📝 파이썬 기초 - 중급05
- 객체와 메모리
- 얕은 복사와 깊은 복사
- 클래스 상속
- 생성자
✏ 객체와 메모리
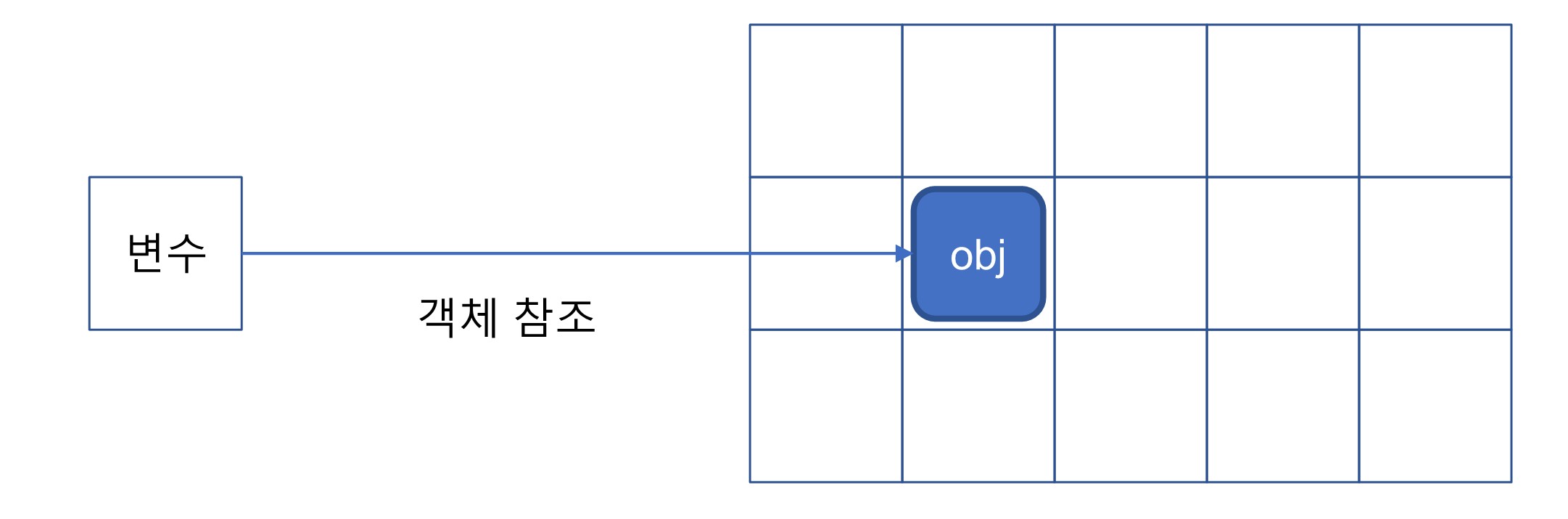
- 변수는 객체의 메모리 주소를 저장하고 이를 이용해서 객체를 참조한다.
class Robot :
def __init__(self, color, height, weight):
self.color =color
self.height = height
self.weight = weight
def robotInfo(self):
print(f'robot color is : {self.color}')
print(f'robot height is : {self.height}')
print(f'robot weight is : {self.weight}')
rb1 = Robot('red', '3m', 10)
rb1.robotInfo()
↓
robot color is : red
robot height is : 3m
robot weight is : 10
rb3 = rb1
rb3.robotInfo()
↓
robot color is : red
robot height is : 3m
robot weight is : 10rb1 과 rb3 모두 같은 곳을 바라본다.
