Handler란?

A Handler allows you to send and process [Message](https://developer.android.com/reference/android/os/Message.html) and Runnable objects associated with a thread's [MessageQueue](https://developer.android.com/reference/android/os/MessageQueue.html). - 구글문서
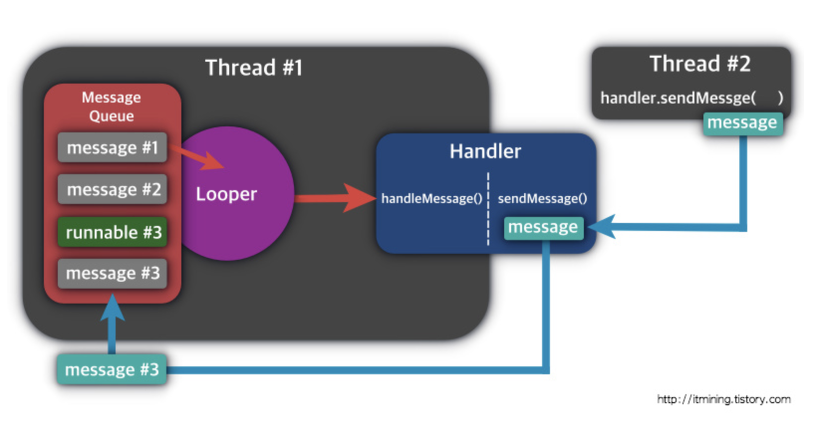
구글문서에는 Message 와 MessageQueue 를 통해 설명하고 있다. Handler 를 이해하기 위해서는 Message, MessageQueue 그리고 Looper 에 대해 알고 있어야 한다.
Thread
프로그램 안에서 실행을 담당하는 하나의 흐름
MessageQueue
Message 를 담는 자료구조
Message
Parcelable 형태의 객체로 Message 클래스를 보면 어떤 형태의 데이터가 전달되는지 확인 할 수 있다.
public final class Message implements Parcelable {
public static final Creator<Message> CREATOR = null;
public int arg1;
public int arg2;
public Object obj;
public Messenger replyTo;
public int sendingUid = -1;
public int what;
....그림에서와 같이 스레드당 1개씩 가지고 있습니다. 또한 Looper 별로 MessageQueue를 가지고 있습니다. MessageQueue 에서 Message 를 꺼내 Handler 로 전달하는 작업을 처리합니다. 메인스레드에서는 Looper 를 이미 가지고 있어 개발자가 관여하지 않아도 되지만 작업스레드에서는 Looper 를 직접 작성하고 실행시켜야 합니다.
<Looper를 생성하는 방법>
Looper.prepare() : 작업스레드를 위한 루퍼를 준비한다.
Looper.loop() : 큐에서 메시지를 꺼내 핸들러로 전달
class LooperThread extends Thread {
public Handler mHandler;
@Override
public void run() {
Looper.prepare();
mHandler = new Handler() {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
}
};
Looper.loop();
}-
서로 다른 쓰레드간의 통신을 위한 장치로 쓰인다
-
MessageQueue 에 보낼 데이터를 넣고 Looper 를 통해 처리할 데이터를 받고 보내는 중간 브로커 같은 역활을 한다.
-
기본 생성자를 통해 Handler 를 생성하면 해당 Handler 를 호출한 스레드의 MessageQueue 와 Looper 에 자동 연결된다.
예제) public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private int mMainValue = 0; private int mSubValue = 0; private TextView mainText, subText; private Handler mHandler; @Override protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); mainText = findViewById(R.id.mainText); subText = findViewById(R.id.subText); findViewById(R.id.btnIncrease).setOnClickListener(view -> { mMainValue++; mainText.setText(String.valueOf(mMainValue)); }); // 기본 생성자를 통해 Handler 를 생성하면 // 해당 Handler 를 호출한 스레드의 MessageQueue 와 Looper 와 자동 연결된다. mHandler = new Handler() { @Override public void handleMessage(Message msg) { if(msg.what == 0) { subText.setText(String.valueOf(mSubValue)); } } }; Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { while (true) { mSubValue++; //sendEmptyMessage 함수를 통해 데이터 전달 //파라미터로 보낸 값은 message의 what에 대입된다. mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(0); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }); thread.setDaemon(true); thread.start(); } } // ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- // MainAcitivty.class 외부에서 초기화 하는 예제 public class ExerciseActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private int mMainValue = 0; private int mSubValue = 0; private TextView mainText, subText; private Handler mHandler; @Override protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_exercise); mainText = findViewById(R.id.mainText); subText = findViewById(R.id.subText); findViewById(R.id.btnIncrease).setOnClickListener(view -> { mMainValue++; mainText.setText(String.valueOf(mMainValue)); }); mHandler = new Handler() { @Override public void handleMessage(Message msg) { if(msg.what == 0) { mSubValue = msg.arg1; subText.setText(String.valueOf(mSubValue)); } } }; BackThread backThread = new BackThread(mHandler); backThread.setDaemon(true); backThread.start(); } } class BackThread extends Thread { int backValue = 0; Handler handler; BackThread(Handler handler){ this.handler = handler; } @Override public void run() { while(true){ backValue++; // 메세지를 생성 //Message msg = new Message(); Message msg = Message.obtain(); msg.what = 0; msg.arg1 = backValue; handler.sendMessage(msg); // 메인스레드의 핸들러에 메세지 보내기 try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }Handler 를 BackThread의 생성자로 보내 외부 클래스에서 메인스레드에 접근할 수 있는 중간 브로커 역활을 해줌
정리
안드로이드 앱에서는 오직 Main 스레드에서만 View 를 업데이트 할 수 있습니다. 이러한 점을 명심하고 Thread 와 Handler 를 사용하면 더욱 안정적인 멋진 앱을 만들 수 있다.
