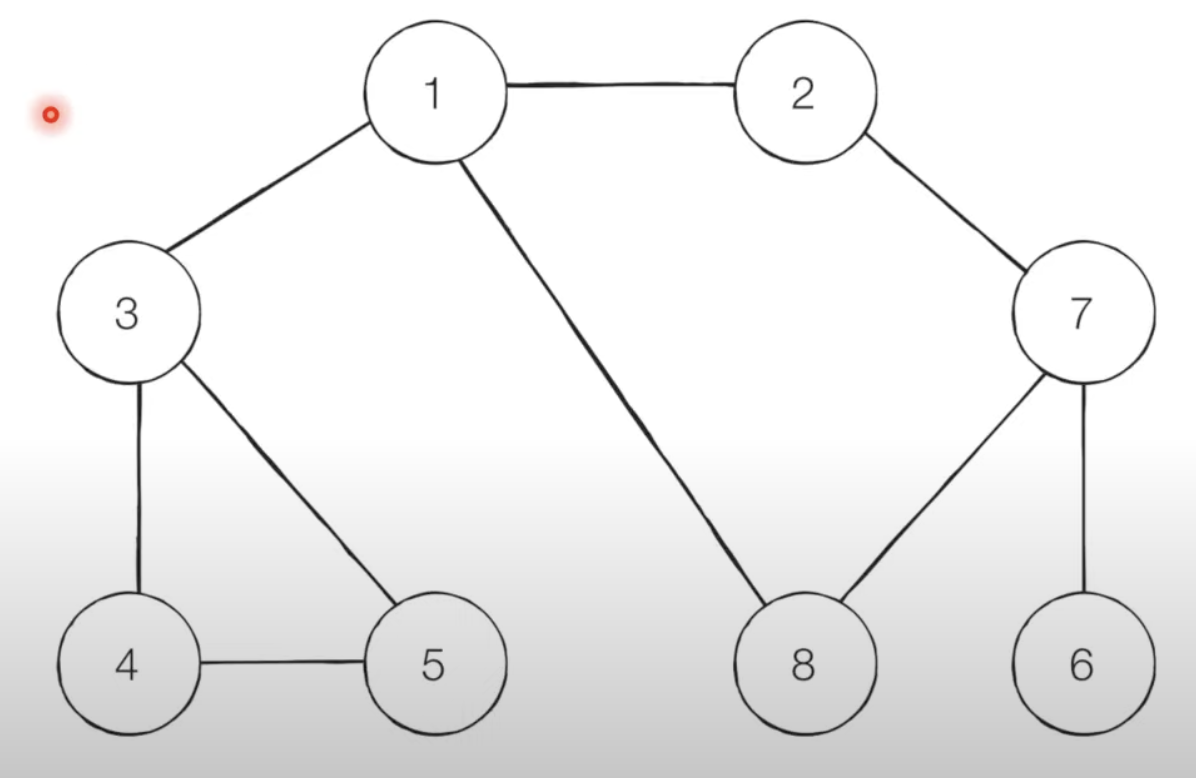
위의 그래프를 dfs bfs로 순회해보자
DFS(Depth-First Search)
- DFS는 깊이 우선 탐색이라고도 부르며 그래프에서 깊은 부분을 우선적으로 탐색하는 알고리즘.
- DFS는 스택 자료구조(혹은 재귀 함수)를 이용한다.
- 탐색 시작 노드를 스택에 삽입하고 방문 처리
- 스택의 최상단 노드에 방문하지 않은 인접한 노드가 하나라도 있으면 그 노드를 스택에 넣고 방문처리. 방문하지 않은 인접노드가 없으면 스택에서 최상단 노드를 꺼낸다.
- 더 이상 2번의 과정을 수행할 수 없을때 까지 반복한다.
step 0 (방문 기준: 번호가 낮은 인접 노드부터
시작 노드 1.
탐색 순서 1-> 2 -> 7 -> 6 -> 8 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 순으로 방문한다.
최대한 깊게 들어간다.
BFS(Breadth-First Search)
- BFS는 너비 우선 탐색이라고도 부르며 그래프에서 가장 가까운 노드부터 우선적으로 탐색하는 알고리즘.
- BFS는 큐 자료구조를 이용한다.
- 탐색 시작 노드를 큐에 삽입하고 방문 처리
- 큐에서 노드를 꺼낸뒤 해당 노드에 인접 노드 중 방문하지 않은 노드를 모두 큐에 삽입하고 방문 처리. 방문하지 않은 인접노드가 없으면 스택에서 최상단 노드를 꺼낸다.
- 더 이상 2번의 과정을 수행할 수 없을때 까지 반복한다.
step 0 (방문 기준: 번호가 낮은 인접 노드부터
시작 노드 1.
탐색 순서 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 8 -> 7 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6 순으로 방문한다.
package com.ll;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Main {
static boolean[] visited = new boolean[9];
static ArrayList<Integer>[] graph = new ArrayList[9];
static Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
public static void bfs(int x) {
q.add(x);
visited[x] = true;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int a = q.poll();
System.out.print(a + " ");
for (int i = 0; i < graph[a].size(); i++) {
int y = graph[a].get(i);
if (!visited[y]) {
q.add(y);
visited[y] = true;
}
}
}
}
public static void dfs(int x) {
visited[x] = true;
System.out.print(x + " ");
for (int i = 0; i < graph[x].size(); i++) {
int y = graph[x].get(i);
if (!visited[y]) {
dfs(y);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 8; i++) {
graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
graph[1].add(2);
graph[1].add(3);
graph[1].add(8);
graph[2].add(1);
graph[2].add(7);
graph[3].add(1);
graph[3].add(4);
graph[3].add(5);
graph[4].add(3);
graph[4].add(5);
graph[5].add(3);
graph[5].add(4);
graph[6].add(7);
graph[7].add(2);
graph[7].add(6);
graph[7].add(8);
graph[8].add(1);
graph[8].add(7);
Arrays.fill(visited, false);
// dfs(1);
System.out.println();
bfs(1);
}
}