MS를 만들 때 개발자는 애플리케이션을 구성하는 각 마이크로서비스의 구현 방식에 대한 기본 패턴을 정립해야 한다. 각 마이크로서비스는 고유하되, 상용구 코드를 제거하는 프레임워크를 사용하고 마이크로서비스 각 부분이 일관된 방식으로 배치되어 있는지 확인해야 한다.
⭐ 스프링부트로 간단한 마이크로서비스 생성
✔ 의존성 추가
✏️ license-service/pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.thoughtmechanix</groupId>
<artifactId>licensing-service</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>Eagle Eye Licensing Service</name>
<description>Licensing Service</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.3.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
<!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<start-class>com.thoughtmechanix.licenses.Application</start-class>
<docker.image.name>johncarnell/tmx-licensing-service</docker.image.name>
<docker.image.tag>chapter2</docker.image.tag>
</properties>
<build>
<plugins>
<!-- We use the Resources plugin to filer Dockerfile and run.sh, it inserts actual JAR filename -->
<!-- The final Dockerfile will be created in target/dockerfile/Dockerfile -->
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-resources-plugin</artifactId>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>copy-resources</id>
<!-- here the phase you need -->
<phase>validate</phase>
<goals>
<goal>copy-resources</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<outputDirectory>${basedir}/target/dockerfile</outputDirectory>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/docker</directory>
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
</resources>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>com.spotify</groupId>
<artifactId>docker-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.1.1</version>
<configuration>
<imageName>${docker.image.name}:${docker.image.tag}</imageName>
<dockerDirectory>${basedir}/target/dockerfile</dockerDirectory>
<resources>
<resource>
<targetPath>/</targetPath>
<directory>${project.build.directory}</directory>
<include>${project.build.finalName}.jar</include>
</resource>
</resources>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>| 키워드 | 내용 |
|---|---|
| spring-boot-starter-parent | 라이브러리 간 의존성 관리 및 버전 충돌에 대한 이슈를 예방해줌 |
| spring-boot-starter-actuator | 스프링 부트 애플리케이션에서 제공하는 여러가지 정보를 모니터링하기 할 수 있게 도와줌 |
| spring-boot-starter-web | Spring MVC를 사용하여 RESTful을 포함한 웹 애플리케이션을 구축하기 위한 시작 장치로 Tomcat을 기본 내장 컨테이너로 사용할 수 있게 해줌 |
| spring-boot-devtools | Spring Boot에서 개발 편의를 위해 제공하는 라이브러리로 클래스 로딩 문제 진단, 속성 기본값, 자동 재시작, 라이브 리로드, 전역 설정, 원격 애플리케이션 등의 기능을 제공함 |
| maven-resources-plugin | 메이븐에 스프링 부트 애플리케이션의 빌드와 배포를 위한 스프링 전용 메이븐 플러그인을 포함하도록 지시 |
✔ 스프링 부트 애플리케이션 부팅
스프링 부트로 간단한 마이크로서비스를 시작한 후 반복하며 기능을 전달하기 위해선 라이선싱 서비스의 마이크로서비스에 다음 2개의 클래스를 생성해야 한다.
- 스프링 부트가 애프리케이션을 시작하고 초기화하는 데 사용되는 Spring Bootstrap 클래스
- 마이크로서비스에서 호출할 수 있는 HTTP 엔드포인트를 노출하는 Spring Controller 클래스
✏ Application.java
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}| 키워드 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| @SpringBootApplication | @SpringBootApplication는 스프링 부트 프레임워크에 이 클래스가 프로젝트의 부트스트랩 클래스라고 지시한다 |
| SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args) | 스프링 부트 서비스를 시작하기 위해 호출한다 |
@SpringBootApplication는 자바 클래스 경로에 다른 스프링 빈이 있는지 찾기 위해 모든 클래스를 스캔한다.
📑 스프링 빈은 다음 애너테이션을 사용해 정의할 수 있다.
- @Component, @Service, @Repository 애너테이션이 붙은 클래스를 정의한다
- @Configuration 애너테이션이 붙은 클래스에 스프링 빈을 생성하기 위한 @Bean 생성자 메서드를 정의한다.
