1. 다양한 타입의 출력
Java IO객체는 인스턴스를 만들고 모두 사용하게 되면, 해당 객체를 폐기하는 class 메소드를 사용해야 한다(즉 폐기를 해야함).
다만 이를 작성하지 않더라도, exception이 발생하지 않았을 경우 자동으로 해당 객체를 종료시킬 수 있는 구문으로 작성할 수도 있다.
1-1. DataOutputStream을 활용한 write
DataOutputStream은 다양한 type의 data을 write할 수 있는 클래스로 사용할 수 있는데, 장식대상 클래스를 덮는 형식으로 관련한 메소드를 사용할 수 있다.
※ file 관련한 output 클래스를 사용하게 된다면, file을 write할 수 있는 메소드를 사용할 수 있게 된다.
※ try - with resource - catch - finally
public class fileStream{
public static void main(String[] args){
try(
//OutputStream
//File stream을 활용하여 output 대상을 특정짓는다.
DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("data.txt"));
){
out.writeInt(10); //data가 저장되지 않고, data byte 형식으로 저장(4 byte)
out.writeBoolean(true); //boolean - 1 byte
out.writeDouble(20.5); //double - 8 byte
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}위에서 out stream을 통해 data를 write한다면, FileoutputStream에서 설정한 파일 경로와 상태를 기반으로 write 및 생성한다.
1-2. DataOutputStream 읽기
Write한 data를 시스템이 읽기(Input)위해선, 별도의 input stream을 활용하여 읽어야 한다.
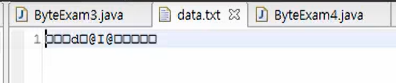
위와 같이 write한 data를 시스템에서 바로 읽어들이지 못하기 때문이다.
input stream이 필요한 이유를 여기서 알 수 있다.
이를 토대로 위에서 저장한 data를 읽는 stream을 구현해보자.
public class InputStream{
public void main(String[] args){
try( //다양한 type의 data 읽기
DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("data.txt"));
){
int i = in.readInt(); //정수형 data 읽기
boolean b = in.readBoolean(); //boolean data 읽기
..
System.out.println(i);
System.out.println(b);
}
}
}2. 참조자료
프로그래머스 강의 - File 단위 입출력
https://programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/9/lessons/318
