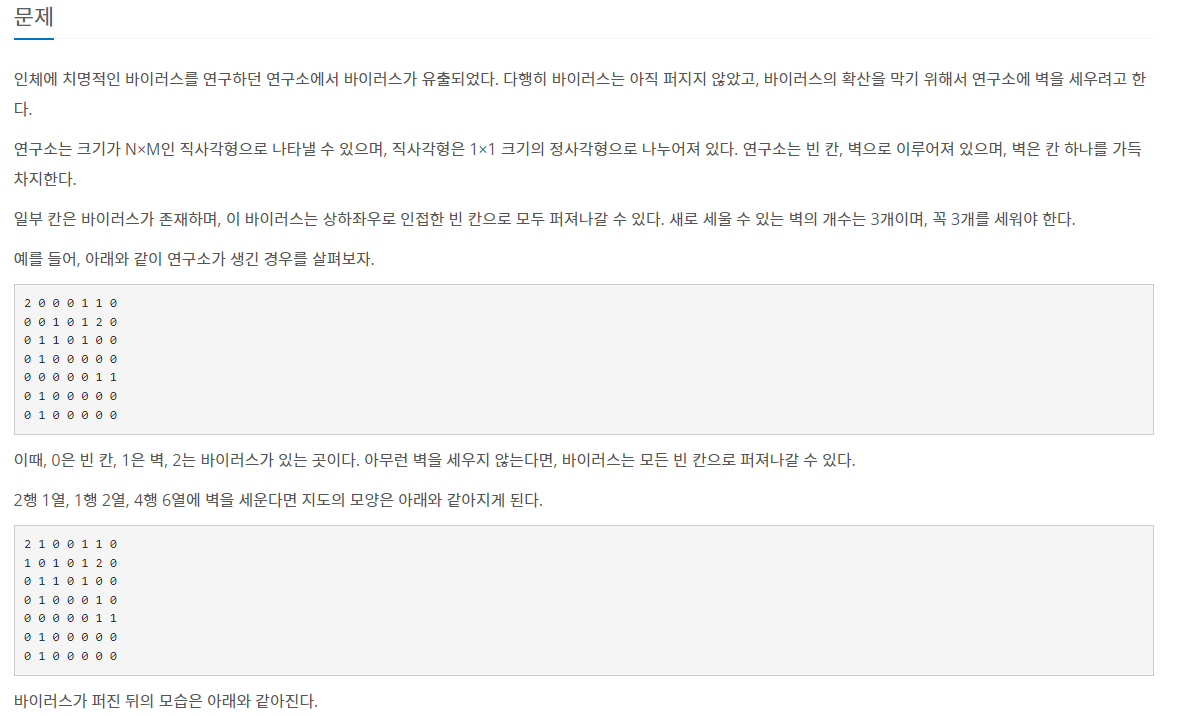
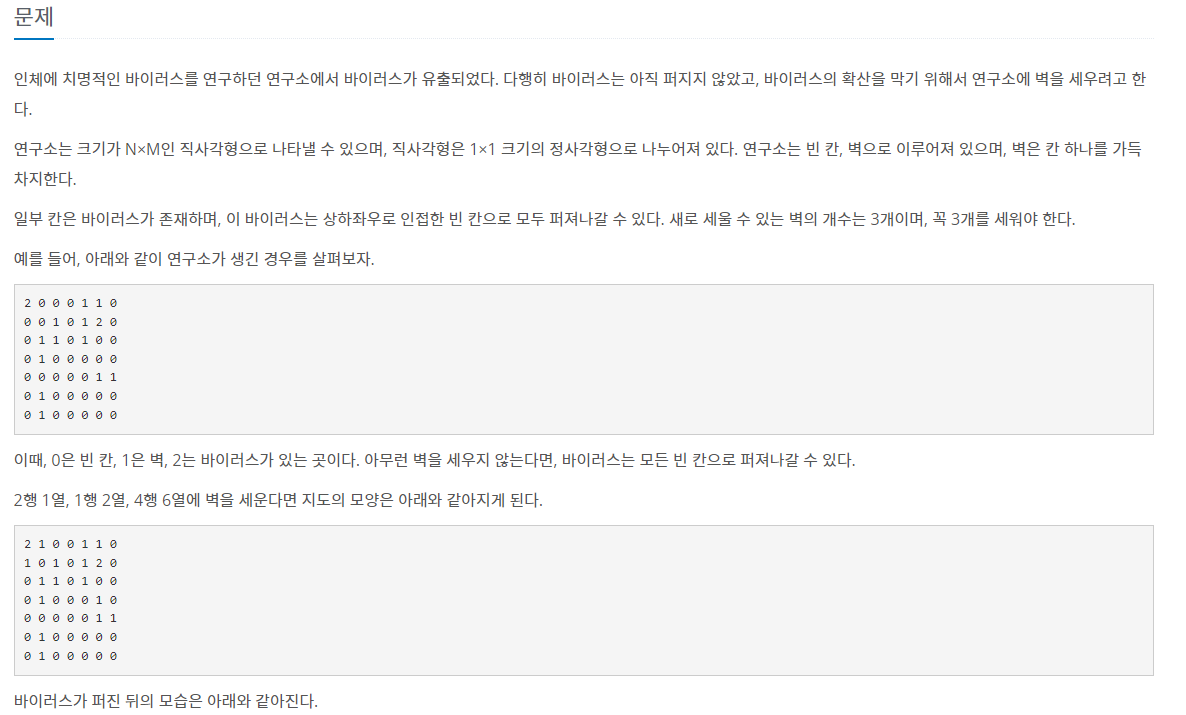