✏ 얕은 복사와 깊은 복사
- 얕은 복사
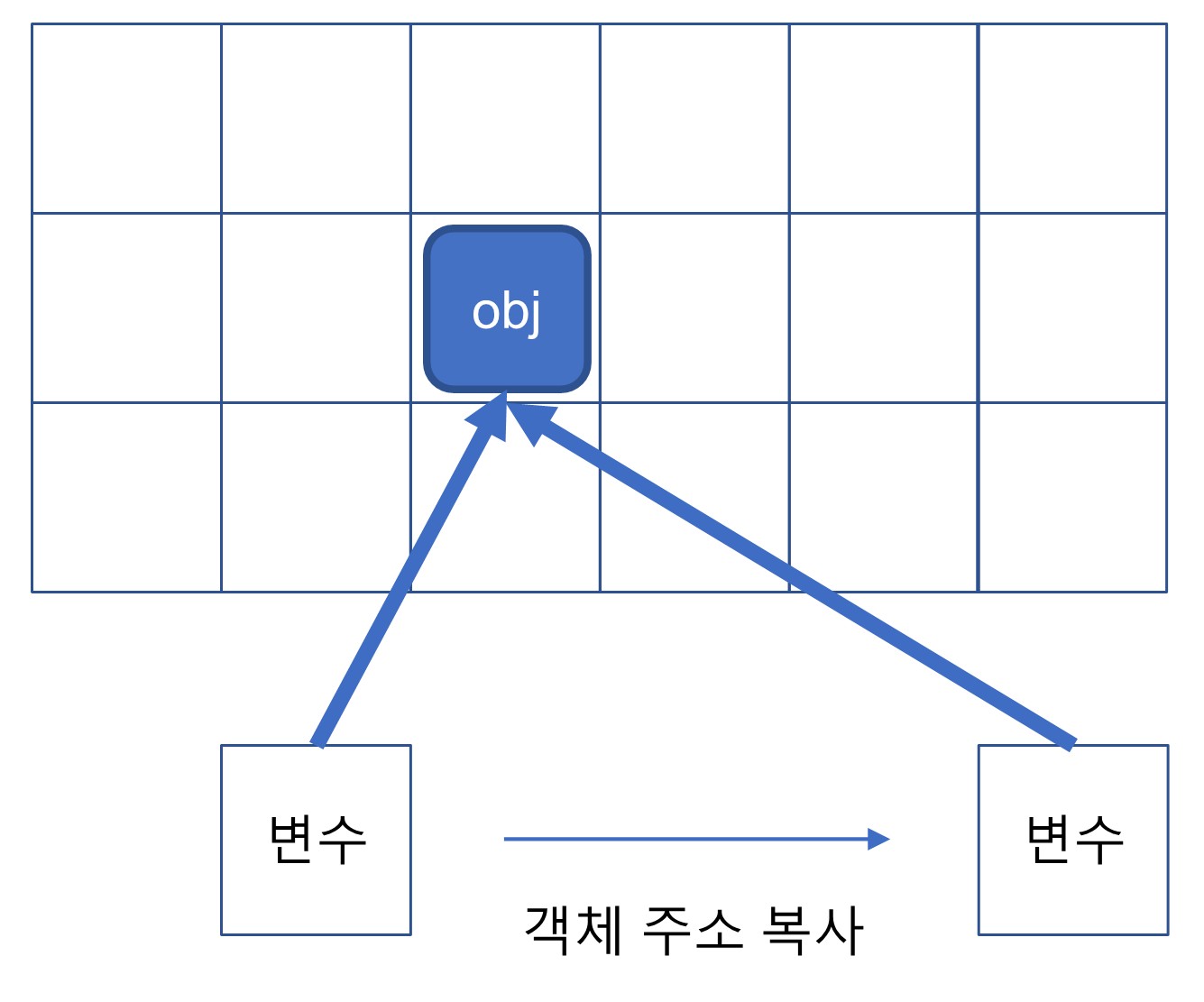
- 얕은 복사란, 객체 주소를 복사하는 것으로 객체 자체가 복사되지 않는다.
class Info :
def __init__(self, num, str):
self.num = num
self.str = str
def thisInfo(self):
print(f'num : {self.num}')
print(f'str : {self.str}')
tc1 = Info(5,'hi')
tc1.thisInfo()
↓
num : 5
str : hi
# 얕은 복사
tc2 = tc1
tc2.thisInfo()
↓
num : 5
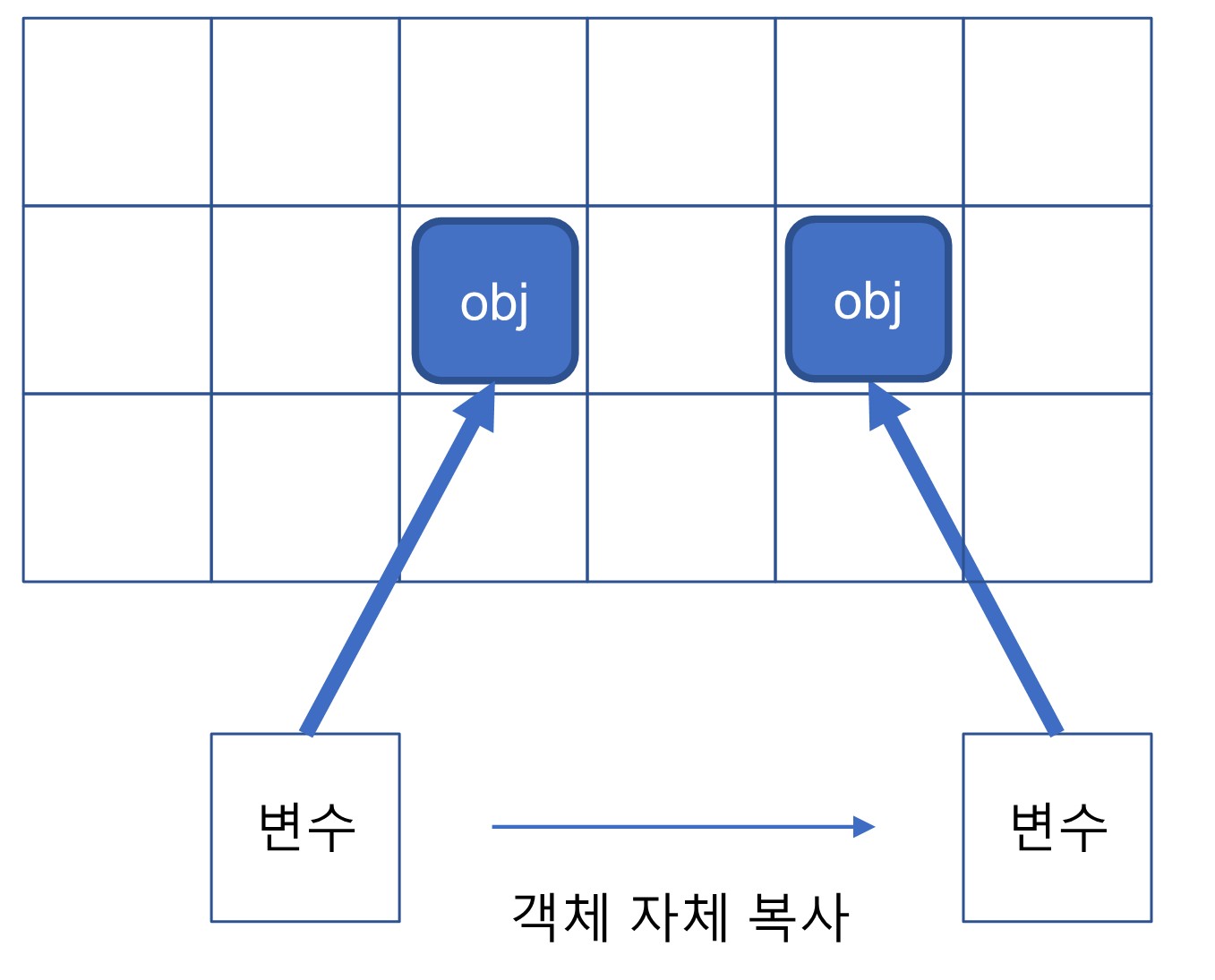
str : hi- 깊은 복사
- 깊은 복사란, 객체 자체를 복사하는 것으로 또 하나의 객체가 만들어진다.
# 깊은 복사 방법
import copy
scores = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
copyScore = []
copyScore = copy.copy(scores)
print(f'id(scores) : {id(scores)}')
print(f'id(copyScore) : {id(copyScore)}')
copyScore = scores.copy()
print(f'id(scores) : {id(scores)}')
print(f'id(copyScore) : {id(copyScore)}')
for s in scores:
copyScore.append(s)
print(f'id(scores) : {id(scores)}')
print(f'id(copyScore) : {id(copyScore)}')
copyScore.extend(scores)
print(f'id(scores) : {id(scores)}')
print(f'id(copyScore) : {id(copyScore)}')
copyScore = scores[:]
print(f'id(scores) : {id(scores)}')
print(f'id(copyScore) : {id(copyScore)}')✏ 클래스 상속
- 클래스는 또 다른 클래스를 상속해서 내 것처럼 사용할 수 있다.
class FirstClass:
def firstOne(self):
print('[firstOne] called!')
def firstTwo(self):
print('[firstTwo] called!')
class SecondClass(FirstClass):
def secondOne(self):
print('[secondOne] called!')
myClass = SecondClass()
myClass.secondOne() -> [secondOne] called!
myClass.firstOne() -> [firstOne] called!
myClass.firstTwo() -> [firstTwo] called!✏ 생성자
-
객체가 생성될 때 생성자를 호출하면 init()가 자동 호출된다.
-
super()
- 상위 클래스의 속성을 초기화하기 위해서 super()를 이용한다.
