사실 JS에서의 class는 c++, Java같은 하나의 별개 object로서의 class가 아니라, function에 더 가깝다.
➡️ "class"는 이해 + 코딩을 돕기 위한 "syntatic sugar" 일 뿐. (문법적 설탕; 같은 원리의 코드를 이용 및 이해하기 쉽게 새로운 형식으로 포장한 것.)
➡️ JavaScript에서 class를 만들고, console.log(typeOf(classname));을 실행해볼 시 직접 쉽게 확인할 수 있다.
function 형식으로 표현한 class
-
class 정의 : 마치 constructor을 정의하듯 class를 정의함
function classname (instanceVariable) { // constructor contents } -
instance method :
classname.prototype.methodname = ...의 형태로 따로 정의해준다.
예시 :width,height두 개의 instance variable과isSquare()하나의 class method를 가지는 classRectanglefunction Rectangle = (width, height) { this.width = width; this.height = height; } Rectangle.prototype.isSquare = function () { return this.width === this.height; }아래 class syntax 코드와 비교
class Rectangle { constructor(width, height) { this.width = width; this.height = height; } isSquare() { return this.width === this.height; } }
prototype는?
특정 function (즉 class)의 모든 instance method를 포함하는 object. (최상위 class인 object에게서, 모든 하위 class instance들이 상속받는 property라 할 수 있다.)
-
prototype로
classnameclass에funcname클래스 메서드 추가하기classname.prototype.funcname() = function(){...}위와 같이 `classname.prototype`에 `funcname` method를 추가하면, 모든 `classname` instance가 이 method를 공유하며 method에 접근할 수 있다.또한 위의
Rectangle에서 보였듯, class의prototype에 추가된 method 내부에서는this.문법으로 class instance variable에 접근할 수 있다. (class method로 치부되므로) -
예시 :
String.prototype.trim()➡️ String instance에trim()을 부를 수 있다는 뜻 (즉 trim은String에 대한 instance method임)
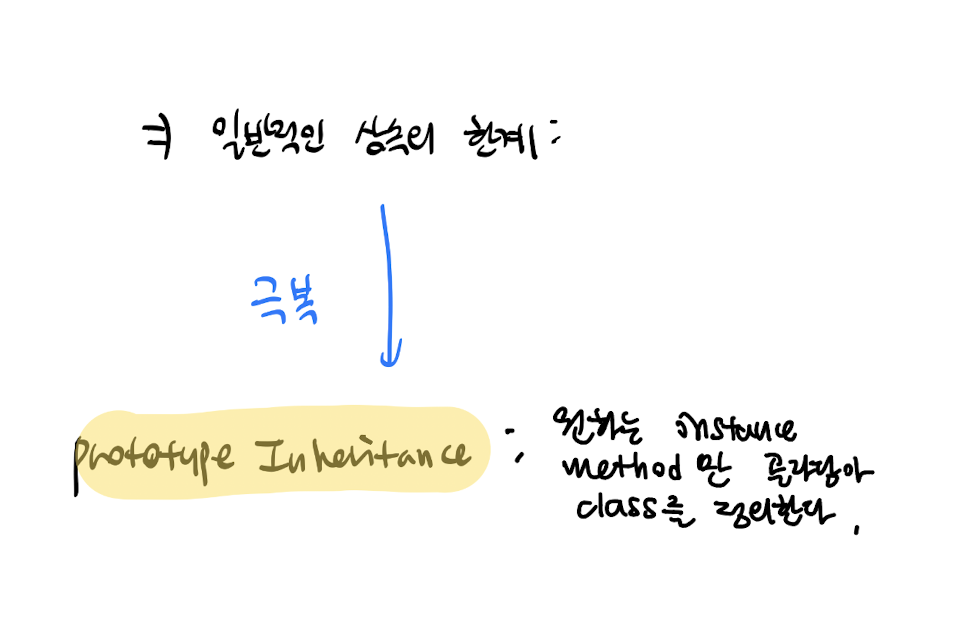
프로토타입 상속 - Prototypical Inheritance
-
일반적인 상속의 한계 :
한 클래스를 상속Inherit하면, 그 클래스가 가지고 있는 모든 member function(=instance method)가 함께 온다.
상속받을 parent class의 모든 member function이 필요하다면 괜찮지만, 일부만 필요한 경우에는 다소 쓸모없는 측면이 있다. (ex. 원치 않는 일정이 있는 패키지 여행의 비애)
이를 극복할 수 있는 것이 Javascript의 prototype inheritance이다.
-
prototype inheritance : 원하는 instance method만 골라담아 class를 정의할 수 있는 상속.
-
앞에서 class==function임을 이야기하면서, function 표현법으로 class에 instance method를 추가하기 위해선 그 class(=function) type의 prototype에 메서드를 추가하면 된다고 설명했다.
➡️ 비슷하게 새로운 class를 정의할 때, 다른 class(=parent class)에서 가져오고 싶은('상속'받고 싶은) instance method가 있다면,class1.prototype.func1 = class2.prototype.func2;와 같이 parent class prototype에서 메서드를 가져와서 child class prototype에 추가하는 방식으로 원하는 instance method만 선택적으로 상속받을 수 있다!
➡️ 이렇듯 일반적인extends를 이용하는 상속과는 달리, 클래스 전체가 아닌 원하는 method들만 prototype를 통해 상속받는 것을 Prototype Inheritance이다.즉 prototype inheritance를 사용하면, 다른 class의 method를 원하는 대로 조합해서 새로운 class를 만들 수 있다.
-
-
ex. prototype inheritance로
GorillaBanana클래스 만들기-
function syntax :
function Gorilla() { } function Banana() { } function GorillaBanana() { } Gorilla.prototype.eat = function() { console.log("Gorilla eats"); } Banana.prototype.peel = function() { console.log("Banana peeled"); } // Extend our GorillaBanana with the Gorilla's eat() method GorillaBanana.prototype.eat = Gorilla.prototype.eat; // Extend our GorillaBanana with Banana's peel() method GorillaBanana.prototype.peel = Banana.prototype.peel-> eat, peel 메서드만 상속할 수 있다.
extends를 사용하지 않고 class를 정의한 후 prototype를 이용하여Gorillaclass에서는.eat만,Bananaclass에서는.peel만 가져온다!
⇒ 고릴라를 만들고 싶다고 해서 전체 정글을 가져오는 대신, 바나나를 까서 먹는 고릴라만 가져올 수 있는 것 -
class 형식 :
class Gorilla { eat() { console.log("Gorilla eats"); } } class Banana { peel() { console.log("Banana peeled"); } } class GorillaBanana {} // Selectively copy the methods GorillaBanana.prototype.eat = Gorilla.prototype.eat; GorillaBanana.prototype.peel = Banana.prototype.peel; const gb = new GorillaBanana(); gb.eat(); // "Gorilla eats" gb.peel(); // "Banana peeled"
-
일반적인 extends를 이용한 상속 뒤에도 사실 prototypical inheritance가 작동한다.
⇨ parent class의 모든 member function을 가져오는 형태로!
즉, Javascript에서 inheritance의 기본 원리는 prototype inheritance라는 것.