문제

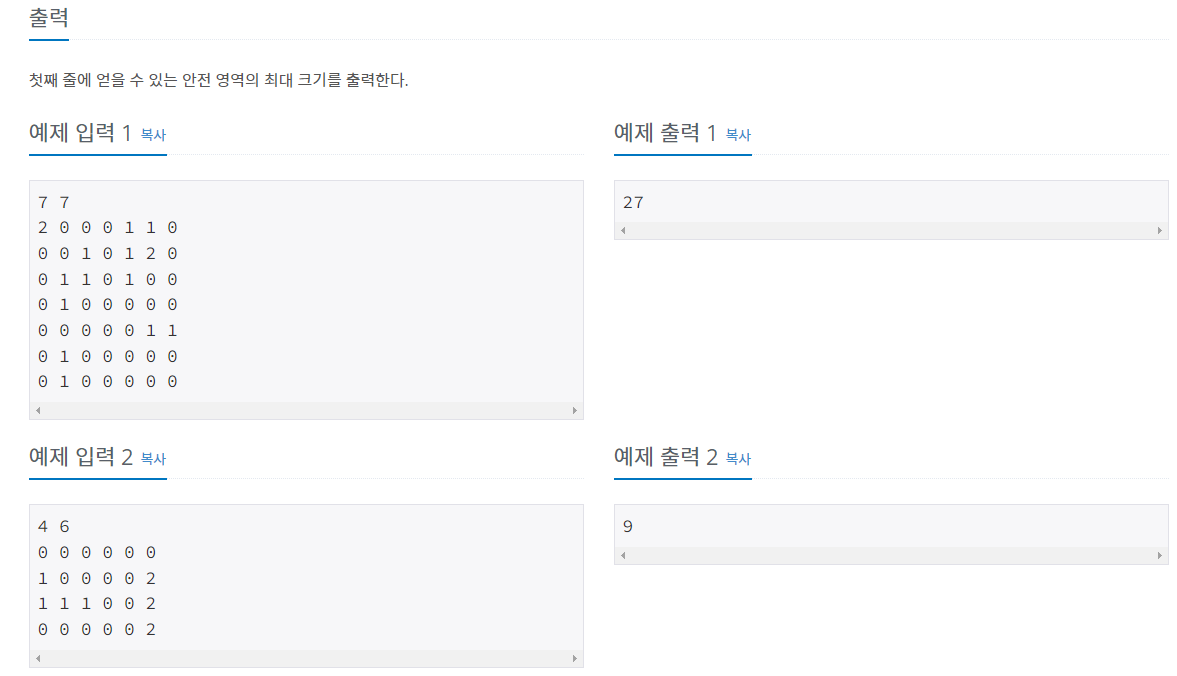
출력
아이디어
이문제는 BFS 너비우선 탐색으로 풀 수 있는 문제이다.
