고차함수 추가 개념 : .for.Each()
filter, map, reduce 와 같이 배열의 내장 고차 함수이며, 동시에 배열 메서드이다,
.for.Each() 는 주어진 callback을 배열에 있는 각 요소에 대해 오름차순으로 한번씩 실행한다. 다만 삭제했거나 초기화하지 않은 인덱스 속성에 대해선 실행하지 않는다.
.for.Each() 로 처리할 요소의 범위는 최초 callback 호출 전에 설정된다.
.for.Each() 호출을 시작한 후 배열에 추가한 요소는 callback이 방문하지 않는다. 또한 방문하기 전 삭제한 요소 또한 방문하지 않는다.
또한 forEach()는 각 배열 요소에 대해 한 번씩 callback함수를 실행한다. map()과 reduce()와는 달리 undefined 반환하기 때문에 메서드 체인의 중간에 사용할 수 없다.
- 예제
**//초기화하지 않은 값의 반복 생략**
const arraySparse = [1,3,,7]
let numCallbackRuns = 0
arraySparse.forEach(function(element){
console.log(element)
numCallbackRuns++
})
console.log("numCallbackRuns: ", numCallbackRuns)
// 1
// 3
// 7
**//for 반복문을 forEach()로 바꾸기**
const items = ['item1', 'item2', 'item3'];
const copy = [];
// 이전
for (let i=0; i<items.length; i++) {
copy.push(items[i]);
}
// 이후
items.forEach(function(item){
copy.push(item);
});콜백함수 추가개념
콜백은 함수 자체를 연결하는 것(함수 실행을 연결하는게 아니다)
//함수예제
function handleClick() {
console.log('button clicked); //handleClick함수의 값은 undefined이다.
}
⭕️ ducument.querySelector('#btn').onclick = handleClick;
⭕️ ducument.querySelector('#btn').onclick = function(){
handleClick;();
}
⭕️ ducument.querySelector('#btn').onclick = handleClick.bind();
❌ducument.querySelector('#btn').onclick = handleClick();
비동기
- blocking : 하나의 작업이 끝날 때까지 이어지는 작업을 막는 것
- 동기적(synchronous) : 시작 시점과 완료 시점이 같은 상황
- Node.js는 non-blocking하고 비동기적(asynchronous)으로 작동하는 런타임이다.
