[Next] Next.js(Route Handlers) + React-Query + Intersection Observer 활용한 무한스크롤 구현
Next.js의 Route Handlers와 React-Query, Intersection Observer, Supabase 를 활용하여 무한스크롤을 구현하였다.
많은 블로그 글을 보았지만, Next의 Route Handlers를 사용한 글을 찾아보기 힘들어 직접 남긴다.
우선 리액트 쿼리의 useInfiniteQuery Hook을 알아야 한다.
useInfiniteQuery
const {
data: myPost,
isLoading: isMyPostLoading,
hasNextPage,
fetchNextPage,
} = useInfiniteQuery({
queryKey: ['mypage', 'bookmark', 'post', userId],
queryFn: ({ pageParam = 0 }) => getUserPost(userId, pageParam as number),
getNextPageParam: (lastPage, allPages, lastPageParam) => {
const nextPage = lastPageParam + 1;
return lastPage.length === 0 ? undefined : nextPage;
},
initialPageParam: 0,
});
useInfiniteQuery란? Data Fetching이 일어날 때 마다 기존 리스트 데이터에 Fetched Data 를 추가하고자 할 때 유용하게 사용할 수 있는 React-query hook이다.
기존의useQuery와 같이queryKey와queryFn을 사용한다.
pageParam
pageParam은 useInfiniteQuery가 현재 어떤 페이지에 있는지 확인할 수 있는 파라미터 값
기본 값은 undefined이기 때문에 값이 없을 경우 initialPageParam으로 0 넣어주도록 설정해놓았다.
그리고 데이터를 조회해올 때 pageParam값을 api 요청할 때 파라미터 값으로 넣어 사용할 수 있다.
getNextPageParam
getNextPageParam과 fetchNextPage은 공통적으로 다음 페이지에 있는 데이터를 조회할 때 사용된다.
파라미터 값으로 크게 lastPage, allPages, lastPageParam 값을 전달받을 수 있다.
lastPage 는 useInfiniteQuery 를 이용해 호출된 가장 마지막에 있는 페이지 데이터를 의미
allPages는 useInfiniteQuery 를 이용해 호출된 모든 페이지 데이터를 의미
lastPageParam 은 가장 마지막 페이지의 pageParam 을 가져온다. queryFn의 매개변수로 들어간 pageParam의 값을 가져온다.
나의 경우 마지막 페이지의 호출데이터가 없으면
undefined를 호출하여 데이터 호출을 더이상 하지 않고 데이터가 존재하면 nextPage를 호출하였다.
hasNextPage
호출할 다음 페이지가 있는지 구분하는 boolean 값 이다. pageParam이 담겨있다면 true이고 아니면 false이다.
fetchNextPage
fetchNextPage는 다음 페이지의 데이터를 호출할 때 사용한다.
Intersection Observer
Intersection observer는 기본적으로 브라우저 뷰포트(Viewport)와 설정한 요소(Element)의 교차점을 관찰하며, 요소가 뷰포트에 포함되는지 포함되지 않는지, 더 쉽게는 사용자 화면에 지금 보이는 요소인지 아닌지를 구별하는 기능을 제공한다.
이 기능은 비동기적으로 실행되기 때문에, scroll 같은 이벤트 기반의 요소 관찰에서 발생하는 렌더링 성능이나 이벤트 연속 호출 같은 문제 없이 사용할 수 있다.

new IntersectionObserver()를 통해 생성한 인스턴스(io)로 관찰자(Observer)를 초기화하고 관찰할 대상(Element)을 지정한다.
생성자는 2개의 인수(callback, options)를 가진다.
const io = new IntersectionObserver(callback, options) // 관찰자 초기화
io.observe(element) // 관찰할 대상(요소) 등록callback
관찰할 대상(Target)이 등록되거나 가시성(Visibility, 보이는지 보이지 않는지)에 변화가 생기면 관찰자는 콜백(Callback)을 실행한다.