✔ 스프링 부트 컨트롤러
Controller 클래스는 서비스의 엔드포인트를 노출하고 유입되는 HTTP 요청 데이터를 요청을 처리할 자바 메서드와 매핑한다.
✏ LicenseServiceController
import com.thoughtmechanix.licenses.model.License;
import com.thoughtmechanix.licenses.services.LicenseService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value="v1/organizations/{organizationId}/licenses")
public class LicenseServiceController {
@Autowired
private LicenseService licenseService;
@RequestMapping(value="/{licenseId}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public License getLicenses(@PathVariable("organizationId") String organizationId, @PathVariable("licenseId") String licenseId) {
//return licenseService.getLicense(licenseId);
return new License()
.withId(licenseId)
.withOrganizationId(organizationId)
.withProductName("Teleco")
.withLicenseType("Seat");
}
@RequestMapping(value="{licenseId}",method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public String updateLicenses(@PathVariable("licenseId") String licenseId) {
return String.format("This is the put");
}
@RequestMapping(value="{licenseId}",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String saveLicenses(@PathVariable("licenseId") String licenseId) {
return String.format("This is the post");
}
@RequestMapping(value="{licenseId}",method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT)
public String deleteLicenses(@PathVariable("licenseId") String licenseId) {
return String.format("This is the Delete");
}
}| 키워드 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| @RestController | REST 기반 서비스라 명시하고 서비스 요청 및 응답을 JSON으로 자동으로 직렬화 및 역직렬화한다. |
