🔍 Problem
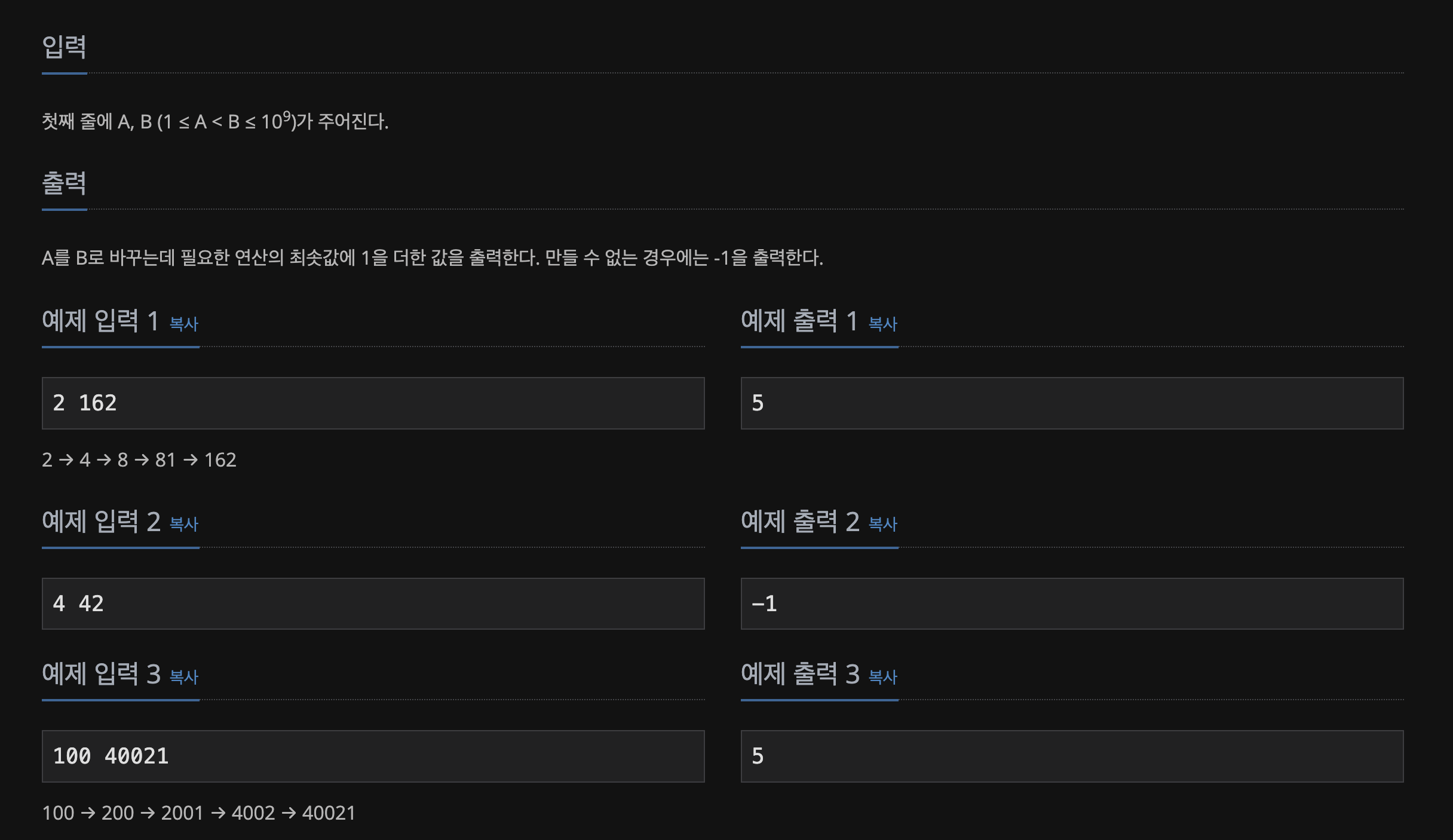
📃 Input&Output
📒 해결 과정
가. 역순으로 계산하는데, 계산 과정 중. 홀수 및 짝수 경우를 나눠서 계산한다.
A가 2이고 B가 162면 162를 2로 만드는 연산을 시작한다.
역순 연산 중 A와 B가 같으면 연산을 종료한다.
나. 먼저 연산할 B가 홀수일 때
경우의 수는 다음과 같다.
