Reference
- Call Stack — MDN 100%
Articles
- Understanding Javascript Call Stack, Event Loops — Gaurav Pandvia 100%
- Understanding the JavaScript Call Stack — Charles Freeborn 100%
- Javascript: What Is The Execution Context? What Is The Call Stack? — Valentino Gagliardi 50%
- What is the JS Event Loop and Call Stack? — Jess Telford 100%
- Understanding Execution Context and Execution Stack in Javascript — Sukhjinder Arora 0%
- How JavaScript Works: An Overview of the Engine, the Runtime, and the Call Stack — Alexander Zlatkov 100%
- The Ultimate Guide to Execution Contexts, Hoisting, Scopes, and Closures in JavaScript — Tyler McGinnis 나중에
- How JavaScript Works Under The Hood: An Overview of JavaScript Engine, Heap and, Call Stack — Bipin Rajbhar 100%
Definition
Mechanism or structure which interpreter keeps track of functions that are called
-
Script calls function
interpreter adds function's execution context to Call Stack, starts executing the function
-
function execution is finished
interpreter removes function's execution context from Call Stack, resumes execution where it left of
-
stacks takes up more space than assigned
"stack overflow"
What is execution context?
Execution context is an abstract concept of environment where code is executed. Here is my guide to execution context.
Example
function greeting() {
sayHi(); //
}
function sayHi() {
return 'Hi';
}
greeting(); // -
When code reaches to
greeting();, greeting function's execution context is added to Call Stack. -
Execute all lines in greeting function. When code reaches to
sayHi();, sayHi function's execution context is added to Call Stack. -
Execute all lines in sayHi function. When it's over, return execution to the line that invoked sayHi function, continue executing rest in greeting function. Remove sayHi function's execution context from Call Stack.
-
Execute all lines in greeting function. When it's over, return execution to the line that invoked greeting function, execute rest of the code. Remove greeting function's execution context from Call Stack.
Features of Call Stack
As you see the later one that is pushed, gets out first. For example, sayHi function has been added later than greeting function, but it has been removed first. We call it LIFO(Last in First out).
Also, Call Stack is for storing data temporarily. As execution of functions are finished, call stack becomes empty.
Additionally, all of execution contexts are added in order and executed in order. So we say the Call Stack is synchronous.
Javascript Engine
Definition
program that executes Javascript code. V8 Engine of Chrome, node.js, electron is one of JS engine. V8 Engine is high-performance, open source Javascript & Web Assembly engine.
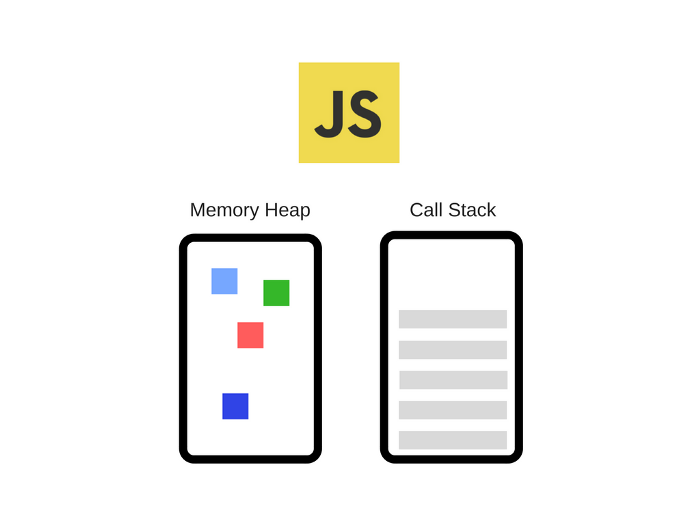
JS Engine consists of Memory Heap and Call Stack. We have learned about Call Stack, so what is memory heap?
Memory Heap
Memory Heap is unstructured memory used for memory allocation of variables and objects.
JS Runtime
Definition
Environment where Javascript program is executed
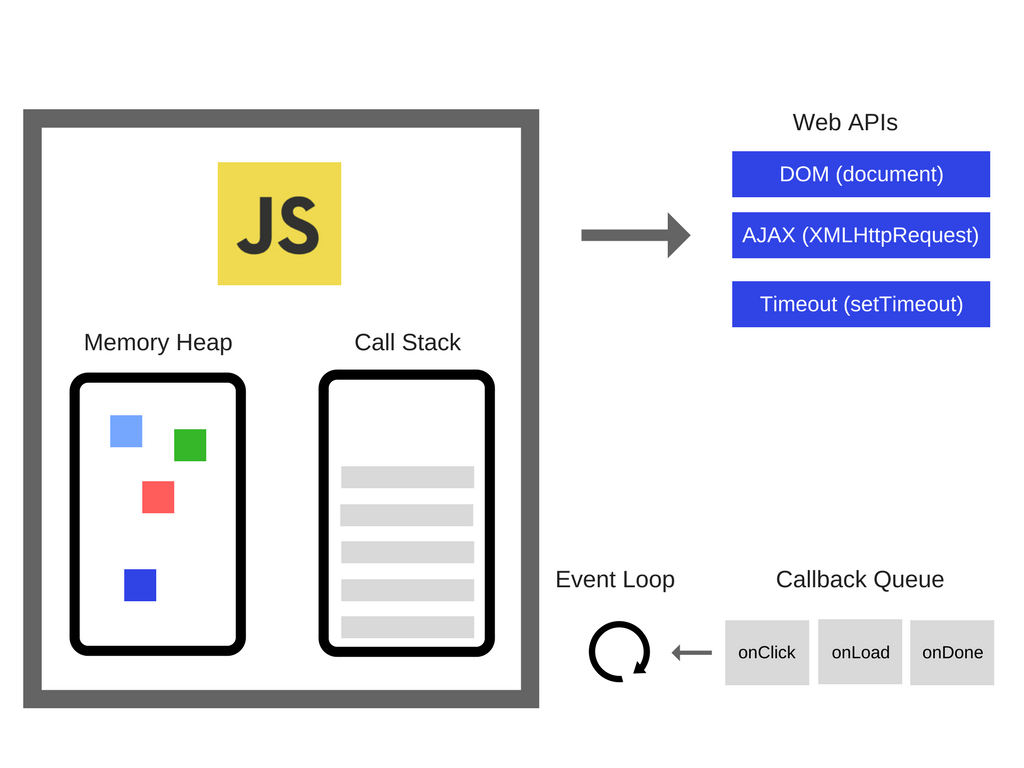
Why do we need Concurrency?
When Call Stack has remained functions to execute, browser can't actually do anything, which we call it blocked. So,
- if function called takes huge amount of time, it will stuck for a long time.
- if there are too many stacks, browser wouldn't respond to user for a long time.
Both cases decrease the user experiences.
Web APIs
Handle async events like DOM events, http requests, setTImeout, etc. It is created by browser, not JS engine. Web API pushes the callback onto Callback Queue when it's done executing.
Callback Queue
list of messages to be processed and associated to callback functions
Event Loops
So who chooses when the functions in Callback Queue to be executed? Event Loops does. Event Loops both Call Stack and Callback Queue and pushes the first thing on Queue to Stack when Stack is completely empty.