| @RequestMapping(value="v1/organizations/{organizationId}/licenses") | 이 클래스의 모든 HTTP 엔드포인트는 /v1/organization/{organizationId}/licenses 경로를 기반으로 노출된다 |
| @RequestMapping(value="/{licenseId}",method = RequestMethod.GET) | /v1/organization/{organizationId}/licenses/{licenseId}로 GET 엔드포인트를 생성한다 |
| getLicenses(@PathVariable("organizationId") String organizationId, @PathVariable("licenseId") String licenseId) | URL의 두 매개변수 organizationId, licenseId를 매서드 매개변수로 매핑한다 |
✏ 포스트맨 api 테스트 결과
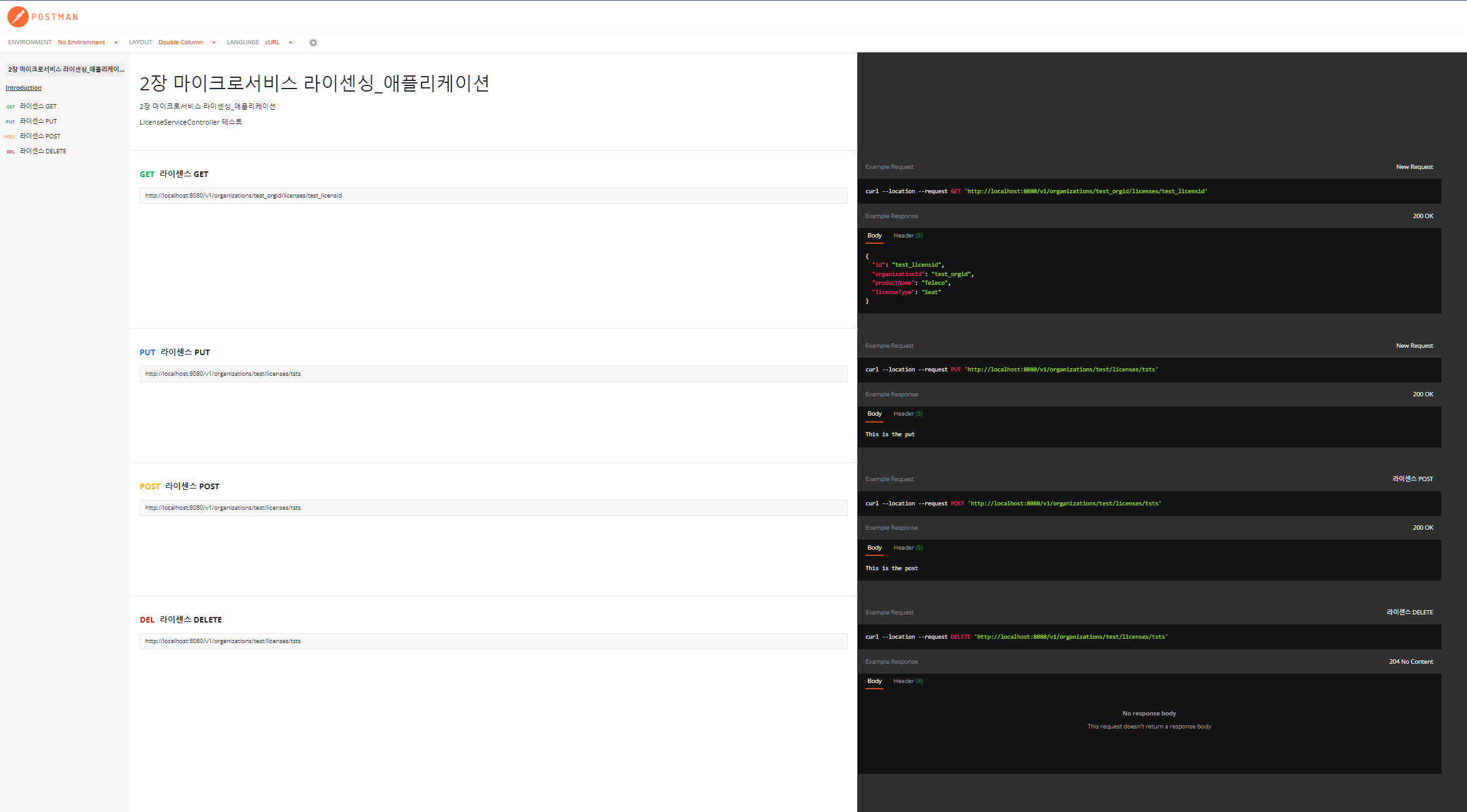
📑 @RestController의 이해
@RestController는 클래스 수준의 자바 애너테이션으로 스프링 컨테이너에 이 자바 클래스가 REST 기반 서비스에 사용된다고 알리는 역할을 한다. 서비스에 JSON이나 XML로 전달된 데이터의 직렬화를 자동으로 처리하며, 전통적인 스프링 @Controller와 달리 Controller 클래스에서 ResponseBody 클래스로 반환할 필요가 없는데, @RestController 에 @ResponseBoody가 포함되기 때문이다.
📑 엔드포인트 네이밍 규칙
- ✏ 서비스가 제공하는 리소스를 알 수 있는 명확한 URL 이름을 사용할 것
- ✏ 리소스 간 관계를 알 수 있는 URL을 사용할 것
- ✏ URL 버전 체계를 일찍 세울 것
URL과 엔드포인트는 서비스 소유자와 서비스 소비자 간 계약을 의미함. 일반적 패턴 중 하나는 모든 엔드포인트 앞에 버전 번호를 붙이는 것임
📑 REST 이해
| 특징 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| 서비스 호출 프로토콜로 HTTP를 사용 | 서비스는 HTTP 엔드포틴트로 노출되고 HTTP 프로토콜을 사용해 서비스와 데이터를 교환한다 |
| 서비스 행동 양식을 HTTP 표준 동사에 매핑 | REST 서비스의 행동 양식을 HTTP 동사인 POST, GET, PUT, DELETE에 매핑함. 그리고 이 동사는 CRUD 함수에 매핑함 |
| 서비스끼리 교환하는 모든 데이터 직렬화 형식으로 JSON을 사용 | JSON은 마이크로서비스에서 입출력 데이터의 직렬화를 위한 거의 표준이 되었음. JSON은 자바스크립트 기반 웹 프런트엔드에 사용되는 데이터 직렬화 및 역질렬화를 위한 원시 형식 (native format)임 |
| HTTP 상태 코드를 사용해 서비스 호출 상태를 전달 | HTTP 프로토콜은 서비스의 성공, 실패 상태 등을 상태 코드로 나타냄. |
서비스간 통신을 위해 JSON보다 효율적인 매커니즘 프로토콜도 존재함. Apache Thrift 프레임워크를 이요하면 바이너리 프로토콜로 서로 통신할 수 있는 다중 언어 서비스를 구축할 수 있따. Apache Avro는 클라이언트와 서버 호출 간 데이터를 바이너리 포맷으로 상호 변환할 수 있는 데이터 직렬화 프로토콜이다.