- 1의자리 숫자가 "1"이면 해당 숫자를 뺀다.
if (s_B.substring(s_B.length() - 1).equals("1")) {
B = Integer.parseInt(s_B.substring(0, s_B.length() - 1));
}
1이면 뒤에 1을 빼주고 다시 while문 초기으로 돌아간다.
- 1의 자리 숫자가 "1"이 아닐 때
else{
break
}더 이상 연산을 할 수 없으므로 while문(연산)을 종료한다.
다. 연산할 B가 짝수일 때
텍스트
// 짝수
else {
B /= 2;
}B를 2로 나눈다.
❗ Trouble shooting
가. BFS 용량 초과
BFS로 풀고 싶었지만 방문 확인 배열을 까지 만들어야해서 Greedy로 풀었다. 사실 BFS로 풀어보려 했지만 안될거 알고도 그냥 해봤다.
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int A = sc.nextInt();
int B = sc.nextInt();
int[] vst = new int[B + 1];
BFS(A, B, vst);
int res = vst[B];
if (res == 0) {
System.out.println(-1);
} else {
System.out.println(vst[B]);
}
}
static void BFS(int n, int max, int[] vst) {
Queue<Integer> que = new LinkedList<>();
que.add(n);
vst[n] = 1;
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
int v = que.remove();
int nv[] = new int[2];
nv[0] = v * 2;
nv[1] = Integer.parseInt(Integer.toString(v) + "1");
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
if (nv[i] <= max) {
if (vst[nv[i]] == 0) {
vst[nv[i]] = vst[v] + 1;
que.add(nv[i]);
}
}
}
}
}
}
💻 Code
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class P16953 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int A = sc.nextInt();
int B = sc.nextInt();
int cnt = 1;
while (A <= B) {
if (A == B) {
break;
}
// 홀수
if (B % 2 == 1) {
String s_B = (Integer.toString(B));
if (s_B.substring(s_B.length() - 1).equals("1")) {
B = Integer.parseInt(s_B.substring(0, s_B.length() - 1));
} else {
break;
}
}
// 짝수
else {
B /= 2;
}
cnt++;
}
if (A == B) {
System.out.println(cnt);
} else {
System.out.println(-1);
}
}
}
🎸 기타
가. String1.equals(String2)
String1과 String2가 같은지 확인하고 싶을 때 사용하는 함수이다.
나. Java에서 큐 라이브러리
import java.util.*
Queue<T> que = new LinkedList<>();하면되고 함수들은 다음과 같다.
add()remove()peek()isEmpty()
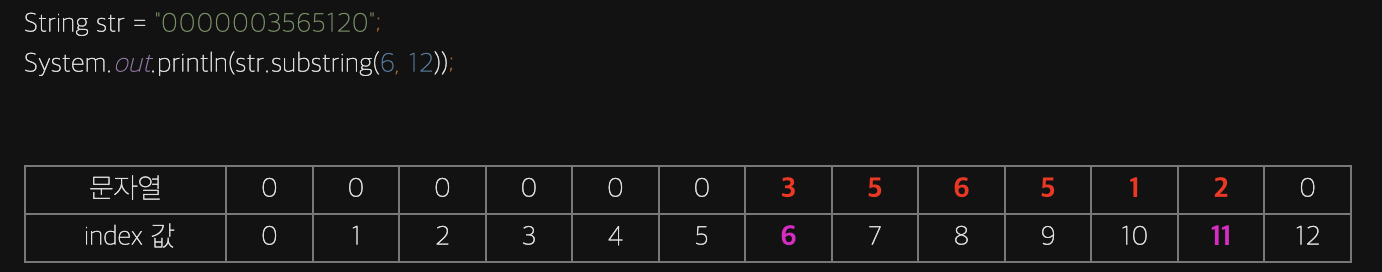
다. String.subString(beginIndex, EndIndex)
String에서 문자열을 자르고 싶다면 위 함수를 사용하면 되고 각각 파라미터의 의미는 아래와 같다.
beginIndex: 잘라서 얻고싶은 문자열의 첫번째 인덱스EndIndex: 잘라서 얻고싶은 문자열의 마지막 인덱스 +1
예시 (출처 : 쉬운코딩이 최고님의 Tistory)
🤔 느낀점
Java와 친해지고 있는 중이다.