의식의 흐름
MUI를 잘 사용하다가 문득, MUI 컴포넌트는 테마를 어떻게 가져오는거지? 에 대한 의문이 생겼다.
import Button from '@mui/material/Button';여타 Provider 나 별도 CSS 파일은 import할 필요 없이, 컴포넌트만 덩그러니 가져오면 되는 이 간편한 방식이 새삼스레 대체 어떻게 작동할 수 있는 것인지 궁금증을 갖기 시작했다.
// mui-material/src/Button/Button.js
{
...(ownerState.variant === 'text' &&
ownerState.color !== 'inherit' && {
backgroundColor: theme.vars
? `rgba(${theme.vars.palette[ownerState.color].mainChannel} / ${
theme.vars.palette.action.hoverOpacity
})`
: alpha(theme.palette[ownerState.color].main, theme.palette.action.hoverOpacity),
// Reset on touch devices, it doesn't add specificity
'@media (hover: none)': {
backgroundColor: 'transparent',
},
}),
...(ownerState.variant === 'outlined' &&
ownerState.color !== 'inherit' && {
border: `1px solid ${(theme.vars || theme).palette[ownerState.color].main}`,
backgroundColor: theme.vars
? `rgba(${theme.vars.palette[ownerState.color].mainChannel} / ${
theme.vars.palette.action.hoverOpacity
})`
: alpha(theme.palette[ownerState.color].main, theme.palette.action.hoverOpacity),
// Reset on touch devices, it doesn't add specificity
'@media (hover: none)': {
backgroundColor: 'transparent',
},
}),
...
}그도 그럴 것이 Button 컴포넌트의 소스 코드가 이렇게 요란하기 때문이다. static한 값은 없고, 전부 theme 과 ownerState 라는 객체에서 가져오고 있다. 나는 이런 객체를 어디에서도 정의하거나 import한 적이 없는데, 어떻게 잘 꾸며진 Button 이 렌더링되는 걸까?
우선 우리가 Button 을 import 하는 순간 어떤 일이 일어나는지 보자.
// mui-material/src/Button/Button.js
...
return (
<ButtonRoot
ownerState={ownerState}
className={clsx(contextProps.className, classes.root, className)}
component={component}
disabled={disabled}
focusRipple={!disableFocusRipple}
focusVisibleClassName={clsx(classes.focusVisible, focusVisibleClassName)}
ref={ref}
type={type}
{...other}
classes={classes}
>
{startIcon}
{children}
{endIcon}
</ButtonRoot>
);
});우리가 import 해온 Button 컴포넌트를 렌더링하려 하면, Button.js 파일의 이 ButtonRoot 컴포넌트가 리턴되는 것이다.
// mui-material/src/Button/Button.js
const ButtonRoot = styled(ButtonBase, {
shouldForwardProp: (prop) => rootShouldForwardProp(prop) || prop === 'classes',
name: 'MuiButton',
slot: 'Root',
overridesResolver: (props, styles) => {
const { ownerState } = props;
return [
styles.root,
styles[ownerState.variant],
styles[`${ownerState.variant}${capitalize(ownerState.color)}`],
styles[`size${capitalize(ownerState.size)}`],
styles[`${ownerState.variant}Size${capitalize(ownerState.size)}`],
ownerState.color === 'inherit' && styles.colorInherit,
ownerState.disableElevation && styles.disableElevation,
ownerState.fullWidth && styles.fullWidth,
];
},
})(
({ theme, ownerState }) => ({
...theme.typography.button,
minWidth: 64,
padding: '6px 16px',
borderRadius: (theme.vars || theme).shape.borderRadius,
...
})
...ButtonRoot 는 이렇게 생겼다. 생긴 걸 보니 이 녀석은 그냥 HTML button 컴포넌트를 감싸서 만든 게 아니라, styled() 함수가 리턴한 컴포넌트였다.
그러니까, 우리가 Button 컴포넌트를 import 해와서 사용하면 Button.js → return ButtonRoot → const ButtonRoot = styled(...) 이 순서대로 코드를 읽어오게 될 것이다.
이 styled 함수는 뭘까?
