프로세스와 스레드 (Process vs Thread)
1) 프로세스란?
프로세스(Process)는 일반적으로 cpu에 의해 메모리에 올려져 실행중인 프로그램을 말하며, 자신만의 메모리 공간을 포함한 독립적인 실행 환경을 가지고 있습니다. 우리가 사용하는 프로그램 중 일부는 여러 프로세스간 상호작용을 하는 것일수도 있습니다.
자바 JVM(Java Virtual Machine)은 주로 하나의 프로세스로 실행되며, 동시에 여러 작업을 수행하기 위해서 멀티 스레드를 지원하고 있습니다.
2) 스레드란?
스레드(Thread)는 프로세스안에서 실질적으로 작업을 실행하는 단위를 말하며, 자바에서는 JVM(Java Virtual Machine)에 의해 관리됩니다. 프로세스에는 적어도 한개 이상의 스레드가 있으며, Main 스레드 하나로 시작하여 스레드를 추가 생성하게 되면 멀티 스레드 환경이 됩니다. 이러한 스레드들은 프로세스의 리소스를 공유하기 때문에 효율적이긴 하지만 잠재적인 문제점에 노출될 수도 있습니다.
프로세스와 스레드의 차이점
프로세스는 운영체제로부터 자원을 할당받는 작업 단위이다. 애플리케이션이 하나의 프로세스가 되고, 그 안에서 여러 개의 스레드가 할당 받은 자원을 이용하여 실행 단위로 존재할 수 있다. 즉 스레드는 하나의 프로세스 안에서 여러 실행의 흐름이라고 생각하면 됩니다.
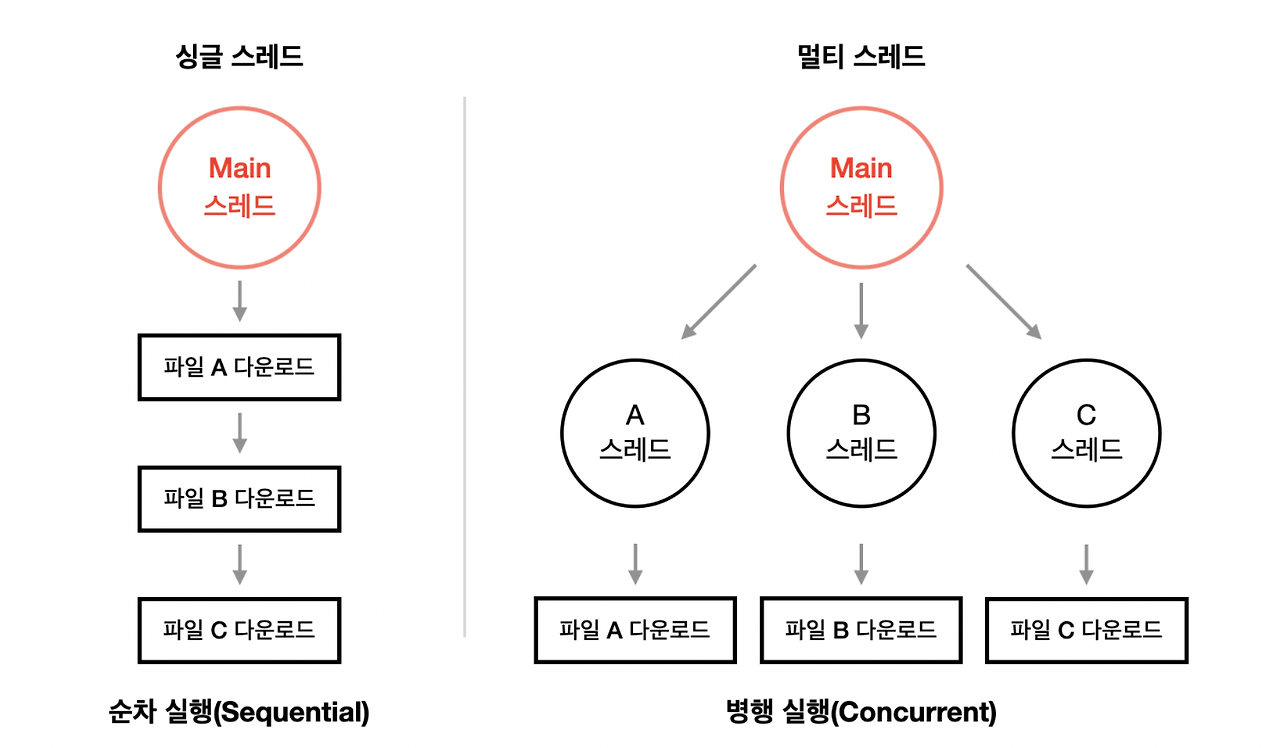
- 멀티스레딩이란?
