Bean과 ApplicationContext의 관계
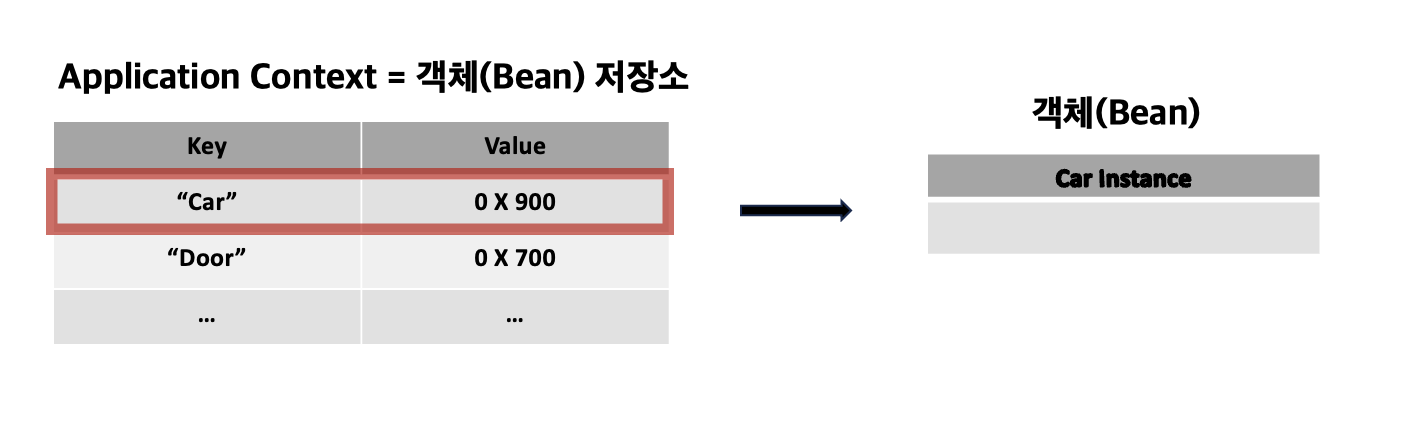
Bean : Spring Container가 관리하는 객체
Spring Container(= Application Context) : Bean 저장소, Bean을 저장, 관리(생성, 소멸, 연결@ AutoWired,@ Resourse)
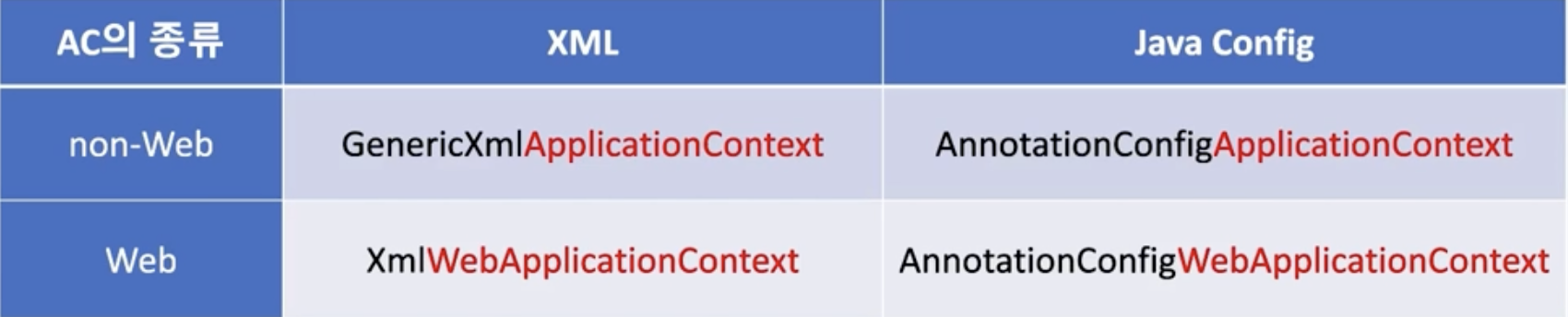
SpringContainer 종류와 기능
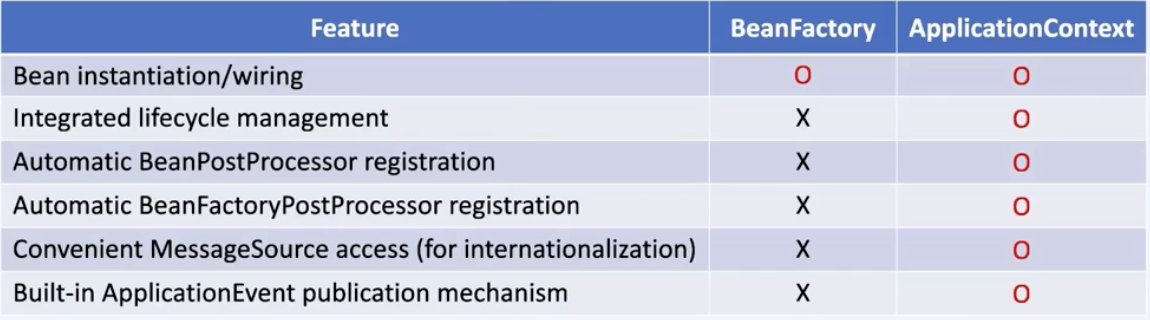
- BeanFactory : Bean(객체)를 생성, 연결 등의 기본 기능을 정의 (Parent)
- ApplicationContext : BeanFactory를 확장해서 여러 기능을 추가 정의 (Child)
ApplicationContext 생성
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext()에 매개변수로 전달한 "di3.AppConfig.class" 파일에서 생성한 ApplicationContext의 환경을 설정한다.
