Exception
예측한 예외처리와 예측하지 못한 예외처리를 알아본다.
var list = List.of("Hello");
var element = list.get(1);
log.info("element : {}", element);일부러 예외를 발생시켜보고 GET요청을 보내보자
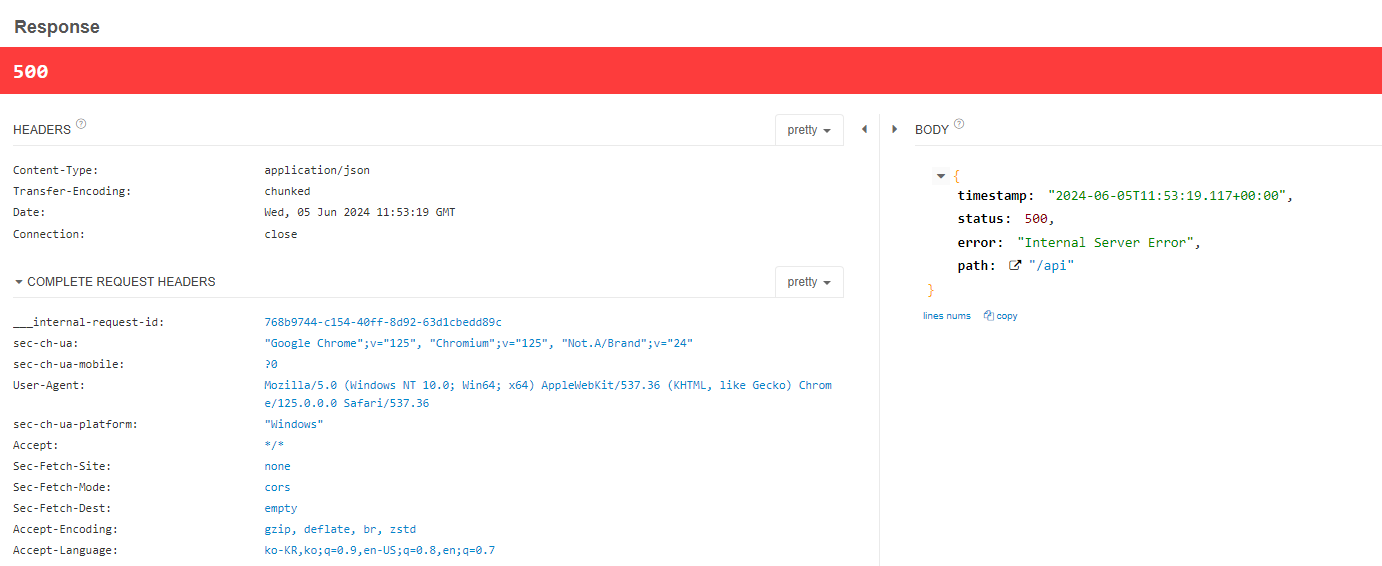

로그에도 같은 예외가 발생했다.
BODY를 보면 Json으로 내려오는 것을 볼 수 있다.
하지만 광범위한 코드의 예외를 하나하나 처리하는 것은 매우 비효율적이기 때문에 글로벌한 처리가 필요할 것이다.
@RestControllerAdvice
public class RestApiExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(value = {Exception.class})
public ResponseEntity exception(Exception e){
log.error("RestApiExceptionHandler", e);
return ResponseEntity.status(200).build();
}
}@RestContollerAdvice는 전역 REST API에서 발생하는 예외를 잡아줄 수 있는 어노테이션이다.
@ExceptionHandler는 해당 예외를 처리해주는 어노테이션으로
위 코드에서는 Exception 아래의 모든 예외를 처리할 수 있다.
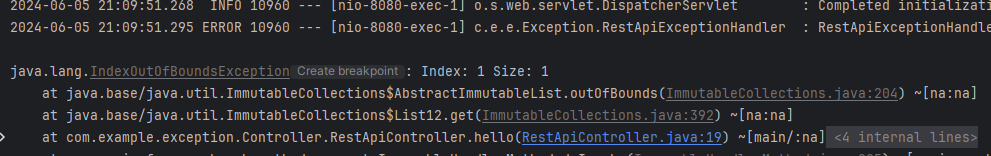
어디에서 예외가 발생했는지, 어떤 예외인지, 에러 메세지는 뭔지 모두 확인 할 수 있다.
우리가 위에서 발생시킨 에러는 OutOfBoundException이므로
해당 예외만 처리해보자
@ExceptionHandler(value = {IndexOutOfBoundsException.class})
public ResponseEntity outOfBound(IndexOutOfBoundsException e){
log.error("IndexOutOfBoundsException", e);
return ResponseEntity.status(200).build();
}메세지도 다르게 출력하고 에러 내용도 정확히 명시해준다.
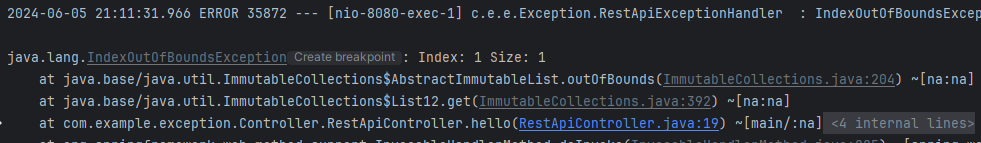
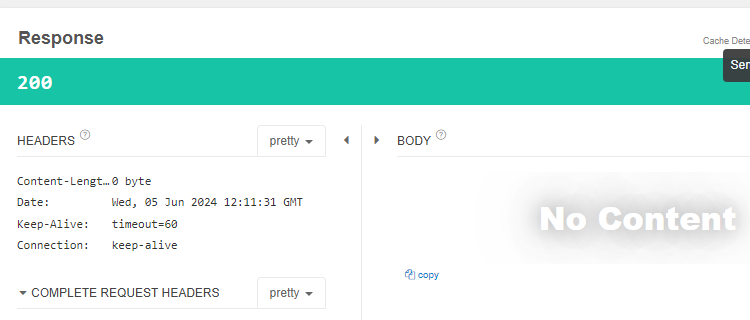
잘 응답이 됐고, 메세지 또한 잘 뜨는 것을 볼 수 있다.
Global Exception
같은 Controller 패키지에
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/b")
public class RestApiBController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public void hello(){
throw new NumberFormatException("Number format Exception");
}
@ExceptionHandler(value = {NumberFormatException.class})
public ResponseEntity numberFormatException(NumberFormatException e){
log.error("RestApiBController", e);
return ResponseEntity.ok().build();
}
}이같은 B Controller를 추가하고 GET 요청을 한다면
이처럼 처리를 해주는데, @RestController 전역의 예외를 처리해주는 것을 볼 수 있다.
localhost:8080의 /api와 /api/b/hello루트의 요청에도 모두 예외를 처리해준 것이다.
하지만 Controller 부분이 길어진다면 해당 방법을 추천하지는 않는다.
특정 클래스 혹은 패키지
B Controller의 핸들러를 주석처리하고
@RestControllerAdvice(basePackages = "com.example.exception.Controller")핸들러 클래스의 어노테이션을 수정하면 com.example.exception.Controller경로의 예외를 처리하겠다는 뜻이다.

베이스 패키지를 통해서 다른 컨트롤러의 내용이 발생하지 않으면 직접 다른 패키지를 추가해보는 것도 좋다.
@RestControllerAdvice(basePackageClasses = {RestApiController.class})잡을 클래스를 지정할 수 있고, 배열로 여러 클래스를 지정할 수도 있다.