class P_class:
def __init__(self,n1, n2):
print('[P_class] __init__() called')
self.n1 = n1
self.n2 = n2
print(f'n1, n2 : {self.n1, self.n2}')
class C_class(P_class):
def __init__(self,n3, n4):
print('[C_class] __init__() called')
super().__init__(n3, n4)
self.n3 = n3
self.n4 = n4
print(f'n1, n2 : {self.n1, self.n2}')
call = C_class(10, 20)
↓
[C_class] __init__() called
[P_class] __init__() called
pN1, pN2 : (10, 20)
cN1, cN2 : (10, 20)- 🔎 실습
class MidScore :
def __init__(self, s1, s2, s3):
print('[MidScore] __init__() called')
self.mid_kor_score = s1
self.mid_eng_score = s2
self.mid_mat_score = s3
def printScore(self):
print(f'mid_kor_score : {self.mid_kor_score}')
print(f'mid_eng_score : {self.mid_eng_score}')
print(f'mid_mat_score : {self.mid_mat_score}')
class EndScore(MidScore) :
def __init__(self, s1, s2, s3, s4, s5, s6):
print('[EndScore] __init__() called')
super().__init__(s1, s2, s3)
self.end_kor_score = s4
self.end_eng_score = s5
self.end_mat_score = s6
self.midScore = [self.mid_mat_score, self.mid_kor_score, self.mid_eng_score]
self.endScore = [self.end_eng_score, self.end_mat_score, self.end_kor_score]
self.scores = self.midScore + self.endScore
print(self.printScore())
def printScore(self):
super().printScore()
print(f'end_kor_score : {self.end_kor_score}')
print(f'end_eng_score : {self.end_eng_score}')
print(f'end_mat_score : {self.end_mat_score}')
def getTotalScore(self):
self.midTotalScore = sum(self.midScore)
self.endTotalScore = sum(self.endScore)
self.totalScore = sum(self.scores)
print(f'중간고사 점수 합계 : {self.midTotalScore}')
print(f'기말고사 점수 합계 : {self.endTotalScore}')
print(f'총 점수 합계 : {self.totalScore}')
def getAvgScore(self):
midAvgScore = self.midTotalScore / len(self.midScore)
endAvgScore = self.endTotalScore / len(self.endScore)
avgScore = self.totalScore / len(self.scores)
print(f'중간고사 평균 점수 : {midAvgScore}')
print(f'기말고사 평균 점수 : {endAvgScore}')
print(f'총 평균 점수 : {avgScore}')
def getTotal(self):
EndScore.getTotalScore(self)
EndScore.getAvgScore(self)
getScore = EndScore(90, 95, 88, 67, 78, 77)
getScore.getTotalScore()
↓
mid_kor_score : 90
mid_eng_score : 95
mid_mat_score : 88
end_kor_score : 67
end_eng_score : 78
end_mat_score : 77
None
중간고사 점수 합계 : 273
기말고사 점수 합계 : 222
총 점수 합계 : 495
getScore.getAvgScore()
↓
mid_kor_score : 90
mid_eng_score : 95
mid_mat_score : 88
end_kor_score : 67
end_eng_score : 78
end_mat_score : 77
None
중간고사 평균 점수 : 91.0
기말고사 평균 점수 : 74.0
총 평균 점수 : 82.5
getScore.getTotal()
↓
mid_kor_score : 90
mid_eng_score : 95
mid_mat_score : 88
end_kor_score : 67
end_eng_score : 78
end_mat_score : 77
None
중간고사 점수 합계 : 273
기말고사 점수 합계 : 222
총 점수 합계 : 495
중간고사 평균 점수 : 91.0
기말고사 평균 점수 : 74.0
총 평균 점수 : 82.5✏ 다중 상속
- 2개 이상의 클래스를 상속한다.
class Tiger :
def thisTiger(self):
print('I\'m tiger')
class Rion :
def thisRion(self):
print('I\'m rion')
class Bear :
def thisBear(self):
print('I\'m bear')
class Animal(Tiger, Rion, Bear) :
def __init__(self):
pass
zoo = Animal()
zoo.thisTiger() -> I'm tiger
zoo.thisRion() -> I'm rion
zoo.thisBear() -> I'm bear- ⚠ 다중 상속은 남발하면 안됨
- 다중 상속의 늪에 빠질 수 있음
✏ 오버라이딩
- 하위 클래스에서 상위 클래스의 메서드를 재정의(override)한다.
class Triangle:
def __init__(self, w, h):
self.width = w
self.height = h
def printTriangleInfo(self):
print(f'width : {self.width}')
print(f'height : {self.height}')
def getArea(self):
return self.width * self.height / 2
class newTriangle(Triangle):
def __init__(self, w, h):
super().__init__(w, h)
def getArea(self):
return print(f'triangleArea : {super().getArea()}㎠')
ta = newTriangle(10, 7)
ta.getArea()
↓
triangleArea : 35.0㎠✏ 추상클래스
- 상위 클래스에서 하위 클래스에 메서드 구현을 강요한다.
from abc import ABCMeta
from abc import abstractmethod
class Car(metaclass=ABCMeta):
@abstractmethod
def drive(self):
pass
class drivingCar:
def __init__(self, b, y):
self.licence = b
self.year = y
def drive(self):
if self.licence == '0' and self.year <= 2023 :
print('운전 가능')
else :
print('운전 불가능')
in1 = input('운전면허 소지 유 -> 0, 무 -> 1 :')
in2 = int(input('면허증 취득 연도를 적어주세요 예) 2023 :'))
ca = drivingCar(in1, in2)
ca.drive()
↓
운전면허 소지 유 -> 0, 무 -> 1 :0
면허증 취득 연도를 적어주세요 예) 2023 :2016
운전 가능

