@ConfigurationProperties
문제 상황
DataSourceProperties 빈에 Vault 를 통해 받아온 값을 셋팅하기 위해
Vault 템플릿 조회 역할을 하는 VaultOperationService 빈을 만들어 주입받으려 했다.
생성자 주입을 하면 예외(ensure that @constructorbinding has not been applied to regular bean)가 발생하고 @Autowired 를 사용하면 에러가 발생하지 않았다.
왜 그런지 원인 파악을 하지 않고 PR 을 올렸는데 바로 질문이 들어왔다….
@Primary
@Configuration
@Profile(value = {"dev"})
public class RdsConnectionProps extends DataSourceProperties {
@Autowired
private VaultOperationService vaultOperationService;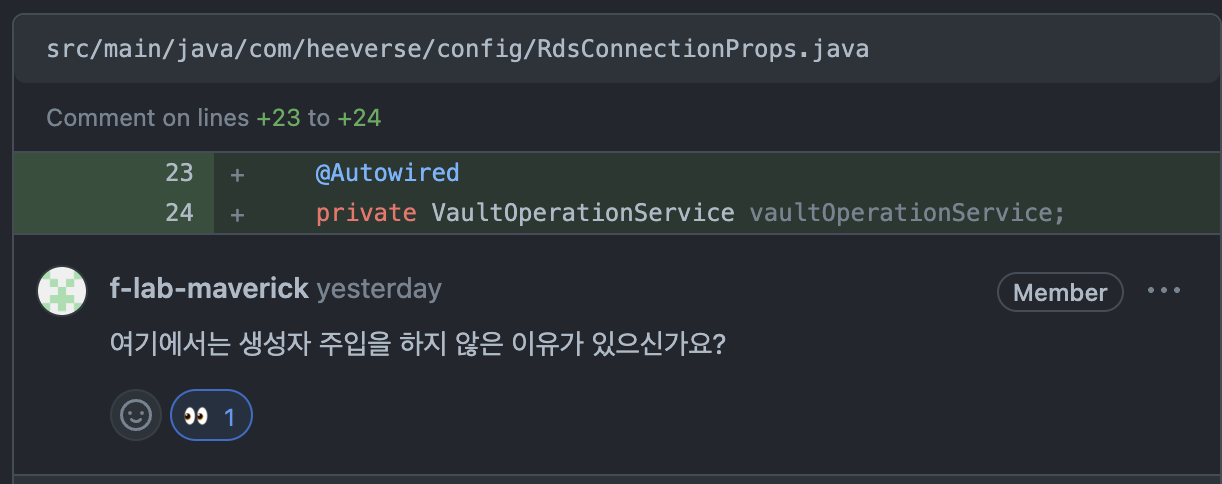
원인을 파악하기 위해 내가 모르는 것을 선별하고 차례로 학습하겠다.
- @ConfigurationProperties 선언된 클래스가 어떻게 사용되는가?
ensure that @constructorbinding has not been applied to regular bean이 예외 메세지가 의미하는 것이 뭔가?
@ConfigurationProperties
환경 설정 파일의 값을 클래스로 맵핑 하라는 선언이다.
예시) DataSourceProperties
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
public class DataSourceProperties implements BeanClassLoaderAware, InitializingBean {어디서 사용되나?
그렇다면 @ConfigurationProperties 어노테이션이 선언된 클래스는 어디서 사용되는 것일까?
@EnableConfigurationProperties 에서 사용된다. 환경설정값이 맵핑된 빈을 주입받아 자동 구성에 사용된다.

값을 어떻게 매핑하나?
환경 설정 파일의 값을 클래스로 어떻게 맵핑하는지 파악해보자
/**
* Internal class **used by** the {@link ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor} to
* **handle the actual** {@link ConfigurationProperties @ConfigurationProperties} binding.
*
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @author Phillip Webb
*/
class ConfigurationPropertiesBinder {ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor 이 요청하면
ConfigurationPropertiesBinder 에서 값을 바인딩한다.
ConfigurationPropertiesBinder 클래스 Structure 로 메서드 시그니처를 조회해보니
bind() 메서드에서 수행하는것같다. 내용을 보자
BindResult<?> bind(ConfigurationPropertiesBean propertiesBean) {
Bindable<?> target = propertiesBean.asBindTarget();
ConfigurationProperties annotation = propertiesBean.getAnnotation();
BindHandler bindHandler = getBindHandler(target, annotation);
return getBinder().bind(annotation.prefix(), target, bindHandler);
}ConfigurationPropertiesBean 참조값으로 바인딩할 타겟을 조회하고 핸들러에게 위임하는 것 같다.
ConfigurationPropertiesBean 은 어떤 역할을 하는지 보자.
/**
* Provides **access to {@link ConfigurationProperties @ConfigurationProperties} bean**
* details, regardless of if the annotation was used directly or on a {@link Bean @Bean}
* factory method. **This class can be used to access {@link #getAll(ApplicationContext)
* all} configuration properties beans in an ApplicationContext**, or
* {@link #get(ApplicationContext, Object, String) individual beans} on a case-by-case
* basis (for example, in a {@link BeanPostProcessor}).
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @since 2.2.0
* @see #getAll(ApplicationContext)
* @see #get(ApplicationContext, Object, String)
*/
public final class ConfigurationPropertiesBean {ConfigurationPropertiesBean 을 통해 어플리케이션 컨텍스트에 등록된 모든 Configuration Properties 이 맵핑된 Bean 에 접근이 가능하다.
