println("---")
println(newString("Hello"))
log()
}결과
📌 정리
코틀린에서는 static 키워드 없이도 object 선언, companion object, 톱레벨 함수와 프로퍼티를 사용해 유사한 기능을 구현할 수 있습니다. 각각의 방법은 코틀린의 철학을 반영해 안전하고 간결한 코드 작성을 가능하게 합니다.