- 또한 JavaScript도 비동기적 실행(Asynchronous execution)을 하고 있다.
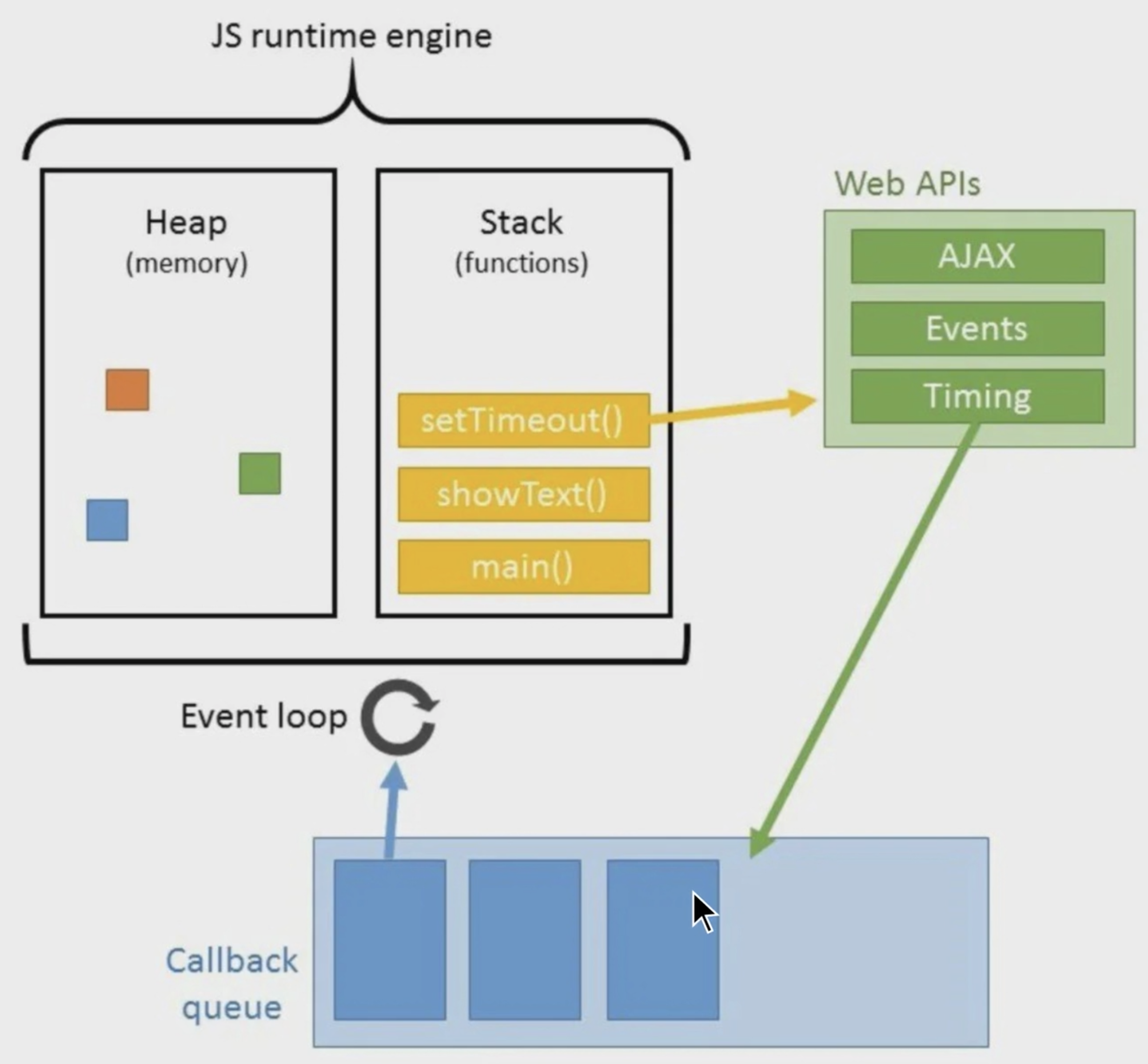
동기적 vs 비동기적 코드
- 동기적 코드
- 대표사례 : 웹사이트 들어가기
fucntion waitSync(ms) {
let start = Date.now();
let now = start;
while(now - start < ms){
now = Date.now();
}
} //현재 시각과 시작 시각을 비교해 ms 범위 내에서 무한 루프를 도는 blocking 함수
function drink(person, coffee) {
console.log(person + '는' + coffee + '를 마십니다');
}
function orderCoffeeSync(coffee) {
console.log(coffee + '가 접수 되었습니다.');
waitSync(2000); //2초 후에
return coffee;
}
let customers = [
{name : 'steve',
request : '카페라떼' },
{ name : 'john',
request : '아메리카노' }];
//call Synchronously(동기)
customers.forEach(function(customer) {
let coffee = orderCoffeeSync(customer.request);
drink(customer.name, coffee);
});→ 결과 : 접수와 메뉴를 받는 것이 순차적으로 이뤄진다.
- 비동기적 코드
- 대표 사례 : 유튜브 영상이 로딩 시, 댓글창이나, 연관 동영상 시청 가능
fucntion waitAync(callback, ms){
setTimeout(callback, ms);
} //특정시간 이후에 callback함수가 실행되겠금 하는 브라우저 내장 기능이다.
function drink(person, coffee) {
console.log(person + '는' + coffee + '를 마십니다');
}
let customers = [
{name : 'steve',
request : '카페라떼' },
{ name : 'john',
request : '아메리카노' }];
function orderCoffeeSync(menu, callback) {
console.log(coffee + '가 접수 되었습니다.');
waitSync(function() {
callback(menu);
}, 4000);
}
//call Asynchronously(비동기)
customers.forEach(function(customer) {
orderCoffeeSync(customer.request, function(coffee) {
drink(customer.name, coffee);
});
});→ 결과 : 접수와 메뉴를 받는 것이 비순차적으로 이뤄진다.