여기서 어려운 점은 BFS , 벽을 세울 수 있는 모든 경우의 수의 조합을 생각해야 한다는 것이다.
단순한 문제 였다면 입력에 벽의 개수가 주어지고 벽을 세울 수 있는 좌표가 주어졌을 것이다.
그러나 이 문제는 3개의 벽을 가지고 할 수 있는 경우의 수를 모두 구해야 하기 때문에
경우의 수 하나를 진행 할 때마다 결과값을 제외한 데이터가 독립적이여야 한다.
- 벽을 세울 수 있는 모든 경우의 수를 구한다.
- 벽을 세운 후 바이러스를 퍼뜨린다.
- 바이러스를 퍼뜨린 후 안전영역의 크기를 구한다.
- 안전영역의 최대 값을 비교한다.
- 1~4를 반복한다.
단순하게 SUDO 코드를 작성하면 위와 같이 나온다.
이제 코드를 한번 살펴보자.
코드
Main 함수
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// 0 == 빈칸 , 1 == 벽 , 2 == 바이러스
// 3개의 벽을 세워야함
// 바이러스는 상하좌우로 퍼짐
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int[] wh = Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
int h = wh[0];
int w = wh[1];
originArr = new int[h][w];
for (int i = 0; i < h; i++){
originArr[i] = Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
}
combination(originArr , 0 , new int[3][2] , new boolean[h][w]);
System.out.println(max);
}입력을 받는 Main 함수 이다. 간단하게 입력을 받고 경우의 수를 구하는 combination 함수를 호출한다.
참고로 originArr은 입력을 받은 배열을 저장하는 배열이다.
각각의 경우의 수마다 originArr을 복사해서 사용하기 때문에
originArr을 변경 할 일이 없다. 따라서 데이터의 독립성을 유지 할 수 있다.
combination 함수
public static void combination(int[][] arr , int depth , int[][] combi ,boolean[][] visited){
if(depth == 3){
int[][] copyArr = copyArr(arr);
for (int i = 0; i < combi.length; i++){
copyArr[combi[i][0]][combi[i][1]] = 1;
}
solution(copyArr);
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < arr[i].length; j++){
if(arr[i][j] == 0 && !visited[i][j]){
combi[depth][0] = i;
combi[depth][1] = j;
visited[i][j] = true;
combination(arr , depth+1 , combi,visited);
visited[i][j] = false;
}
}
}
}
자 이제 combination 함수를 살펴보자.
당연하게도 combination 함수는 경우의 수를 구하는 함수이다.
조합을 구하는 방식은 다들 알 거라고 생각된다. 일반적으로 재귀를 이용해서 구한다.
중복되는 경우를 제외하기 위해 visited 배열을 사용했다.
depth가 3이 되면 벽을 세운 후 solution 함수를 호출한다. depth가 3이 되면 3개의 벽을 세운 것이다.
데이터의 독립성을 위해서 copyArr 함수를 이용해서 originArr을 복사해서 사용한다.
구한 경우의 수를 이차원 배열에 반영 시켜준 후 solution 함수를 호출한다.
함수 호출은 총 4번 되는데 3번은 벽을 세우는 경우의 수를 구하는 것이고 마지막 1번은 solution 함수를 호출하는 것이다.
solution 함수
public static void solution(int[][] copyArr){
for (int i = 0; i < copyArr.length; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < copyArr[0].length; j++){
if(copyArr[i][j] == 2){
spreadVirus(copyArr, i, j);
}
}
}
int safeArea = countSafeArea(copyArr);
max = Math.max(max, safeArea);
}
함수를 분리 했기 때문에 코드가 간결하다. solution 함수는 바이러스를 퍼뜨리는 함수와 안전영역을 세는 함수로 나누어져 있다.
바이러스를 퍼뜨리는 함수는 spreadVirus 함수이고 안전영역을 세는 함수는 countSafeArea 함수이다.
