1) 탐색 알고리즘 A
- Strategy
- Input data and Data structure : unsorted array
- sequential search- Algorithm
int seqSearch(int[] E, int n, int K)
int ans, index;
ans = -1; // Assume failure
for(index = 0; index < n; index++)
if(K == E[index])
ans = index; // Success!
break; // Done!
return ans;- Analysis A
- W(n) = n
- A(n) = q[(n+1)/2] + (1-q)n
(K가 array의 마지막이거나, 존재하지 않을 때 평균 수행시간)- Optimality A
- F(n) = n이므로 Algorithm A는 Optimal 하다.2) 탐색 알고리즘 B
- Strategy
- Input data and Data structure : 오름차순으로 정렬된 Array
- sequential search- Algorithm
- int seqSearch(int[] E, int n, int K)
A와 동일- Analysis B
- W(n) = n
- A(n) = q[(n+1)/2] + (1-q)n
A와 알고리즘이 같으므로 분석내용 또한 같다- Optimality B
정렬되었음을 그닥 활용하지 않아 효율성은 없다.3) 탐색 알고리즘 C
- Strategy
- Input data and Data structure : 오름차순으로 정렬된 Array
- sequential search :
entry에서 K보다 큰 값을 만나면 알고리즘을 종료한다.- Algorithm
int seqSearchMod(int[] E, int n, int K)
int ans, index;
ans = -1; // Assume failure
for(index = 0; index < n; index++)
if(K>E[index]) continue;
if(K<E[index]) break; //Done!
//K==E[index]
ans = index; //Find it
break;
return ans;- Analysis C

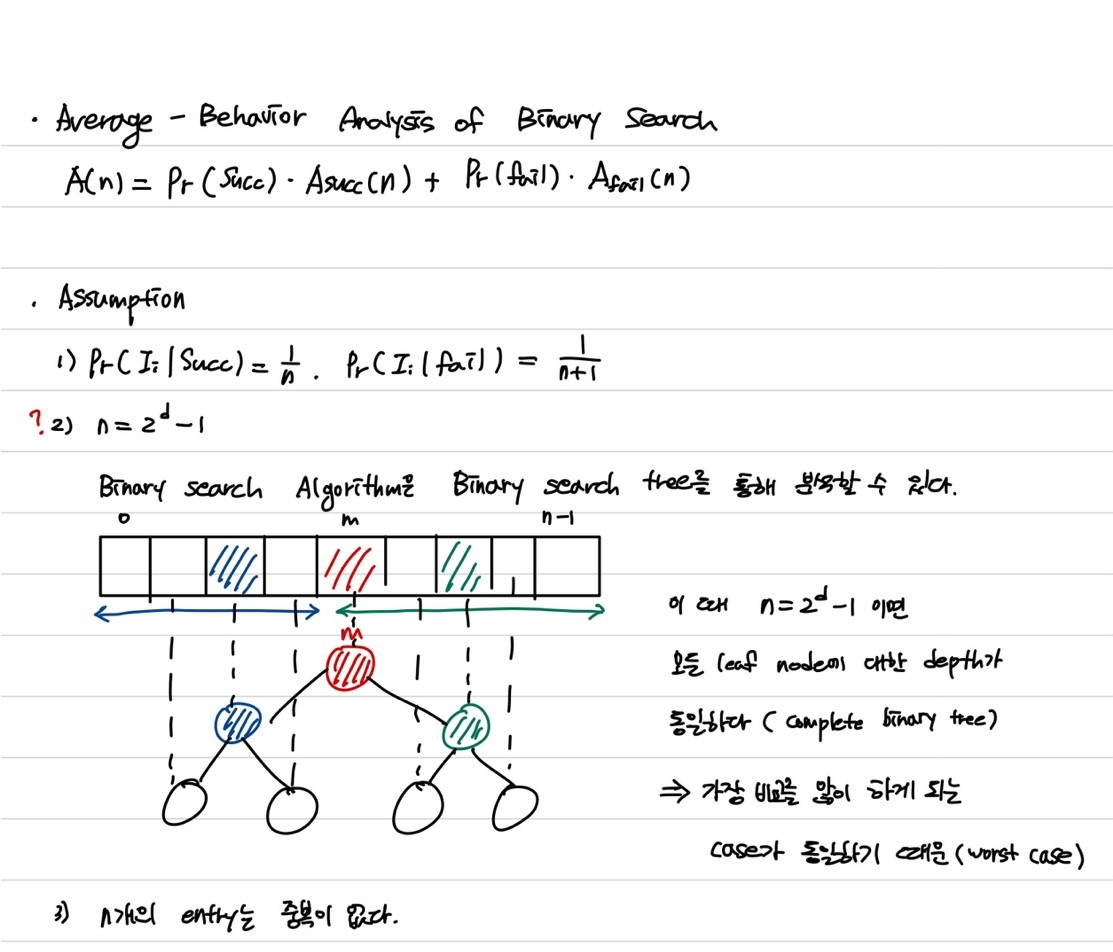
4) 탐색 알고리즘 D : Binary Search
- Strategy
- K값을 array의 중간값과 비교한다
- 한번의 비교에 entry의 나머지 절반을 제거한다.
