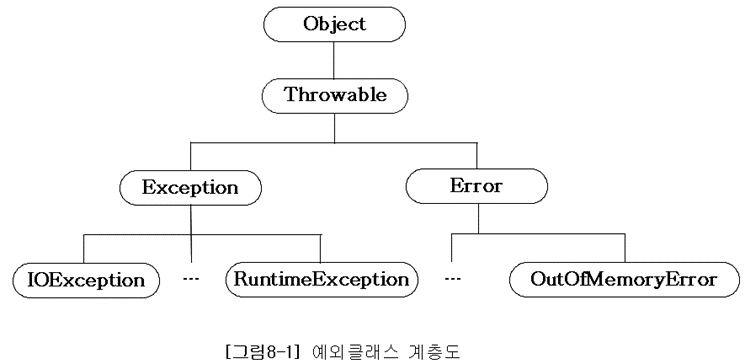
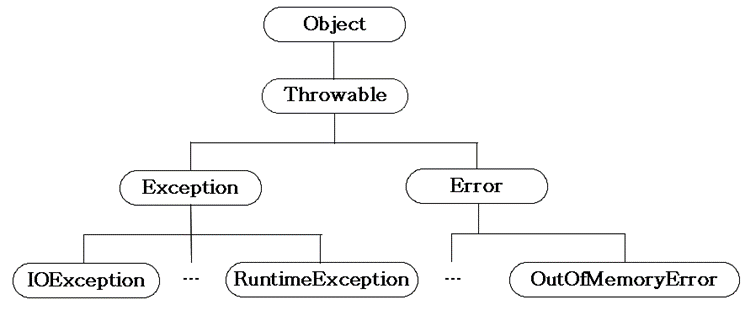
1. 자바 예외 클래스 계층 구조.
2. 매개변수가 1개인 생성자.
public class RuntimeException extends Exception {
....
/** Constructs a new runtime exception with the specified detail message.
* The cause is not initialized, and may subsequently be initialized by a
* call to {@link #initCause}.
*
* @param - message the detail message. The detail message is saved for
* later retrieval by the {@link #getMessage()} method.
*/
public RuntimeException(String message) {
super(message);
}
...
}-
message만 매개변수로 받아서 부모 생성자를 호출하는
super()에 전달해줌. -
RuntimeException은
Exception을 상속 받고 있으므로 Exception의 생성자가 호출됨.
public class Exception extends Throwable {
....
public Exception(String message) {
super(message);
}
....
}- Exception의 생성자를 호출하는데 여기서도 마찬가지로 super()가 사용되고 있음.
- Exception은
Throwable을 상속 받고 있으므로 Throwable의 생성자가 호출됨.
public class Throwable implements Serializable {
private transient Object backtrace;
private String detailMessage;
private static class SentinelHolder {
public static final StackTraceElement STACK_TRACE_ELEMENT_SENTINEL =
new StackTraceElement("", "", null, Integer.MIN_VALUE);
public static final StackTraceElement[] STACK_TRACE_SENTINEL =
new StackTraceElement[] {STACK_TRACE_ELEMENT_SENTINEL};
}
private static final StackTraceElement[] UNASSIGNED_STACK = new StackTraceElement[0];
private Throwable cause = this;
private StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = UNASSIGNED_STACK;
....
public Throwable() {
fillInStackTrace();
}
public Throwable(String message) {
fillInStackTrace();
detailMessage = message;
}
....
public String getMessage() {
return detailMessage;
}
....
}
- 결국 RuntimeException의 조상의 조상인 Throwable의 생성자를 호출한 꼴.
- 전달 받은 message는 Throwable의
detailMessage에 저장됨.
- 전달 받은 message는 Throwable의
2-1. Ex.
class MyCustomException extends RuntimeException {
public MyCustomException(String message) {
super(message);
}↑위와 같은 형식으로RuntimeException을 상속받아서 많이 사용함.
public class temp3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3};
int value = numbers[5]; // ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
throw new MyCustomException("배열 인덱스 오류");
}
}
}-- 실행 결과 --
Exception in thread "main" com.java.fm.alrorithm.MyCustomException: 배열 인덱스 오류
at com.java.fm.alrorithm.temp3.main(temp3.java:9)생성자중매개변수가 1개인걸 사용하게 되면 위처럼예외 메시지만 출력될 뿐.원래 발생한 예외에 대한 정보는 없음.
3. 매개변수가 2개인 생성자.
public class RuntimeException extends Exception {
....
/**
* Constructs a new runtime exception with the specified detail message and
* cause. <p>Note that the detail message associated with
* {@code cause} is <i>not</i> automatically incorporated in
* this runtime exception's detail message.
*
* @param message the detail message (which is saved for later retrieval
* by the {@link #getMessage()} method).
* @param cause the cause (which is saved for later retrieval by the
* {@link #getCause()} method). (A {@code null} value is
* permitted, and indicates that the cause is nonexistent or
* unknown.)
* @since 1.4
*/
public RuntimeException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
....
}- message와 발생 원인(cause)을 매개변수로 받아서 부모 생성자를 호출하는 super()에 전달해줌.
Throwable cause는 이 예외가 왜 발생했는지에 대한 근본적인 원인을 담고 있는 객체.
- RuntimeException은 Exception을 상속 받고 있으므로 Exception의 생성자가 호출됨.
public class Exception extends Throwable {
....
public Exception(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
....
}- Exception의 생성자를 호출하는데 여기서도 마찬가지로 super()가 사용되고 있음.
- Exception은
Throwable을 상속 받고 있으므로 Throwable의 생성자가 호출됨.
public class Throwable implements Serializable {
private transient Object backtrace;
private String detailMessage;
....
private Throwable cause = this;
....
public Throwable() {
fillInStackTrace();
}
public Throwable(String message, Throwable cause) {
fillInStackTrace();
detailMessage = message;
this.cause = cause;
}
....
public String getMessage() {
return detailMessage;
}
public synchronized Throwable getCause() {
return (cause==this ? null : cause);
}
....
}
- 결국 RuntimeException의 조상의 조상인 Throwable의 생성자를 호출한 꼴.
- 전달 받은 message, cause는 Throwable의 멤버필드인
detailMessage,cause에 저장됨.
- 전달 받은 message, cause는 Throwable의 멤버필드인
3-1. Ex.
class MyCustomException extends RuntimeException {
public MyCustomException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
}public class temp3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3};
int value = numbers[5]; // ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
throw new MyCustomException("배열 인덱스 오류", e); // cause 포함
}
}
]-- 실행 결과 --
Exception in thread "main" com.java.fm.alrorithm.MyCustomException: 배열 인덱스 오류
at com.java.fm.alrorithm.temp3.main(temp3.java:18)
Caused by: java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 5 out of bounds for length 3
at com.java.fm.alrorithm.temp3.main(temp3.java:16)- 위처럼 매개변수가 2개인 생성자를 사용하게 되면
예외 메시지뿐만 아니라원인 예외(cause)까지 출력할 수 있음.