위 코드의 생김새를 잘 보면, ButtonRoot는 그냥 styled() 가 아니라 styled()() 의 결과다. 즉, styled() 호출에 의해 어떤 함수가 먼저 리턴되고, 그 함수의 실행 결과가 ButtonRoot 컴포넌트다.
const ButtonRoot = styled(ButtonBase, {...})(
({ theme, ownerState }) => ({...})
)그리고 나의 원래 궁금증을 잊을까봐 다시 적어두지만, theme 과 ownerState 를 어떻게 불러올 수 있는지 알려면 저 styled() 에 의해 리턴된 의문의 함수를 뜯어봐야 하는 듯하다.
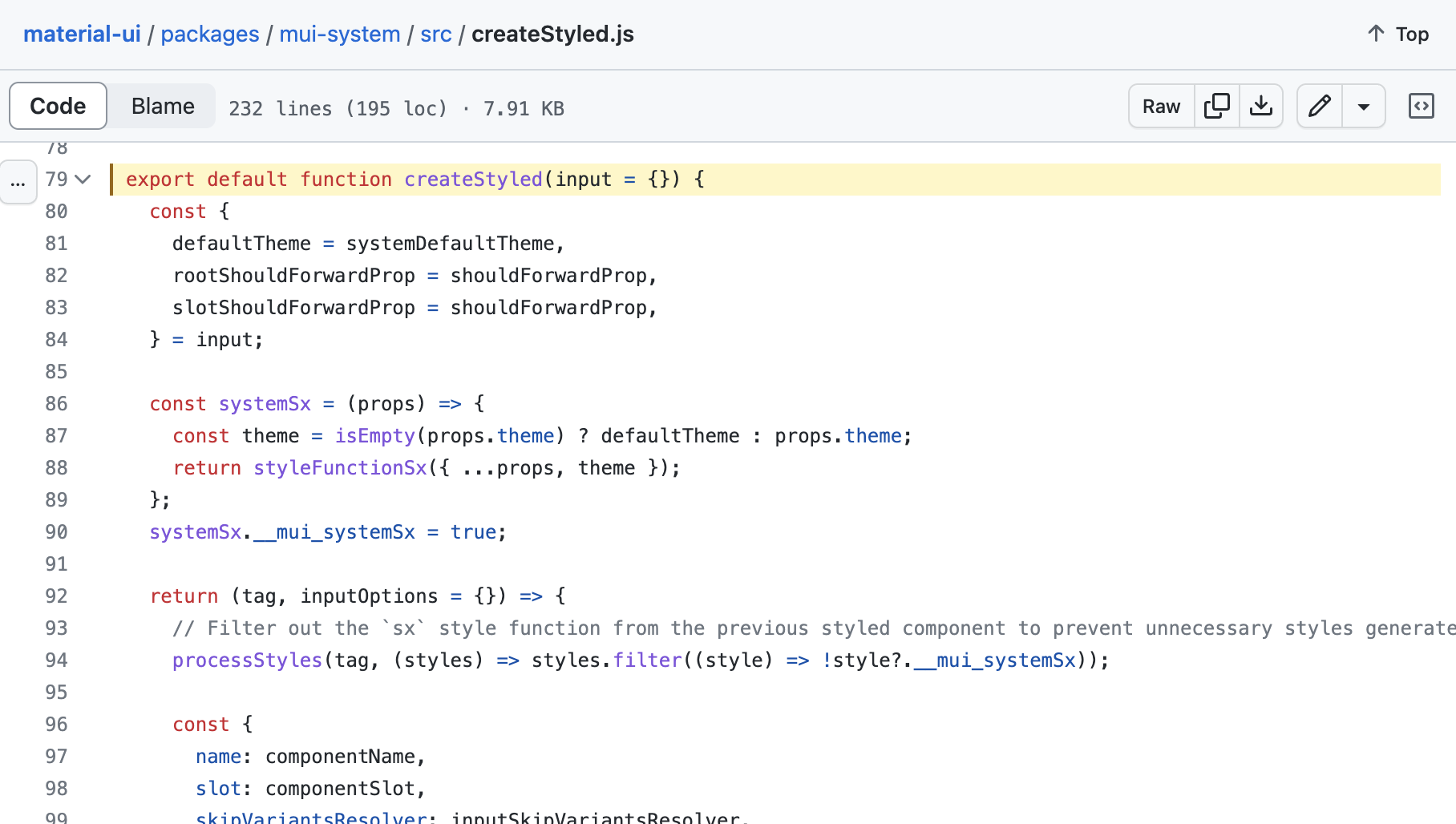
시도: createStyled() 의 리턴값으로 직진
코드를 보니 styled 함수는 @mui/system 라이브러리의 createStyled 함수가 리턴하는 값이다.