콜백은 2개의 인수(entries, observer)를 가진다.
const io = new IntersectionObserver((entries, observer) => {}, options)
io.observe(element)entries
entries는 IntersectionObserverEntry 인스턴스의 배열이다.
ersectionObserverEntry읽기 전용(Read only)의 다음 속성들을 포함한다.
boundingClientRect: 관찰 대상의 사각형 정보(DOMRectReadOnly)intersectionRect: 관찰 대상의 교차한 영역 정보(DOMRectReadOnly)intersectionRatio: 관찰 대상의 교차한 영역 백분율(intersectionRect 영역에서 boundingClientRect 영역까지 비율, Number)isIntersecting: 관찰 대상의 교차 상태(Boolean)rootBounds: 지정한 루트 요소의 사각형 정보(DOMRectReadOnly)target: 관찰 대상 요소(Element)time: 변경이 발생한 시간 정보(DOMHighResTimeStamp)
const io = new IntersectionObserver((entries, observer) => {
entries.forEach(entry => {
console.log(entry) // entry is 'IntersectionObserverEntry'
})
}, options)
io.observe(element)observer
콜백이 실행되는 해당 인스턴스를 참조한다.
const io = new IntersectionObserver((entries, observer) => {
console.log(observer)
}, options)
io.observe(element)주로 사용하는 option
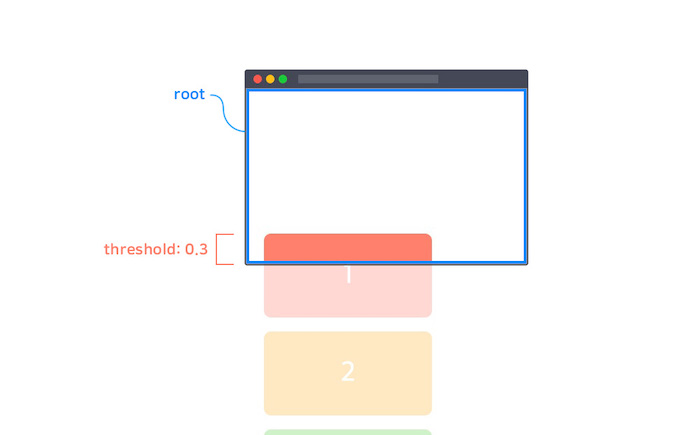
threshold
옵저버가 실행되기 위해 타겟의 가시성이 얼마나 필요한지 백분율로 표시
기본값은 Array 타입의 [0]이지만 Number 타입의 단일 값으로도 작성할 수 있음
const io = new IntersectionObserver(callback, {
threshold: 0.3 // or `threshold: [0.3]`
})
주로 사용하는 Methods
observe
대상 요소의 관찰을 시작
const io1 = new IntersectionObserver(callback, options)
const io2 = new IntersectionObserver(callback, options)
const div = document.querySelector('div')
const li = document.querySelector('li')
const h2 = document.querySelector('h2')
io1.observe(div) // DIV 요소 관찰
io2.observe(li) // LI 요소 관찰
io2.observe(h2) // h2 요소 관찰unobserve
대상 요소의 관찰을 중지
관찰을 중지할 하나의 대상 요소를 인수로 지정해야 한다.
단, IntersectionObserver 인스턴스가 관찰하고 있지 않은 대상 요소가 인수로 지정된 경우 아무런 동작도 하지 않음
const io1 = new IntersectionObserver(callback, options)
const io2 = new IntersectionObserver(callback, options)
// ...
io1.observe(div)
io2.observe(li)
io2.observe(h2)
io1.unobserve(h2) // nothing..
io2.unobserve(h2) // H2 요소 관찰 중지disconnect
IntersectionObserver 인스턴스가 관찰하는 모든 요소의 관찰을 중지합니다.
const io1 = new IntersectionObserver(callback, options)
const io2 = new IntersectionObserver(callback, options)
// ...
io1.observe(div)
io2.observe(li)
io2.observe(h2)
io2.disconnect() // io2가 관찰하는 모든 요소(LI, H2) 관찰 중지useInfiniteQuery와 Intersection Observer를 알아보았으니 구현을해보자!
