📌 학습 목표
- Why good initialization?
- RBM / DBN
- Xavier / He initialize
- Code: mnist_nn_xavier
Why good initialization?
weight(가중치)를 처음에 어떻게 initialize 하느냐에 따라 학습의 결과가 바뀐다.
그럼 어떤 방법이 가장 좋을까?
-
0으로 초기화 한다면?
0으로 초기화를 시키면 backprop시 모든 weight가 모두 0이 되기 때문에 사용하면 안된다.
RBM / DBN
2006년 Hinton 교수가 RBM(Restircted Boltzmann Machine)을 발표한다.
-
RBM(Restircted Boltzmann Machine)
아래 그림은 RBM이다.
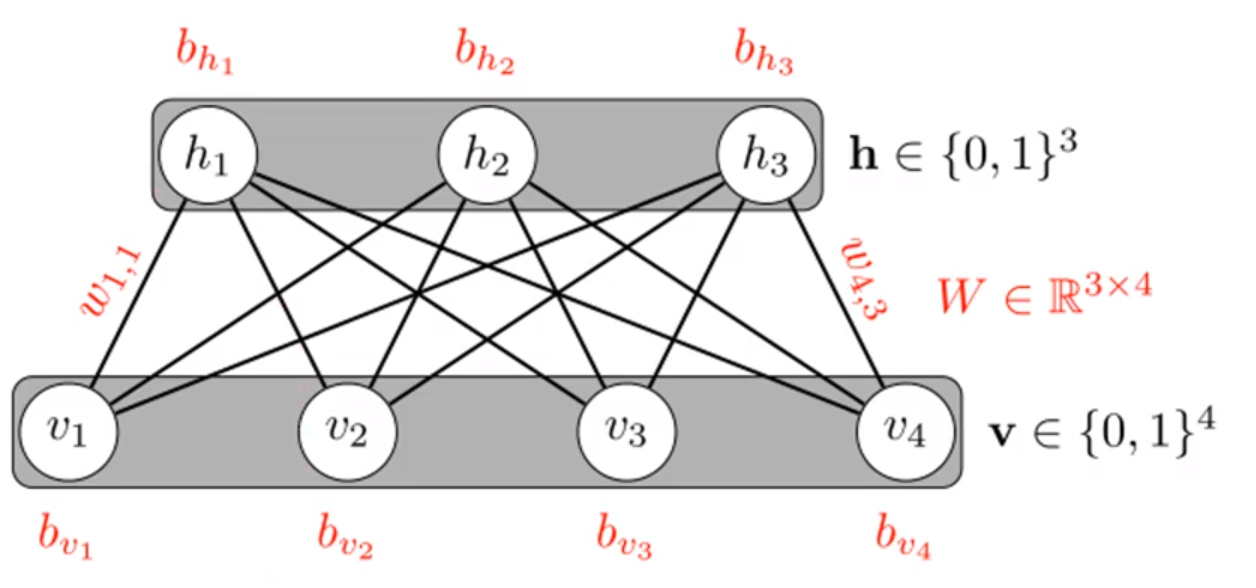
- Restricted : no connections within a layer
한 레이어 내에서는 연결이 없다는 뜻이다.
- KL divergence : compare actual to recreation-
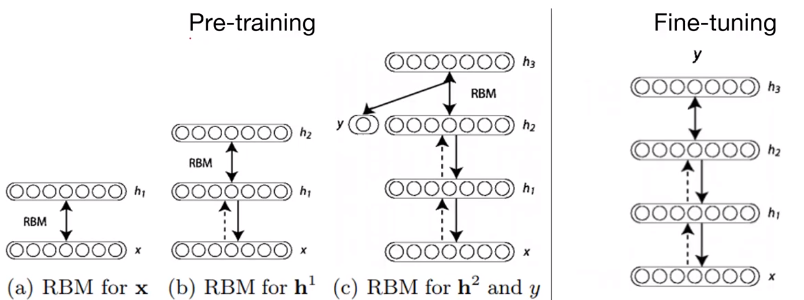
DBN(Deep Belief Network)
Pre-training에서는 RBM을 통해 학습하면서 하나의 레이어를 고정시켜간다. 이는 y를 통해 x'을 유추할 수 있도록 학습시키는 것이다.
이 단계를 마지막 레이어까지 반복한다.
Fine-tuning에서는 Pre-training에서 초기화된 weights들을 사용하여 기존 방식으로 학습한다.
Xavier / He initialization
Xavier 와 He 초기화는 이전 RBM, DBN과 다르게 간단하게 weight를 초기화 시킬 수 있다.
-
Xavier Normal initialization
-
Xavier Uniform initialization
-
He Normal initialization
-
He Uniform initialization
Code: mnist_nn_xavier
xavier를 torch를 이용해 구현해보자.
Xavier Uniform 을 살펴보면 다음과 같이 구현되어있다.
def xavier_uniform_(tensor, gain=1):
fan_in, fan_out = _calculate_fan_in_and_fan_out(tensor)
std = gain * math.sqrt(2.0 / (fan_in + fan_out))
a = math.sqrt(3.0) * std
with torch.no_grad():
return torch.uniform_(-a, a)`이를 이용해 다음과 같이 가중치 초기화된 모델을 학습시킨다.
class SoftmaxClassifierModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(28*28, 256, bias=True).to(device)
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(256, 256, bias=True).to(device)
self.linear3 = nn.Linear(256, 10, bias=True).to(device)
self.relu = torch.nn.ReLU()
torch.nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.linear1.weight)
torch.nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.linear2.weight)
torch.nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.linear3.weight)
self.model = nn.Sequential(self.linear1, self.relu, self.linear2, self.relu, self.linear3).to(device)
def forward(self, x):
return self.model(x)레이어 층은 이전 포스트와 같았지만 정확도는 더 향상된 것을 볼 수 있다.
# Test model using test data
with torch.no_grad():
X_test = mnist_test.data.view(-1, 28*28).float().to(device)
Y_test = mnist_test.targets.to(device)
prediction = model(X_test)
correct_prediction = torch.argmax(prediction, 1) == Y_test
accuracy = correct_prediction.float().mean()
print('Accuracy', accuracy.item())
'''
Accuracy 0.9778000116348267
'''