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext AppConfig
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 | package di3; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; class Car{ Engine engine; Door door; @Override public String toString() { return "Car{" + "engine=" + engine + ", door=" + door + '}'; } } class Engine{} class Door{} public class main { public static void main(String[] args) { // AC를 생성 : AC의 설정파일은 AppConfig.class 자바 설정 // AnnotaionConfigApplicationContext를 사용해서 ApplicationContext를 생성 ApplicationContext AC = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(di3.AppConfig.class); } } | cs |
ApplicationContext 초기 환경 설정 예시
@Congfig 어노테이션을 사용해서 이 클래스 파일이 환경설정 파일임을 선언
@Bean 어노테이션으로 객체를 나타냄
Bean(객체)를 호출하면 선언되어있는 객체를 반환
@Config @Bean
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | package di3; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class AppConfig { @Bean Car car(){ return new Car(); } @Bean Engine engine(){ return new Engine(); } @Bean Door door(){ return new Door(); } } | cs |
ApplicationContext에서 선언한 정보를 가져와서 확인하기
Car car = (Car)AC.getBean("Car")
기본적으로 Bean 객체는 Singleton이다. 즉, 객체를 공유하고 있기때문에 getBean으로 객체를 여러번 호출하더라도 같은 객체가 출력된다.
호출 마다 다른 객체를 생성하고 싶은 경우 위 AppConfig 파일에서 해당 Bean의
@Scope("prototype")으로 scope을 지정해주면 된다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | public class main { public static void main(String[] args) { // AC를 생성 : AC의 설정파일은 AppConfig.class 자바 설정 // AnnotaionConfigApplicationContext를 사용해서 ApplicationContext를 생성 ApplicationContext AC = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(di3.AppConfig.class); Car car = (Car)AC.getBean("car");//ByName 객체(Bean)을 조회 System.out.println("car = " + car); } } | cs |
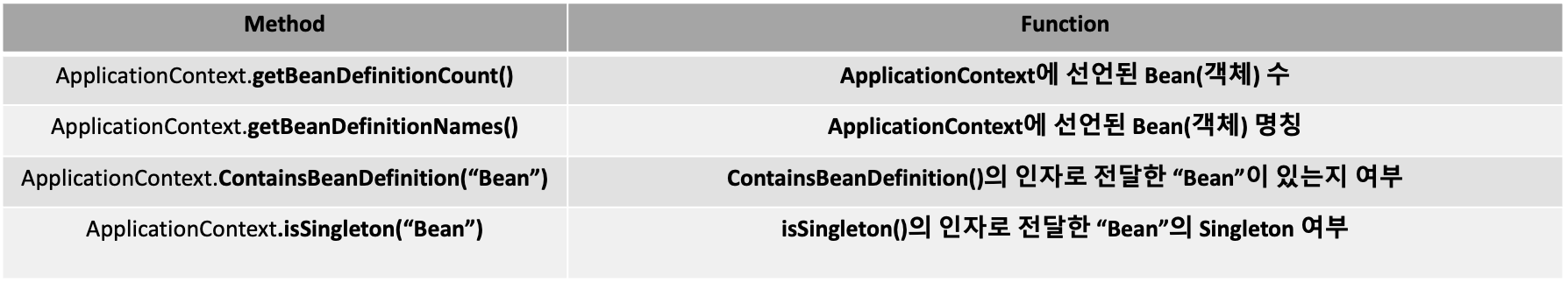
ApplicationContext 메서드