.gif)
🧪 Description
Given the head of a linked list, remove the nth node from the end of the list and return its head.
Example 1:
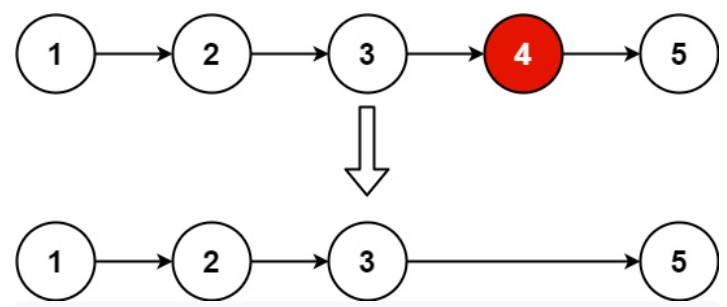
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
Output: [1,2,3,5]Example 2:
Input: head = [1], n = 1
Output: []Example 3:
Input: head = [1,2], n = 1
Output: [1]💊 Solution
기본적인 원리는 다음과 같다. Description의 Example1으로 살펴보자.
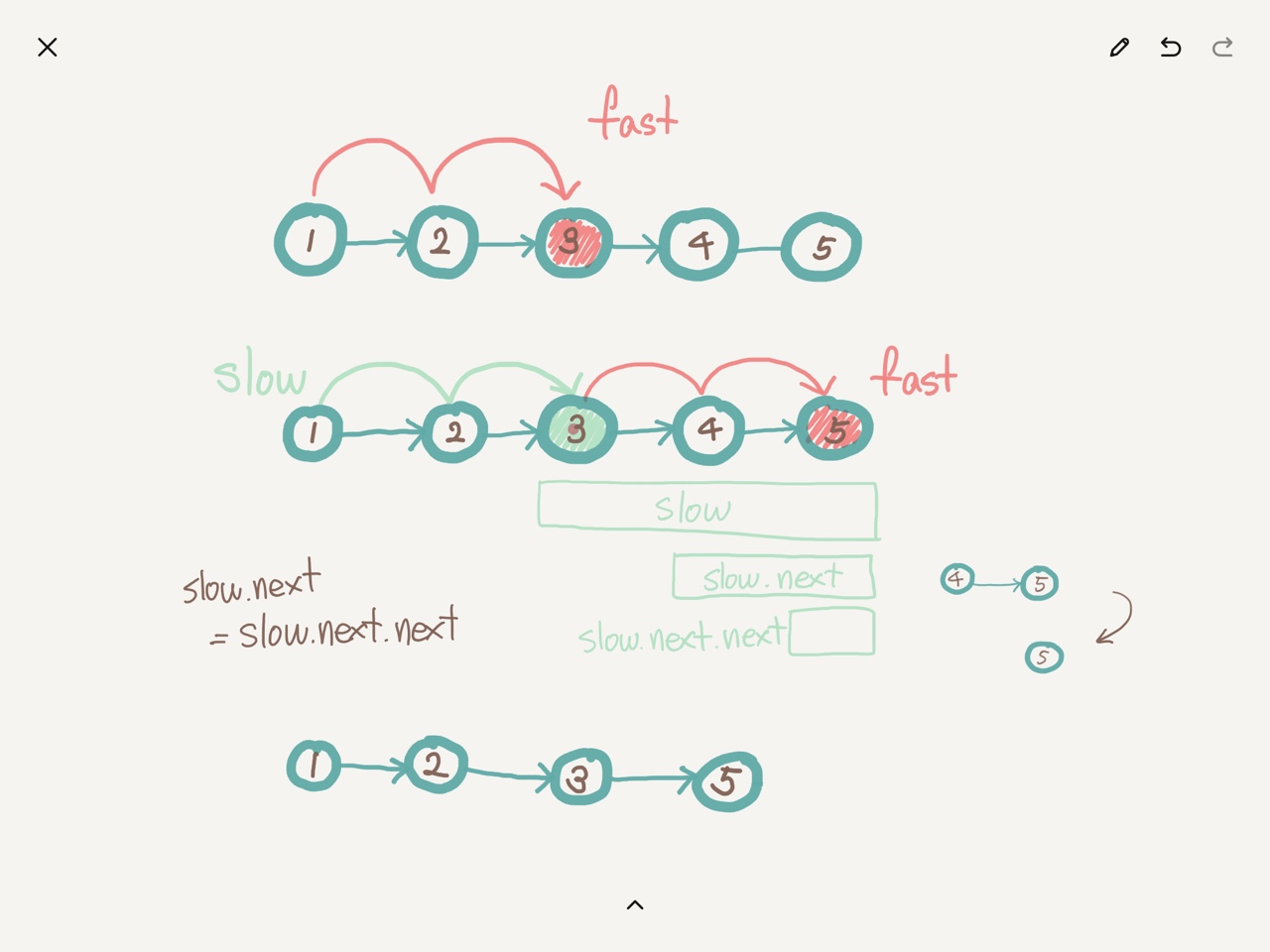
- 끝에서 n번째 노드를 찾아야 하니까, fast 포인터를 먼저 n만큼 이동시켜놓는다.
- fast가 끝에 도달할 때까지 slow와 fast포인터를 똑같이 1씩 이동시키면 slow는 제거해야할 n번째 노드 바로 이전에 위치하게 된다.
- 예시이미지로 예를들면,
slow = [3,4,5]
slow.next = [4,5]
slow.next.next = [5]이다.
slow.next = slow.next.next로 slow다음이 바로 [5]가 되도록 만들면 중간의 노드 4는 삭제되고 [1,2,3,5] 연결리스트가 반환된다.
❌ 1st approach - run time error
var removeNthFromEnd = function(head, n) {
let slow = head;
let fast = head;
while (n > 0) {
n--;
fast = fast.next;
}
while (fast.next !== null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return head;
};여기서 문제는 길이가 1인 연결리스트의 테스트케이스를 통과하지 못했다는 것이었다.
Line 24 in solution.js
while (fast.next !== null) {
^
TypeError: Cannot read property 'next' of null
Input: head = [1], n = 1
Output: []// 내 답안의 결과는 [1] 이었다.n도 그대로 1이고,
길이가 1이니 fast = fast.next를 해줄 수 없어서 그대로 1이 남아 결과로 반환된 것이다.
⭕ 2nd approach
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} n
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var removeNthFromEnd = function(head, n) {
nl = new ListNode(0);
nl.next = head;
let slow = nl;
let fast = nl;
while (n > 0) {
n--;
fast = fast.next;
}
while (fast.next !== null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return nl.next;
};생성자 함수를 이용해 ListNode의 새로운 인스턴스 nl을 만든뒤, 이것을 인자로 전달된 head연결리스트앞에 붙여주었다. 이렇게 하면 [1] 과 같이 한개의 원소만 가진 연결리스트도 이전에 nl이 있으니 nl.next로 1에 접근할 수 있어 에러가 나지 않는다.
그리고 리턴 또한 nl.next값으로 지정해주었다.
🧫 Result
Runtime
64 ms, faster than 99.36% of JavaScript online submissions for Remove Nth Node From End of List.
Memory Usage
40.1 MB, less than 68.11% of JavaScript online submissions for Remove Nth Node From End of List.
이번 문제는 푸는데 어려워서 시간이 꽤 걸렸다. 역시 난이도 Medium.. 연결리스트라는 개념 자체가 생소해서 이해하는데 시간이 걸렸다.
그래도 그만큼 뿌듯한 알고리즘 풀이였다!