하나의 프로세스 내에서 여러 스레드를 동시에 실행시키는 방법을 말한다. 웹 서버는 대표적인 멀티 스레드 응용 프로그램이다.
스레드의 장단점
장점
- 시스템 자원 소모 감소
- 프로세스를 생성하여 자원을 할당하는 요청이 줄어들기 때문에 자원을 효율적으로 관리할 수 있다.
- 시스템 처리량 증가
- 스레드 사이 데이터를 주고 받는 것이 간단해지고 시스템 자원 소모가 줄어들게 된다.
- 스레드 사이의 작업량이 작아 Context Switching이 빠르다.
- 간단 통신 방법으로 프로그램 응답 시간을 단축
- 스레드는 프로세스 내의 Stack 영역을 제외하고 모든 영역을 공유하기 때문에 통신 부담이 적다.
단점
- 주의 깊은 설계가 필요하며, 디버깅이 까다롭다.
- 서로 자원을 소모하다 충돌이 일어날 수 있다.
하나의 스레드에 문제가 발생하면 전체 프로세스가 영향을 받을 수 있다.
- 서로 자원을 소모하다 충돌이 일어날 수 있다.
스래드 생명주기
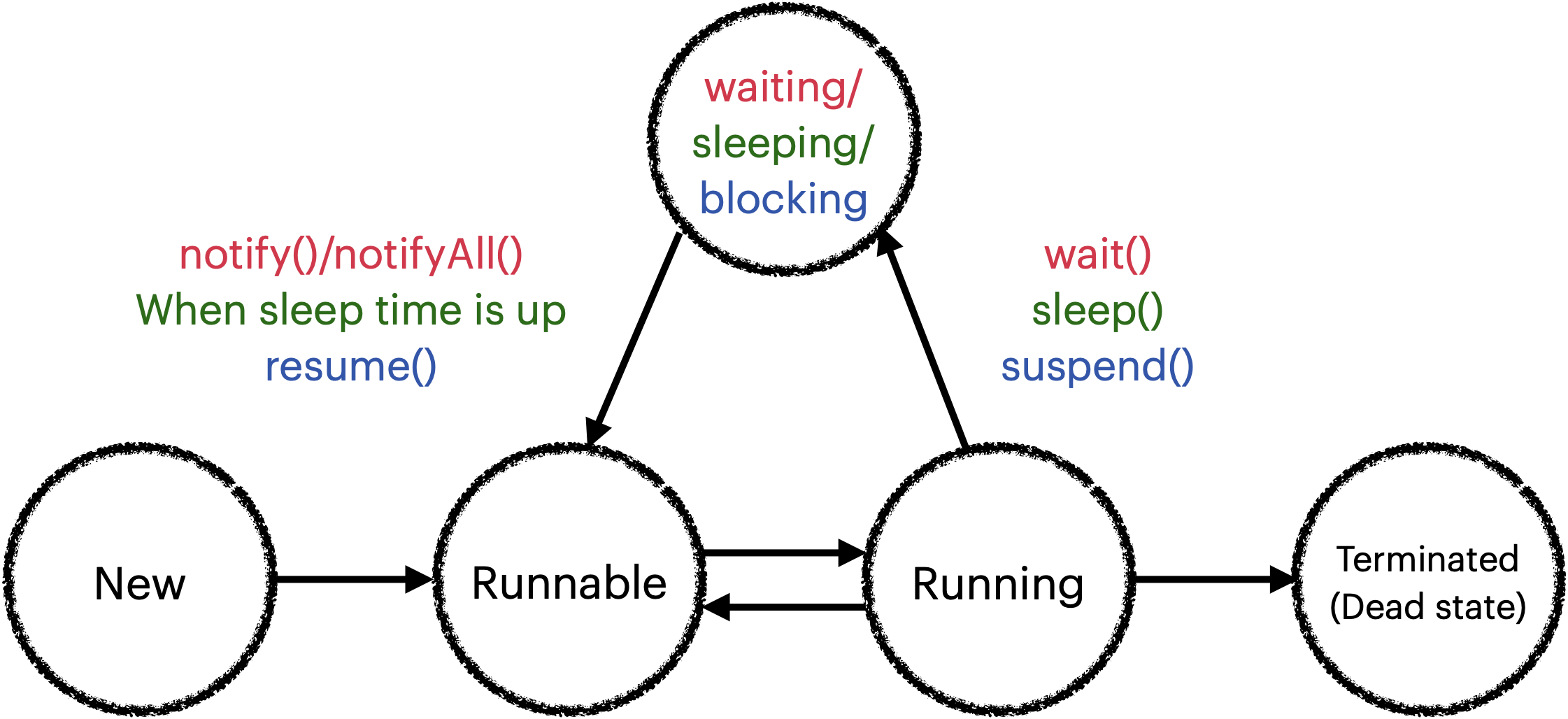
1.New(객체 생성)
- 스레드가 만들어진 상태로 아직 start() 메서드가 호출되지 않은 상태이다.