// mui-material/src/Button/Button.js
import styled, { rootShouldForwardProp } from '../styles/styled';
...// mui-material/src/styles/styled.js
import { createStyled, shouldForwardProp } from '@mui/system';
import defaultTheme from './defaultTheme';
export const rootShouldForwardProp = (prop) => shouldForwardProp(prop) && prop !== 'classes';
export const slotShouldForwardProp = shouldForwardProp;
const styled = createStyled({
defaultTheme,
rootShouldForwardProp,
});
export default styled;위 코드에서 defaultTheme이 뭔지도 궁금하지만, 우선 styled의 정체가 궁금하므로 더 들어가 보자.
// mui-system/src/createStyled.js
export default function createStyled(input = {}) {
...
// styled 함수
// ex. styled('div')(...)
return (tag, inputOptions = {}) => {
...
const {
name: componentName,
slot: componentSlot,
skipVariantsResolver: inputSkipVariantsResolver,
skipSx: inputSkipSx,
overridesResolver,
...options
} = inputOptions;
...
//
const defaultStyledResolver = styledEngineStyled(tag, {
shouldForwardProp: shouldForwardPropOption,
label,
...options,
});
const muiStyledResolver = (styleArg, ...expressions) => {
...
if (Array.isArray(styleArg) && numOfCustomFnsApplied > 0) {
const placeholders = new Array(numOfCustomFnsApplied).fill('');
// If the type is array, than we need to add placeholders in the template for the overrides, variants and the sx styles.
transformedStyleArg = [...styleArg, ...placeholders];
transformedStyleArg.raw = [...styleArg.raw, ...placeholders];
} else if (
typeof styleArg === 'function' &&
styleArg.__emotion_real !== styleArg
) {
// If the type is function, we need to define the default theme.
transformedStyleArg = ({ theme: themeInput, ...other }) =>
styleArg({ theme: isEmpty(themeInput) ? defaultTheme : themeInput, ...other });
}
...
const Component = defaultStyledResolver(transformedStyleArg, ...expressionsWithDefaultTheme);
...
return Component;
};
if (defaultStyledResolver.withConfig) {
muiStyledResolver.withConfig = defaultStyledResolver.withConfig;
}
return muiStyledResolver;
};
}styled 함수를 만드는 createStyled 함수는 130줄 가량 되는 긴 함수다. 위는 세부적인 로직을 제거하고 리턴값을 중심으로 주요 변수만 남겨둔 코드다.
우선, createStyled() 가 리턴한 styled() 함수는 다시 muiStyledResolver 를 리턴한다. 우리가 {theme, ownerState} => ({...}) 콜백함수를 넘겨 컴포넌트를 돌려받는 함수가 이 muiStyledResolver 다.
const muiStyledResolver = (styleArg, ...expressions) => {...}muiStyledResolver 는 간단히, styleArg 와 나머지 파라미터들을 받아 컴포넌트를 리턴하는 함수다. 우리가 넘기는 {theme, ownerState} => ({...}) 콜백함수가 위의 styleArg 파라미터에 들어간다.
if (Array.isArray(styleArg) && numOfCustomFnsApplied > 0) {
const placeholders = new Array(numOfCustomFnsApplied).fill('');
// If the type is array, than we need to add placeholders in the template for the overrides, variants and the sx styles.
transformedStyleArg = [...styleArg, ...placeholders];
transformedStyleArg.raw = [...styleArg.raw, ...placeholders];
} else if (
typeof styleArg === 'function' &&
styleArg.__emotion_real !== styleArg
) {
// If the type is function, we need to define the default theme.
transformedStyleArg = ({ theme: themeInput, ...other }) =>
styleArg({ theme: isEmpty(themeInput) ? defaultTheme : themeInput, ...other });
}styleArg 가 사용되는 부분은 위와 같다.
styleArg.__emotion_real !== styleArg 조건의 의미는 잘 모르겠지만, 주석을 잘 읽어 보면 “If the type is array ~”와 “If the type is function ~” 으로 나뉘어 있는 걸 보아 styleArg 의 타입이 if문을 분기시키는 주요 조건인 듯 하다.
