📚 4주차 미션 정리
🔖 기본 미션 (필수)
클래스의 타입 변환에는 어떤 것이 있는지 정리하고 공유하기
- 자동 타입 변환(업캐스팅 - Upcasting)
- 자식 클래스의 객체가 부모 클래스 타입으로 형변환
Animal a = new Dog(); // 업캐스팅 (자동 형변환)- 강제 타입 변환(다운캐스팅 - Downcasting)
- 업캐스팅된 것을 다시 원상태로 돌리는 것
Dog d = (Dog) a; // 다운캐스팅 (강제 형변환)
a가Dog타입 이면 가능
아니면ClassCastException발생
자세한 내용은 아래에 있습니다
🔖 추가 미션 (선택)
P.389 (07-3) 확인 문제 3번 풀고 풀이과정 설명하기
- 부모 클래스 - HttpServlet(추상 클래스)
package chap07;
public abstract class HttpServlet {
public abstract void service();
}- 자식 클래스 - LoginServlet
package chap07;
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
public void service() {
System.out.println("로그인 합니다");
}
}- 자식 클래스 - FileDownloadServlet
package chap07;
public class FileDownloadServlet extends HttpServlet{
@Override
public void service() {
System.out.println("파일 다운로드합니다.");
}
}- 메인 클래스
package chap07;
public class HttpServletEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
method(new LoginServlet());
method(new FileDownloadServlet());
}
public static void method(HttpServlet servlet){
servlet.service();
}
}
HttpServlet은 추상 클래스이며 그 안에service()라는 추상 메서드를 정의
따라서 자식 클래스에서service()을 구현해야함
자식 클래스
Login,FileDownload는HttpServlet의 자식이기 때문에HttpServlet타입으로도 받기 가능HttpServlet servlet = new LoginServlet(); HttpServlet servlet = new FileDownloadServlet(); 과 같은 말이다
따라서 메서드 내부에서
servlet.service()를 호출하면 오버라이딩된LoginServlet과FileDownloadServlet안의 service 메서드가 호출된다
📌 Chap07 내용 정리 | 상속
클래스 상속
- 부모 클래스 - CellPhone
package chap07;
public class CellPhone {
//필드
String model;
String color;
//생성자
/* public CellPhone() {
//System.out.println("CellPhone() 호출됨");
}
자식 클래스에서 super() 부모 호출 한 곳
*/
//메소드
void powerOn() {System.out.println("전원을 켭니다.");}
void powerOff() {System.out.println("전원을 끕니다.");}
void bell() {System.out.println("벨이 울립니다.");}
void sendVoice(String message) {System.out.println("자기: " + message);}
void receiveVoice(String message) {System.out.println("상대방: " + message);}
void hangUp() {System.out.println("전화를 끊습니다.");}
}- 자식 클래스 - DmbCellPhone
package chap07;
public class DmbCellPhone extends CellPhone {
// 필드
int channel;
// 생성자
DmbCellPhone(String model, String color, int channel) {
//super(); -> 부모 클래스 호출
this.model = model;
this.color = color;
this.channel = channel;
}
// 메소드
void turnOnDmb() {
System.out.println("채널 " + channel + "번 DMB 방송 수신을 시작합니다.");
}
void changeChannelDmb(int channel) {
this.channel = channel;
System.out.println("채널 " + channel + "번으로 바꿉니다.");
}
void turnOffDmb() {
System.out.println("DMB 방송 수신을 멈춥니다.");
}
}- 상속 받은 클래스 - DmbCellPhoneExample
package chap07;
public class DmbCellPhoneExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//DmbCellPhone 객체 생성
DmbCellPhone dmbCellPhone = new DmbCellPhone("자바폰", "검정", 10);
//CellPhone 클래스로부터 상속 받은 필드
System.out.println("모델: " + dmbCellPhone.model);
System.out.println("색상: " + dmbCellPhone.color);
//DmbCellPhone 클래스의 필드
System.out.println("색상: " + dmbCellPhone.channel);
//CellPhone 클래스로부터 상속받은 메소드 호출
dmbCellPhone.powerOn();
dmbCellPhone.powerOff();
dmbCellPhone.sendVoice("여보세오.");
dmbCellPhone.receiveVoice("안녕하세요! 저는 홍길동인데요");
dmbCellPhone.sendVoice("아~ 예 반갑습니다.");
dmbCellPhone.hangUp();