2.Runnable(준비 상태)
- 스레드가 실행되기 위한 준비 단계이다.
start() 메서드를 호출하면 run() 메서드에 설정된 스레드가 Runnable 상태가 된다.
3.Running(실행 상태)
- Runnable(준비 상태)에 있는 스레드 중 우선 순위를 가진 스레드가 결정되면
JVM이 자동으로 run() 메서드를 호출하여 스레드가 Running 상태로 진입한다.
4.Terminated(실행 종료)
- Running 상태에서 스레드가 모두 실행되고 난 후 완료 상태이다.
run() 메서드가 완료되면 스레드가 종료되고, 스레드는 다시 시작할 수 없다.
5.Blocked(지연 상태)
- 객체의 Lock이 풀릴 때까지 기다리는 상태이다.
wait() 메서드에 의해 Blocked 상태가 된 스레드는 notify() 메서드가 호출되면 Runnable 상태가 된다.
sleep(시간) 메서드는 Blocked 상태가 된 스레드를 지정된 시간이 지나면 Runnable 상태가 되도록 한다.
스레드 구현
자바에서 스레드를 만드는 방법은 2가지가 있습니다. 하나는 Thread 클래스를 상속받는 방법과 다른 하나는 Runnable 인터페이스를 구현하는 방법입니다. 자바는 다중 상속을 허용하지 않기 때문에 Thread 클래스를 상속받게 되면 다른 클래스를 상속받을수가 없습니다. 대신 인터페이스인 Runnable을 이용하여 작성하게 되면 이러한 문제점을 해결하실 수 있습니다.
스레드를 생성하고 동작시킴에 있어서 알아두어야 할 점은 사용자가 스레드 객체를 생성하고 실행요청을 하더라도 스레드가 실행되는 것은 전적으로 JVM에 의한 스케쥴러에 따른다는 것입니다. 사용자는 다만 Thread의 여러 메소드들을 통해서 JVM에 해당 명령들이 실행되도록 요청하는 것입니다.
- 스레드 상속 구현 방식
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread mt1 = new MyThread(); // 3.스레드 객체 생성
mt1.start(); // 4.스레드 실행
}
}
class MyThread extends Thread { // 1.Thread 클래스 상속한 클래스 정의
public void run() { // 2.run()메소드 오버라이드 및 스레드 코드 작성
System.out.println(this.getName());
}
}- Runnable 인터페이스 구현 방식
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable r1 = new MyThread(); // 3.Runnable 객체 생성
Thread t1 = new Thread(r1); // 4.Thread 객체 생성
t1.start(); // 5.스레드 실행
}
}
class MyThread implements Runnable { // 1.Runnable 인터페이스를 구현하는 클래스 정의
public void run() { // 2.run()메소드 오버라이드 및 스레드 코드 작성
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}사용 예제
public class MyThread extends Thread {
public MyThread(String string) {
super(string);
}
public void run() {
int count = 0;
while (!this.isInterrupted()) {
System.out.print(this.getName());
HelloWorld.threadSleep(this, 500);
count++;
if (count == 20) {
this.interrupt();
System.out.printf("%n[5]." + this.toString() + "-인터럽트됨]");
}
}
}
}public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread mt1 = new MyThread("*");
MyThread mt2 = new MyThread("#");
mt1.start();
mt2.start();
System.out.printf("%n[1].mt1:" + mt1.isInterrupted() + ", mt2:" + mt2.isInterrupted() + "]");
threadSleep(Thread.currentThread(), 2000);
mt1.interrupt();
System.out.printf("%n[2].mt1:" + mt1.isInterrupted() + ", mt2:" + mt2.isInterrupted() + "]");
threadJoin(mt2);
System.out.printf("%n[3].mt1:" + mt1.isInterrupted() + ", mt2:" + mt2.isInterrupted() + "]");
}
static void threadSleep(Thread t, long time) {
try {
Thread.sleep(time);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.printf("%n[4]." + t.toString() + "-인터럽트됨]");
t.interrupt();
}
}
static void threadJoin(Thread t) {
try {
t.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}[1].mt1:false, mt2:false]#**#*##*
[2].mt1:true, mt2:false]
[4].Thread[*,5,main]-인터럽트됨]################
[5].Thread[#,5,main]-인터럽트됨]
[3].mt1:true, mt2:true]참고 사이트
[Java] 스레드(Thread) 이해하기 -1 : 구조, 상태, 예시
[Java] 자바 - Thread란? 스레드 개념 및 사용방법
Java의 Thread에 대해 알아보자