- 같은 전략을 재귀적으로 반복한다.- Algorithm
- Input : first, last (살펴볼 index의 처음과 끝), K,
정렬된 배열 내에서 index 값이 first와 last 사이에 있는 모든 정수
- Output : K가 존재하는 index값, 혹은 E안에 K가 없을 때 나오는 결과 -1
- 반드시 정렬 된 array에서만 사용한다.int binarySearch(int[] E, int first, int last, int K)
if(last < first) // base case
index = -1; // 재귀문을 탈출할 수 있도록 하는 조건
else
int mid = (first + last) / 2;
if (K == E[mid]) index = mid;
else if(K < E[mid]) index = binarySearch(E, first, mid-1, K)
else index = binarySearch(E, mid+1, last, K)
return index-
Worst Case Analysis
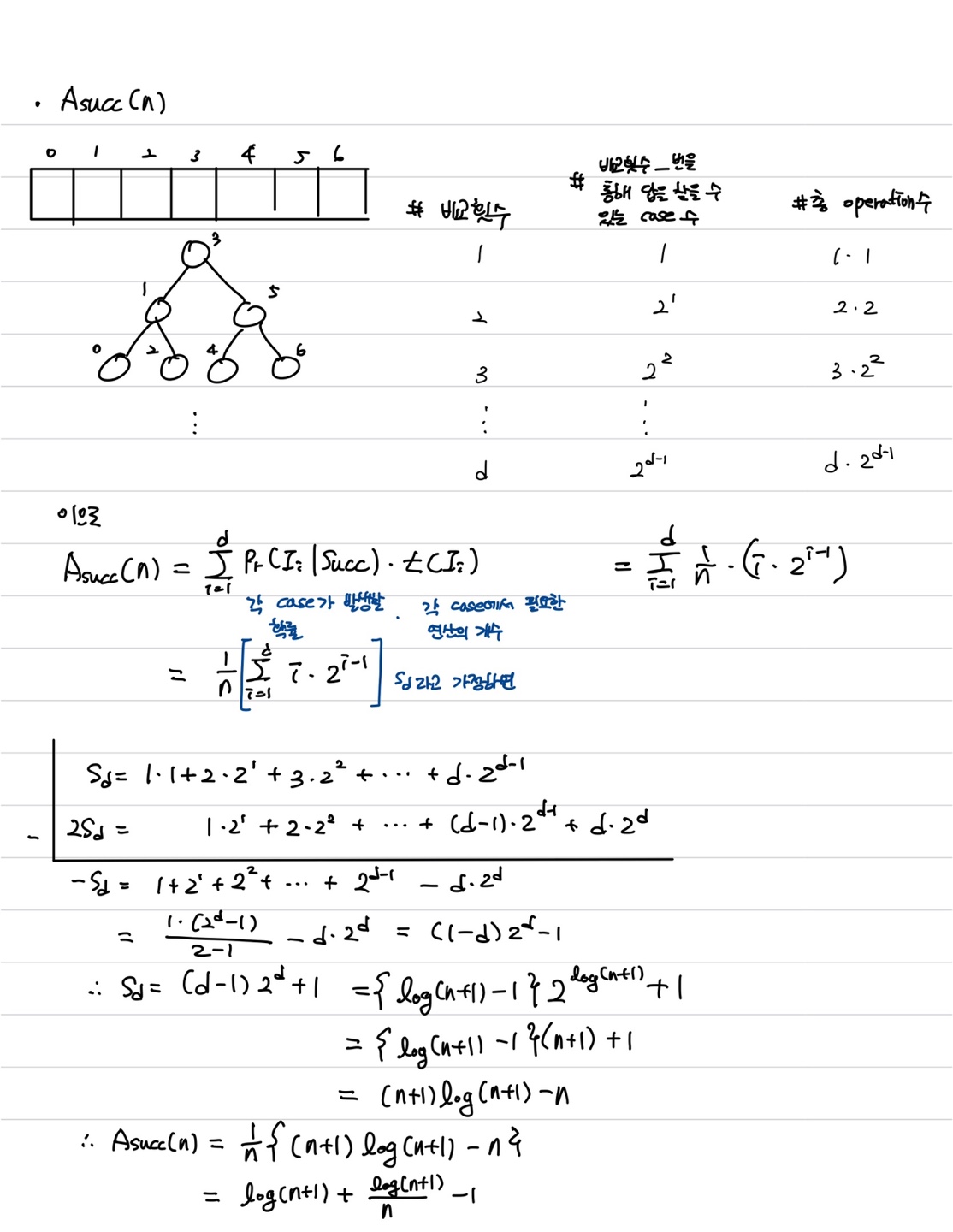
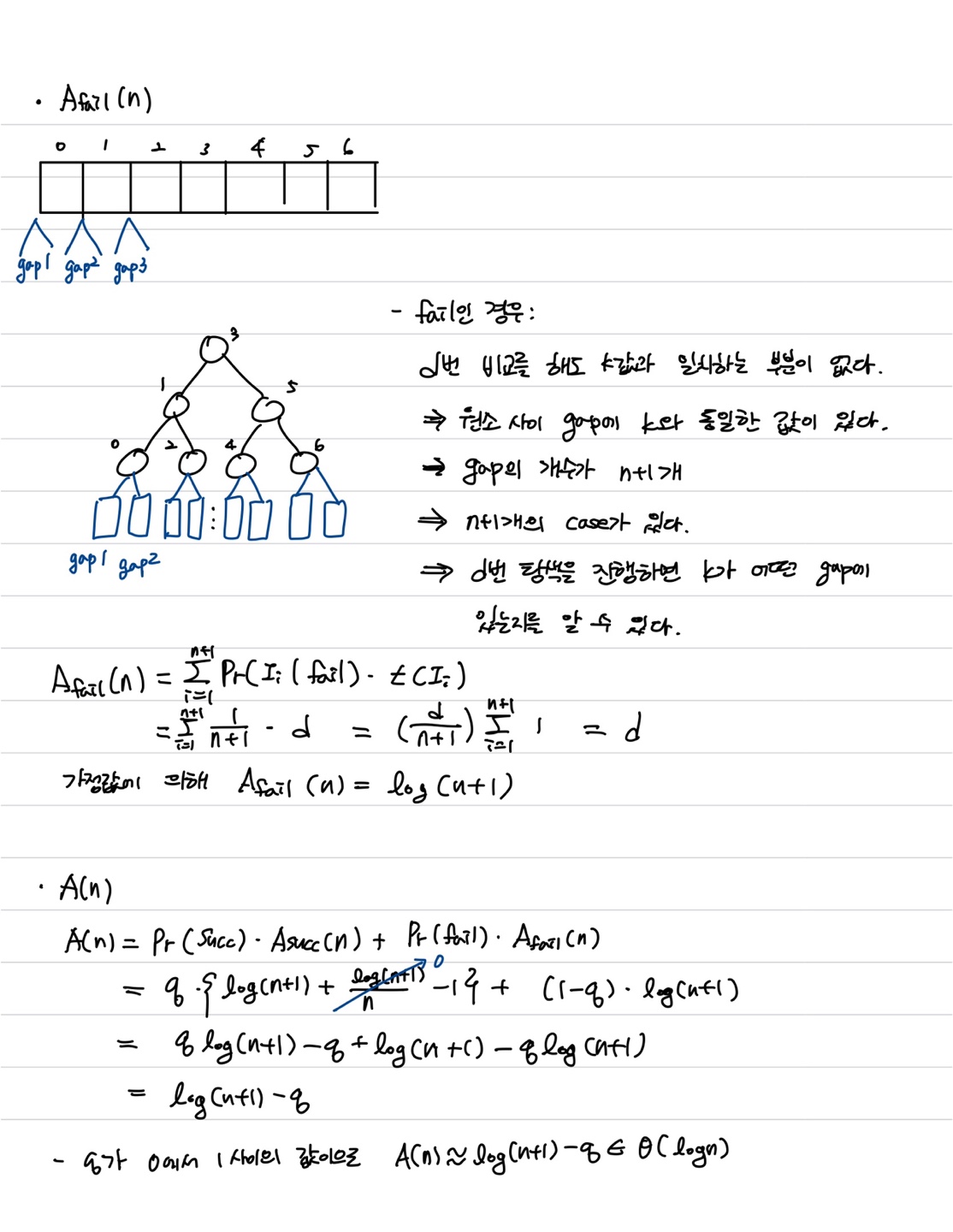
Binary Search 알고리즘의 경우 비교를 한 번 시행할 때 마다 entry의 원소가 절반씩 줄어든다.
최악의 경우 원소가 1개가 남을 때 까지 이를 계속 반복하므로 최악의 경우의 원소의 개수는
n x x x ... x = 1
1이 남을 때 까지 을 곱한 횟수를 d 라고 하면
n x = 1 / d = 이 되고, 최종적으로
= + 1(recursive 호출하기 전에 비교한 것) -
Average-Behavior Analysis of Binary Search