- 간단하게 설명하면 바이러스를 퍼뜨리는 함수는 바이러스가 있는 곳을 기준으로 상하좌우를 탐색하면서 바이러스를 퍼뜨린다. (BFS)
- 안전영역을 세는 함수는 0의 개수를 세는 함수이다.
이렇게 구한 안전영역의 개수를 max와 비교해서 max값을 갱신한다.
spreadVirus 함수와 countSafeArea 함수는 다음과 같다.
spreadVirus 함수
public static void spreadVirus(int[][] copyArr, int x, int y){
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(new int[]{x, y});
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
int[] cur = queue.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
int nx = cur[0] + dx[i];
int ny = cur[1] + dy[i];
if(nx < 0 || nx >= copyArr.length || ny < 0 || ny >= copyArr[0].length) continue;
if(copyArr[nx][ny] == 0){
copyArr[nx][ny] = 2;
queue.offer(new int[]{nx, ny});
}
}
}
}countSafeArea 함수
public static int countSafeArea(int[][] copyArr){
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < copyArr.length; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < copyArr[0].length; j++){
if(copyArr[i][j] == 0){
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}전체 코드
package org.example.boj.bfs;
import org.example.coplit.Solution;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class BFS구현14502연구소 {
static int[][] originArr;
static int max = 0;
static int[] moveX = {0, 0, 1, -1};
static int[] moveY = {1, -1, 0, 0};
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// 0 == 빈칸 , 1 == 벽 , 2 == 바이러스
// 3개의 벽을 세워야함
// 바이러스는 상하좌우로 퍼짐
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int[] wh = Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
int h = wh[0];
int w = wh[1];
originArr = new int[h][w];
for (int i = 0; i < h; i++){
originArr[i] = Arrays.stream(br.readLine().split(" ")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
}
combination(originArr , 0 , new int[3][2] , new boolean[h][w]);
System.out.println(max);
}
public static void combination(int[][] arr , int depth , int[][] combi ,boolean[][] visited){
if(depth == 3){
int[][] copyArr = copyArr(arr);
for (int i = 0; i < combi.length; i++){
copyArr[combi[i][0]][combi[i][1]] = 1;
}
solution(copyArr);
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < arr[i].length; j++){
if(arr[i][j] == 0 && !visited[i][j]){
combi[depth][0] = i;
combi[depth][1] = j;
visited[i][j] = true;
combination(arr , depth+1 , combi,visited);
visited[i][j] = false;
}
}
}
}
public static void spreadVirus(int[][] copyArr , int x , int y){
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(new int[]{x , y});
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
int[] virus = queue.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
int nextX = virus[0] + moveX[i];
int nextY = virus[1] + moveY[i];
if(nextX >= 0 && nextX < copyArr.length && nextY >= 0 && nextY < copyArr[0].length){
if(copyArr[nextX][nextY] == 0){
copyArr[nextX][nextY] = 2;
queue.add(new int[]{nextX , nextY});
}
}
}
}
}
public static void solution(int[][] copyArr){
for (int i = 0; i < copyArr.length; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < copyArr[0].length; j++){
if(copyArr[i][j] == 2){
spreadVirus(copyArr, i, j);
}
}
}
int safeArea = countSafeArea(copyArr);
max = Math.max(max, safeArea);
}
private static int[][] copyArr(int[][] arr){
int[][] copyArr = new int[arr.length][arr[0].length];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
System.arraycopy(arr[i], 0, copyArr[i], 0, arr[0].length);
}
return copyArr;
}
public static int countSafeArea(int[][] arr){
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < arr[0].length; j++){
if(arr[i][j] == 0){
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
}리뷰
구현 문제는 문제를 최대한 작게 나누는 것이 중요한 것 같다. 또한 함수 분리를 통해서 코드를 깔끔하게 짜는 것이 중요한 것을 느꼈다.
나 자신도 구현 문제를 풀다보면 어지러울 때가 많고 왜 이렇게 했지 할 때가 있는데 기능 분리를 통해서 보니 깔끔하게 짜여진 코드가 나왔고 설명하기도 쉬웠다. ![]