//DmbCellPhone 클래스의 메소드 호출
dmbCellPhone.turnOnDmb();
dmbCellPhone.changeChannelDmb(12);
dmbCellPhone.turnOffDmb();
}
}- 여러 개의 부모 클래스 상속 불가
- 부모 클래스에서 private 접근 제한 갖는 필드와 메서드는 상속 대상 제외
- 부모와 자식 클래스가 다른 패키지에 존재한다면 default 접근 제한된 필드와 메서드 제외
메소드 재정의
- 부모 클래스 - Calculator
package chap07;
public class Calculator {
double areaCircle(double r) {
System.out.println("Calculator 객체의 areaCircle() 실행");
return 3.14159 * r * r;
}
}- 자식 클래스 - Computer
package chap07;
public class Computer extends Calculator {
@Override
double areaCircle(double r) {
System.out.println("Computer 객체의 areaCircle() 실행");
return Math.PI * r * r;
}
}- 상속 받은 클래스 - ComputerEx
package chap07;
public class ComputerEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int r = 10;
Calculator calculator = new Calculator();
System.out.println("원면적: " + calculator.areaCircle(r));
System.out.println();
Computer computer = new Computer();
System.out.println("원면적: " + computer.areaCircle(r));
}
}- 부모의 메소드와 자식의 메소드가 동일한 경우 발생
- 오버라이딩이 발생하게 되는 경우 부모 클래스의 메소드는 숨겨지는데 자식 클래스 내부에서 부모 클래스를 호출해야한다면 super() 사용해서 부모 클래스를 호출할 수 있음
접근제한자
- public → 어디서든지 자유롭게 사용 가능
- protected → 같은 패키지 or 자식 클래스에서 사용 가능
- default → 같은 패키지 소속만 사용 가능
- private → 외부에서 사용 불가
→ 내려올 수록 접근 제한이 강화
Final 클래스
- final 키워드를 사용하면 수정 불가
- 클래스 앞에 Final 키워드가 있다면 상속이 불가 → 자식 클래스를 만들수 없음
Final 메소드
- 메소드 앞에 Final 키워드가 있다면 오버라이딩 불가
📌 Chap07-2 내용 정리 | 타입 변환과 다형성
자동 타입 변환
- 프로그램 실행 도중 자동으로 타입 변환이 발생
Animal animal = new Cat();- 부모가 아니더라도 상속 계층에서 상위 타입이라면 발생
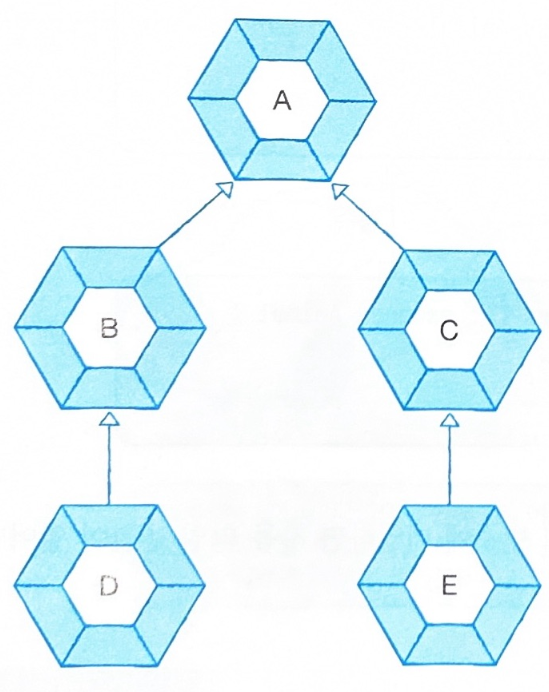
객체 A는 객체 B, C, D, E를 상속 받고 있다
객체 D는 객체 A, B타입을 자동 변환이 가능
객체 E는 객체 A, C타입을 자동 변환이 가능
❌ 객체 D는 C타입으로 변환 불가
❌ 객체 E는 B타입으로 변환 불가
- 자동 타입 변환 예시 코드
package chap07;
class A {}
class B extends A {}
class C extends A {}
class D extends B {}
class E extends C {}
public class AutoTypeEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
B b = new B();
C c = new C();
D d = new D();
E e = new E();
A a1 = b;
A a2 = c;
A a3 = d;
A a4 = e;
B b1 = d;
C c1 = e;
//불가능
//B b3 = e;
//C C2 = d;
}
}강제 타입 변환
- 부모 타입을 자식 타입으로 변환
- 자식 타입이 부모 타입으로 자동 변환 된 후 다시 반대로 변환할 때 사용
A a = new B();
B b = (B) a;
C c = (C) a; //사용 불가능- 부모클래스 - Parent
package chap07;
public class Parent {
public String field1;
public void method1() {
System.out.println("Parent-method1()");
}
public void method2() {
System.out.println("Parent-method2()");
}
}- 자식 클래스 - Child
package chap07;
public class child extends Parent{
public String field2;
public void method3() {
System.out.println("Child-method3()");
}
}- 상속 받은 클래스 - ChildEx
package chap07;
public class ChildEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent parent = new child(); //자동 타입 변환
parent.field1 = "data1";
parent.method1();
parent.method2();
//불가능
//parent.field2 = "data2";
//parent.method3();
child child = (child) parent; //강제 타입 변환
child.field2 = "data2";
child.method3();
}
}- instanceof 연산자
- 어떤 객체가 어느 클래스의 인스턴스인지 확인
- 타입 확인 안하고 강제 타입 변환 사용하면 ClassCast예외 발생
추상 클래스 (abstract)
- 여러 클래스의 공통된 특성을 추출해서 선언한 것
- 상속을 통해 자식 클래스를 만들 수 있게 함(부모 역할만 수행)
- 직접 객체를 생성 못하니 자식 클래스에서 super() 키워드 사용
추상 메서드
- 추상 클래스에서만 선언 가능
- 추상 메서드는 자식 클래스에서 재정의되어 실행 내용 결정 해야함