비동기 함수의 전달 패턴 2가지
1. callback 패턴
let request = 'caffelatte' ;
orderCoffeeAsync(request, function(response) { //response : 주문한 커피 결과
drink(respnse);
}); 2. 이벤트 등록 패턴
let request = 'caffelatte' ;
orderCoffeeAsync(request).onready = function(response) {
drink(respnse);
}); 비동기 주요 사례
1. DOM Element의 이벤트 핸들러
- 마우스, 키보드 입력(click, keydown 등)
- 페이지 로딩(DOMContentLoaded 등)
2. 타이머
- 타이머 API(setTimeout 등)
- 애니메이션 API
3. 서버에 지원 요청 및 응답
- fetch API
- AJAX(XHR)
비동기(async) 함수는 어떻게 제어(handle)할 수 있을까?
방법1. 콜백함수로 제어할 수 있다.
- 하지만 콜백함수로 제어할 경우, 콜백헬에 빠질 수 있다.
방법2. ‘promise’로 제어할 수 있다.
- 콜백헬과 마찬가지로, 프로미스도 프로미스헬에 빠질 수 있다. 하지만
promise chaining과**async await**을 통해 이를 보완할 수 있다.
1. 비동기함수
- 코드의 순서가 정해져 있지 않다.
const printString = (string) => {
setTimeout(function () {
console.log(string);
}, Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1);
};
const printAll = () => {
printString('A');
printString('B');
printString('C');
};
printAll();
console.log(`아래와 같이 비동기 코드는 순서를 보장하지 않습니다!`);
/* 결과
B
A
C;
A
B
C;
와 같이 순서가 보장되지 않는다(제어할 수 없다) */
비동기 함수를 제어할 수 있는 방법 2가지
방법1. Callback 함수
- Callback 함수를 통해 비동기 코드의 순서를 제어할 수 있다(= 비동기 코드를 동기화할 수 있다.)
- 하지만 코드가 길어지면 복잡하고 가독성이 낮은 Callback Hell에 빠지게 된다.
const printString = (string, callback) => {
setTimeout(function () {
console.log(string);
callback();
}, Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1);
};
const printAll = () => {
printString('A', () => {
printString('B', () => {
printString('C', () => {});
});
});
};
printAll();
console.log(
`아래와 같이 Callback 함수를 통해 비동기 코드의 순서를 제어할 수 있습니다!`
);
/* 결과
A
B
C ;--> 순서 제어가 가능하다 */
**//하지만 콜백함수가 길어지면 아래와 같은 콜백헬이 발생할 수 있다.**
const printString = (string, callback) => {
setTimeout(function () {
console.log(string);
callback();
}, Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1);
};
const printAll = () => {
printString('A', () => {
printString('B', () => {
printString('C', () => {
printString('D', () => {
printString('E', () => {
printString('F', () => {
printString('G', () => {
printString('H', () => {
printString('I', () => {
printString('J', () => {
printString('K', () => {
printString('L', () => {
printString('M', () => {
printString('N', () => {
printString('O', () => {
printString('P', () => {});
});
});
});
});
});
});
});
});
});
});
});
});
});
});
});
};
printAll();
console.log(
`아래와 같이 Callback 함수를 통해 비동기 코드의 순서를 제어할 수 있지만 코드가 길어질 수록 복잡해지고 가독성이 낮아지는 Callback Hell이 발생하는 단점이 있습니다.`
);방법2. Promise
const printString = (string) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve();
console.log(string);
}, Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1);
});
};
const printAll = () => {
printString('A')
.then(() => {
return printString('B');
})
.then(() => {
return printString('C');
});
};
printAll();
console.log(
`아래와 같이 Promise를 통해 비동기 코드의 순서를 제어할 수 있습니다!`
);
/* 결과
A
B
C ;--> 순서 제어가 가능하다 */promise 를 통해, 콜백 체인을 제어하는 방식은 다음과 같다.