구현
Intersection observer custom hook
// useIntersectionObserver.ts
import { InfiniteQueryObserverResult } from '@tanstack/react-query';
import { useCallback, useEffect, useState } from 'react';
type Props = {
threshold?: number;
hasNextPage: boolean;
fetchNextPage: () => Promise<InfiniteQueryObserverResult>;
};
export const useIntersectionObserver = ({
threshold = 0.1,
hasNextPage,
fetchNextPage,
}: Props) => {
// 관찰 요소
const [target, setTarget] = useState<HTMLDivElement | null | undefined>(null);
const observerCallback = useCallback<IntersectionObserverCallback>(
(entries) => {
entries.forEach((entry) => {
// 타겟이 화면에 관찰되고, 다음 페이지가 존재할 때 다음 페이지 호출
if (entry.isIntersecting && hasNextPage) {
fetchNextPage();
}
});
},
[fetchNextPage, hasNextPage],
);
useEffect(() => {
if (!target) return;
//Intersection Observer 인스턴스 생성
const observer = new IntersectionObserver(observerCallback, { threshold });
// 타겟 관찰 시작
observer.observe(target);
// 관찰 멈춤
return () => observer.unobserve(target);
}, [observerCallback, threshold, target]);
return { setTarget };
};
useInfiniteQuery custom hook
// useMyPostQuery.ts
import { getUserPost } from '@/app/profile/[id]/_lib/profile';
import { useInfiniteQuery } from '@tanstack/react-query';
import { useParams } from 'next/navigation';
import { useIntersectionObserver } from './useIntersectionObserver';
export const useMyPostQuery = () => {
const params = useParams();
const userId = params.id as string;
const {
data: myPost,
isLoading: isMyPostLoading,
hasNextPage,
fetchNextPage,
} = useInfiniteQuery({
queryKey: ['mypage', 'bookmark', 'post', userId],
queryFn: ({ pageParam = 0 }) => getUserPost(userId, pageParam as number),
getNextPageParam: (lastPage, _, lastPageParam) => {
const nextPage = lastPageParam + 1;
return lastPage.length === 0 ? undefined : nextPage;
},
initialPageParam: 0,
});
const { setTarget } = useIntersectionObserver({
hasNextPage,
fetchNextPage,
});
return { myPost, isMyPostLoading, setTarget };
};
API 요청 함수
// profile.ts
export const getUserPost = async (
userId: string,
pageParam: number,
): Promise<MyPostType> => {
const res = await fetch(
`/api/profile/${userId}/community/user/post/${pageParam}`,
{
method: 'GET',
},
);
const data = await res.json();
return data;
};Next.js Route Handlers + supabase
// api/profile/[id]/community/user/post/[page]/route.ts
import { supabase } from '@/app/api/db';
import { NextRequest, NextResponse } from 'next/server';
export const GET = async (
req: NextRequest,
{ params }: { params: { id: string, page: number } },
) => {
const page = params.page;
const from = page * 4; // 0 4 8 12
const to = page + 3; // 3 7 11
const { data, error } = await supabase
.from('post')
.select(
'id, content, post_pic(photo_url), post_hashtag(tag), like(id), comment(id)',
)
.order('created_at', { ascending: false })
.eq('user_id', params.id)
.range(from, to);
if (error) {
throw new Error(error.message);
}
return NextResponse.json(data);
};
본인은 4개씩 화면에 보여주기 위해 from, to 로직을 위와같이 작성하였다.
트러블 슈팅 및 결론
useInfiniteQuery와 Intersection Observer 를 학습하는데 시간이 꽤 걸렸다.
Next.js Route Handlers 를 활용하여 pageParam 를 넘겨주는것은 어렵지 않았다.
useInfiniteQuery의 pageParam이 계속 처음 값으로 넘어오는 문제점이 있었다.
lastPageParam이 이전의 pageParam 값을 가진다는 것을 알게된 후 +1 씩하여 페이지를 넘겨주어 문제를 해결하였다.
보완점
debounce 혹은 throttle 을 적용하여 이벤트 과다 발생 예방
References
https://heropy.blog/2019/10/27/intersection-observer/
https://s0ojin.tistory.com/58