그럼 이제 다시 ConfigurationPropertiesBinder.bind() 메서드 내용을 살펴보자
//ConfigurationPropertiesBinder.bind()
BindResult<?> bind(ConfigurationPropertiesBean propertiesBean) {
// 바인딩할 타겟 조회
Bindable<?> target = propertiesBean.asBindTarget();
// 바인딩할 타겟에 선언된 ConfigurationProperties 어노테이션 조회
ConfigurationProperties annotation = propertiesBean.getAnnotation();
// 바인딩 핸들러 객체 요청
BindHandler bindHandler = getBindHandler(target, annotation);
// 바인딩 시작
return getBinder().bind(annotation.prefix(), target, bindHandler);
}값을 어떻게 바인딩하는지 대강 감을 잡았으니 디버깅으로 실제 동작 흐름을 파악해보자
ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor 클래스에서 binder 에게 바인딩 요청하기 전에
바인딩할 타겟의 바인딩 방법을 검사한다.
private void bind(ConfigurationPropertiesBean bean) {
if (bean == null) {
return;
}
Assert.state(bean.asBindTarget().getBindMethod() != BindMethod.VALUE_OBJECT,
"Cannot bind @ConfigurationProperties for bean '" + bean.getName()
+ "'. Ensure that @ConstructorBinding has not been applied to regular bean");
try {
this.binder.bind(bean);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new ConfigurationPropertiesBindException(bean, ex);
}
} 바인딩할 타겟의 BindMethod 가 VALUE_OBJECT 가 아닌 경우만 bind() 를 호출한다.
BindMethod이넘을 살펴보자.JAVA_BEAN은 getter/setter 메서드로 값을 맵핑한다.VALUE_OBJECT은 constructor binding 을 한다./** * Configuration property binding methods. * * @author Andy Wilkinson * @since 3.0.8 */ public enum BindMethod { /** * Java Bean using getter/setter binding. */ JAVA_BEAN, /** * Value object using constructor binding. */ VALUE_OBJECT; }
여기까지 중간 정리를 해보면,
내가 선언한 RdsConnectionProps 에 VaultOperationService빈 을 주입할 때
@Autowired를 선언하면BindMethod가JAVA_BEAN이여서 예외가 발생하지 않고생성자 주입을 하면BindMethod가VALUE_OBJECT여서 예외가 발생한 것이다.
그럼 BindMethod 이넘이 언제 셋팅되는지 찾아보자
ConfigurationPropertiesBean
ConfigurationPropertiesBean 을 생성하는 팩토리 메서드에서 셋팅된다.
//ConfigurationPropertiesBean.class
/**
* Return a {@link ConfigurationPropertiesBean @ConfigurationPropertiesBean} instance
* for the given bean details or {@code null} if the bean is not a
* {@link ConfigurationProperties @ConfigurationProperties} object. Annotations are
* considered both on the bean itself, as well as any factory method (for example a
* {@link Bean @Bean} method).
* @param applicationContext the source application context
* @param bean the bean to consider
* @param beanName the bean name
* @return a configuration properties bean or {@code null} if the neither the bean nor
* factory method are annotated with
* {@link ConfigurationProperties @ConfigurationProperties}
*/
public static ConfigurationPropertiesBean get(ApplicationContext applicationContext, Object bean, String beanName) {
Method factoryMethod = findFactoryMethod(applicationContext, beanName);
Bindable<Object> bindTarget = createBindTarget(bean, bean.getClass(), factoryMethod);
if (bindTarget == null) {
return null;
}
bindTarget = bindTarget.withBindMethod(BindMethodAttribute.get(applicationContext, beanName));
if (bindTarget.getBindMethod() == null && factoryMethod != null) {
bindTarget = bindTarget.withBindMethod(JAVA_BEAN_BIND_METHOD);
}
if (bindTarget.getBindMethod() == null) {
bindTarget = bindTarget.withBindMethod(deduceBindMethod(bindTarget));
}
if (bindTarget.getBindMethod() != VALUE_OBJECT_BIND_METHOD) {
bindTarget = bindTarget.withExistingValue(bean);
}
return create(beanName, bean, bindTarget);
}@*ConfigurationProperties* 이 선언된 클래스에 기본 생성자 이외의 생성자가 있으면 VALUE_OBJECT_BIND_METHOD 이 리턴된다. 그래서 BindMethod.VALUE_OBJECT 로 셋팅이 된것이다.
//ConfigurationPropertiesBean.class
/**
* Deduce the {@code BindMethod} that should be used for the given {@link Bindable}.
* @param bindable the source bindable
* @return the bind method to use
*/
static org.springframework.boot.context.properties.bind.BindMethod deduceBindMethod(Bindable<Object> bindable) {
return deduceBindMethod(BindConstructorProvider.DEFAULT.getBindConstructor(bindable, false));
}
private static org.springframework.boot.context.properties.bind.BindMethod deduceBindMethod(
Constructor<?> bindConstructor) {
return (bindConstructor != null) ? VALUE_OBJECT_BIND_METHOD : JAVA_BEAN_BIND_METHOD;
}흠...... 삽질한듯..
의존관계 필드 주입과
생성자 주입 시점이 다른 것이 원인인가??
https://madplay.github.io/post/why-constructor-injection-is-better-than-field-injection