Promise.prototype.catch는 Promise를 반환하며 에러가 난 경우 실행되는 메서드이다.
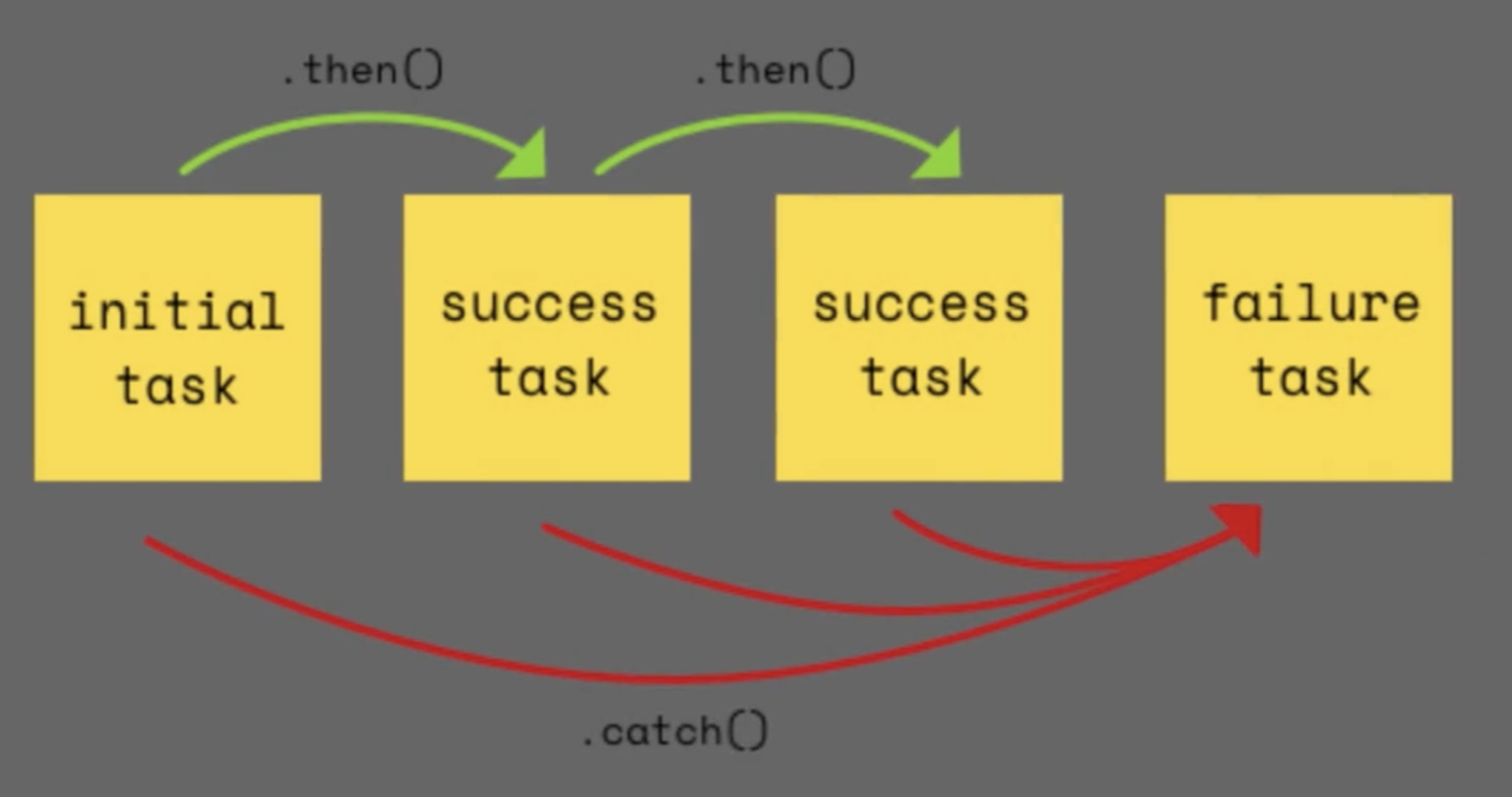
하지만 promise 도 promise Hell이 발생할 수 있다. 이를 위해,
⇒ promise chaining과 async await 를 활용한다.
