문제
You are given a 0-indexed array of integers nums of length n. You are initially positioned at nums[0].
Each element nums[i] represents the maximum length of a forward jump from index i. In other words, if you are at nums[i], you can jump to any nums[i + j] where:
0 <= j <= nums[i] andi + j < n
Return the minimum number of jumps to reach nums[n - 1]. The test cases are generated such that you can reach nums[n - 1].
- 상황 : 현재 위치 (index =
0)에서 시작해서 끝까지 (index =nums.length - 1)도달 항상 가능함 - Input : 현재 위치에서 앞으로 이동할 수 있는 최대 칸
nums - Output : 최소 한으로 이동
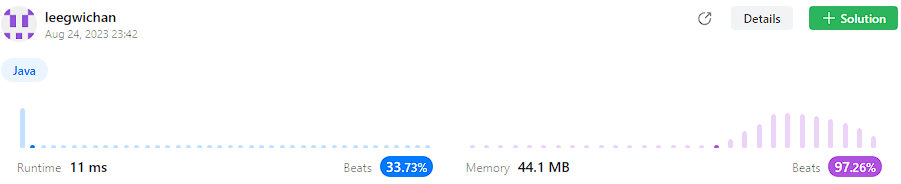
문제 답안
- Time complexity : O(n^2)
- Space complexity: O(1)
class Solution {
public int jump(int[] nums) {
int jumpCount = 0;
int checkPoint = nums.length - 1;
while (checkPoint != 0) {
int position = 0;
while (checkPoint - position > nums[position]) {
position++;
}
checkPoint = position;
jumpCount++;
}
return jumpCount;
}
}
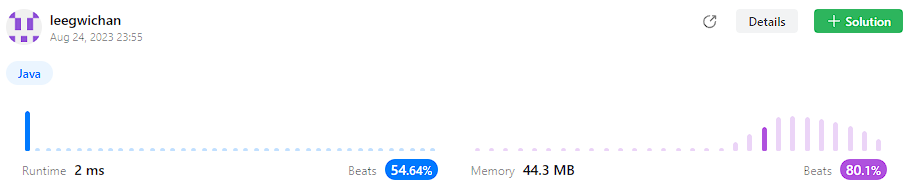
모범 답안
- Time complexity : O(n)
- Space complexity: O(1)
class Solution {
public int jump(int[] nums) {
int ans = 0;
int end = 0;
int farthest = 0;
// Implicit BFS
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; ++i) {
farthest = Math.max(farthest, i + nums[i]);
if (farthest >= nums.length - 1) {
++ans;
break;
}
if (i == end) { // Visited all the items on the current level
++ans; // Increment the level
end = farthest; // Make the queue size for the next level
}
}
return ans;
}
}