문제
You are given two integer arrays nums1 and nums2, sorted in non-decreasing order, and two integers m and n, representing the number of elements in nums1 and nums2 respectively.
Merge nums1 and nums2 into a single array sorted in non-decreasing order.
The final sorted array should not be returned by the function, but instead be stored inside the array nums1. To accommodate this, nums1 has a length of m + n, where the first m elements denote the elements that should be merged, and the last n elements are set to 0 and should be ignored. nums2 has a length of n.
- Input
- m, n은 정수
- 0 <= m, n <= 200
- 1 <= m + n <= 200
- nums1 : 앞 m개는 숫자가 오름차순, 뒤의 n개가 0으로 구성
- nums2 : 숫자 n개가 오름차순으로 되어 있다
- m, n은 정수
- Output
- num1에서 num1, num2의 모든 원소들을 오름차순으로 정렬
문제 풀이 전략
- 각 배열의 맨 앞자리 수를 대상으로 함
- 두 배열 중 하나라도 맨 뒤까지 도달할 때 까지 아래 과정 반복
- 두 대상 중 작은 수를 결과 배열에 앞자리에 집어 넣음
- 넣은 배열은 다음 원소를 대상으로 함
- 끝까지 도달하지 못한 배열의 남은 원소들을 결과 배열에 넣음
문제풀이 전략 수정
- Output을 따로 해야하는 줄 알았는데, nums1을 변경시키는 것이었다.
-> nums1을 따로 복사해서 사용하도록 함
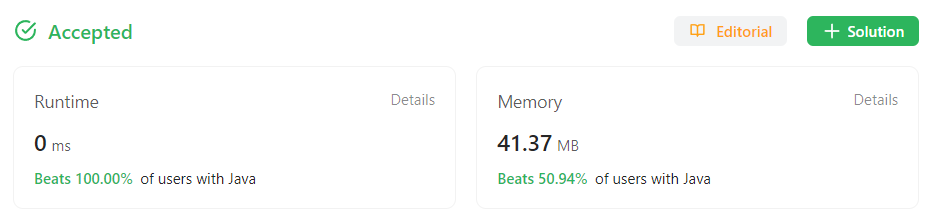
1차 작성
import java.util.Arrays;
class Solution {
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
int[] result = nums1;
nums1 = Arrays.copyOf(nums1, m + n);
int index1 = 0; int index2 = 0; int indexResult = 0;
while (index1 < m && index2 < n) {
if (nums1[index1] <= nums2[index2]) {
result[indexResult] = nums1[index1];
index1++;
} else {
result[indexResult] = nums2[index2];
index2++;
}
indexResult++;
}
if (index1 < m) {
copy(nums1, index1, result, indexResult, m - index1);
}
if (index2 < n) {
copy(nums2, index2, result, indexResult, n - index2);
}
nums1 = result;
}
private void copy(int[] array1, int index1, int[] array2, int index2, int size) {
for (int count = 0; count < size; count++) {
array2[index2 + count] = array1[index1 + count];
}
}
}
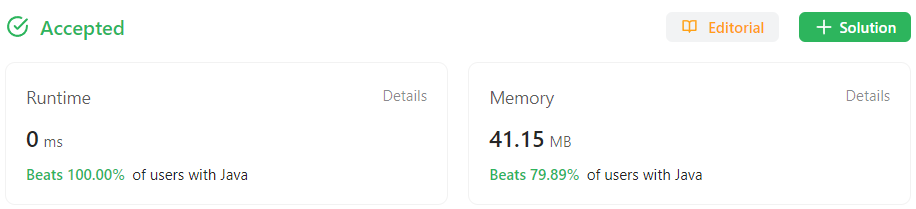
수정 1
System.arraycopy()를 통해 이미 내가 구현한copy()를 더 좋은 성능으로 지원하고 있었다.- 해당 기능을 삭제하고 java에서 제공하는 기능으로 대체함
import java.util.Arrays;
class Solution {
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
int[] result = nums1;
nums1 = Arrays.copyOf(nums1, m + n);
int index1 = 0; int index2 = 0; int indexResult = 0;
while (index1 < m && index2 < n) {
if (nums1[index1] <= nums2[index2]) {
result[indexResult] = nums1[index1];
index1++;
} else {
result[indexResult] = nums2[index2];
index2++;
}
indexResult++;
}
if (index1 < m) {
System.arraycopy(nums1, index1, result, indexResult, m - index1);
}
if (index2 < n) {
System.arraycopy(nums2, index2, result, indexResult, n - index2);
}
nums1 = result;
}
}
모범 답안 찾아보기
- 모범 답안 전략
- nums1이 앞에는 숫자, 뒤에는 0으로 채워져 있음을 생각해서 뒤에서부터 값을 채워나갔다.
- 이를 통해서 따로 nums1의 데이터를 복사하지 않고 구현하였다.
class Solution {
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
int i = m - 1;
int j = n - 1;
int k = m + n - 1;
while (j >= 0) {
if (i >= 0 && nums1[i] > nums2[j]) {
nums1[k--] = nums1[i--];
} else {
nums1[k--] = nums2[j--];
}
}
}
}