1. promise chaining : return을 통해 비동기함수를 제어한다.
function gotoCodestates() {
return new **Promise**((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => { resolve('1. go to codestates') }, 500)
});
}
function sitAndCode() {
return new **Promise**((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => { resolve('2. sit and code') }, 500)
});
}
function eatLunch() {
return new **Promise**((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => { resolve('3. eat lunch') }, 500)
});
}
function goToBed() {
return new **Promise**((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => { resolve('4. goToBed') }, 500)
});
}
gotoCodestates()
.then(data => {
console.log(data)
**return** sitAndCode()
});
.then(data => {
console.log(data)
**return** eatLunch()
});
.then(data => {
console.log(data)
**return** goToBed()
});
.then(data => {
console.log(data)
});
/* 결과
1. go to codestates
2. sit and code
3. eat lunch
4. goToBed
가 순서대로 리턴된다.
*/2. async await : await를 통해 비동기 함수를 동기적으로 사용할 수 있다.
- JavaScript는 ES8에서
async/await키워드를 제공하였다. 이를 통해 romise 코드를 간결하게 작성할 수 있다. - 사용법 : 함수 앞에 async 키워드를 사용하고 async 함수 내에서 await 키워드를 사용한다.
async await로 작성된 코드는await키워드가 작성된 코드가 동작하고 그 다음에 다음 순서의 코드가 동작한다.
// 함수 선언식
async function funcDeclarations() {
await 작성하고자 하는 코드
...
}
// 함수 표현식
const funcExpression = async function () {
await 작성하고자 하는 코드
...
}
// 화살표 함수
const ArrowFunc = async () => {
await 작성하고자 하는 코드
...
}const printString = (string) => {
return new **Promise**((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve();
console.log(string);
}, Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1);
});
};
const printAll = async () => {
**await** printString('A');
**await** printString('B');
**await** printString('C');
};
printAll();
console.log(
`Async/Await을 통해 Promise를 간결한 코드로 작성할 수 있게 되었습니다.`
);
/* 결과
A
B
C ;--> 순서 제어가 가능하다 */타이머 API
setTimeout(callback, millisecond) : 일정 시간 후에 함수를 실행한다.
- setTimeout 함수는 자바스크립트 내장 비동기 함수이다.
- 매개변수(parameter): 실행할 콜백 함수, 콜백 함수 실행 전 기다려야 할 시간 (밀리초)
- return 값: 임의의 타이머 ID
setTimeout(function () {
console.log('1초 후 실행');
}, 1000); //1000밀리초 = 1초이다.
// 123clearTimeout(timerId) : setTimeout 타이머를 종료
- 매개변수(parameter): 타이머 ID
- return 값: 없음
const timer = setTimeout(function () {
console.log('10초 후 실행');
}, 10000);
clearTimeout(timer);
// setTimeout이 종료됨.**setInterval(callback, millisecond) : 일정 시간의 간격을 가지고 함수를 반복적으로 실행
- 매개변수(parameter): 실행할 콜백 함수, 반복적으로 함수를 실행시키기 위한 시간 간격 (밀리초)
- return 값: 임의의 타이머 ID
setInterval(function () {
console.log('1초마다 실행');
}, 1000);
// 345**clearInterval(timerId) : setInterval 타이머를 종료
- 매개변수: 타이머 ID
- return 값: 없음
const timer = setInterval(function () {
console.log('1초마다 실행');
}, 1000);
clearInterval(timer);
// setInterval이 종료됨.