MUI 소스 코드에서는 콜백함수를 넘기고 있으므로, else if 문에서 styleArg 가 사용된 곳을 찾았다.
transformedStyleArg = ({ theme: themeInput, ...other }) =>
styleArg({ theme: isEmpty(themeInput) ? defaultTheme : themeInput, ...other });transformedStyleArg 함수의 파라미터를 사용해 styleArg 의 실행 결과를 리턴하고 있다. 따라서 이 transformedStyleArg 를 실행시키는 곳에서 theme, ownerState 등 파라미터 값을 넣어줄 것이다.
const Component = defaultStyledResolver(transformedStyleArg, ...expressionsWithDefaultTheme);transformedStyleArg 는 최종 리턴값인 Component 를 만드는 defaultStyledResolver 안에서 사용되는 듯하다.
문제: @mui 밖으로 나가야 한다?
const defaultStyledResolver = styledEngineStyled(tag, {
shouldForwardProp: shouldForwardPropOption,
label,
...options,
});defaultStyledResolver 는 또다른 함수 styledEngineStyled 의 리턴값이다. 따라서 이 함수가 어떤 리턴값을 갖는지 알아야, 그 안에서 transformedStyleArg 를 어떻게 실행시키고 있는지도 알 수 있을 것이다. 그래서 다시 한번 더 들어가봤다.
// mui-styled-engine/src/index.js
/* eslint-disable no-underscore-dangle */
import emStyled from '@emotion/styled';
export default function styled(tag, options) {
const stylesFactory = emStyled(tag, options);
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
return (...styles) => {
const component = typeof tag === 'string' ? `"${tag}"` : 'component';
if (styles.length === 0) {
console.error(
[
`MUI: Seems like you called \`styled(${component})()\` without a \`style\` argument.`,
'You must provide a `styles` argument: `styled("div")(styleYouForgotToPass)`.',
].join('\n'),
);
} else if (styles.some((style) => style === undefined)) {
console.error(
`MUI: the styled(${component})(...args) API requires all its args to be defined.`,
);
}
return stylesFactory(...styles);
};
}
return stylesFactory;
}@mui/material 을 한참 벗어나 @mui/styled-engine 까지 왔다. 하지만 여기서 정의된 styled 함수는 @emotion/styled 에 정의된 emStyled 함수의 리턴값을 사용하고 있었다.
여기까지 들어오니 근본적인 의문이 생겼다:
이걸 왜 보고 있지? theme 어디갔지…?
@emotion 은 외부 라이브러리이므로 emStyled 를 들여다본다고 MUI의 theme 이 주입되는 부분을 찾을 수는 없을 것이다. 그럼 위 과정의 어딘가에서 theme 이 들어가고 있는데, 내가 놓쳤다는 이야기가 된다.
생각해볼 점
- theme, ownerState 는 콜백 함수 의 파라미터다.
- 콜백 함수는 어떤 함수를 즉시 실행시키지 않고, 원하는 타이밍에 실행시키기 위해 다른 함수의 파라미터로 넘겨진 함수다.
- 따라서, 이 함수가 ‘실행’ 되는 위치에서 theme 값을 알 수 있는 것은 맞다.
- styled 뿐만 아니라
sxprops,components객체에서도 theme 에 접근할 수 있다.// sx props <Box sx={ ({theme, ownerState}) => ({...}) } /> // components variants: [ { props: { variant: 'outlined', color: 'secondary' }, style: ({ theme }) => ({ borderColor: theme.palette.secondary.p50, }), }, ]- 이 때에도 마찬가지로 콜백 함수의 형태로 사용된다.
- 의문: components 객체는 theme 의 구성 요소인데 theme에 접근할 수 있다?
- 따라서 sx와 components 객체의 스타일링 역시 styled 안에서 resolve 되는 형태일 것으로 추측해볼 수 있다.
- 컴포넌트를 생성할 때 styled 함수를 사용하므로, sx prop 및 theme 의 컴포넌트 객체 모두 styled 함수 안에서 integrate 되어야 의도한 형태의 컴포넌트가 렌더링될 수 있다.
- createStyled 안에서 sx 와 component 객체를 핸들링하는 로직이 있었는지 찾아보자.
- 이 때에도 마찬가지로 콜백 함수의 형태로 사용된다.
