🔍 Problem
⚡️ 사용한 알고리즘
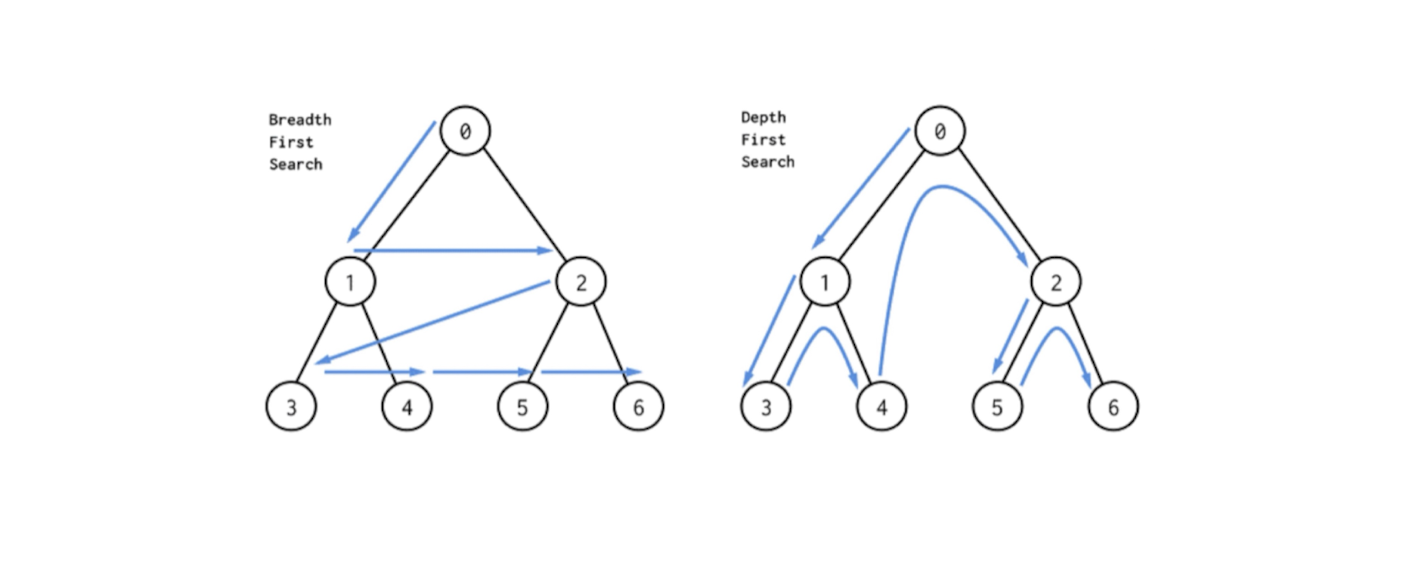
BFS와 DFS
📃 Input&Output
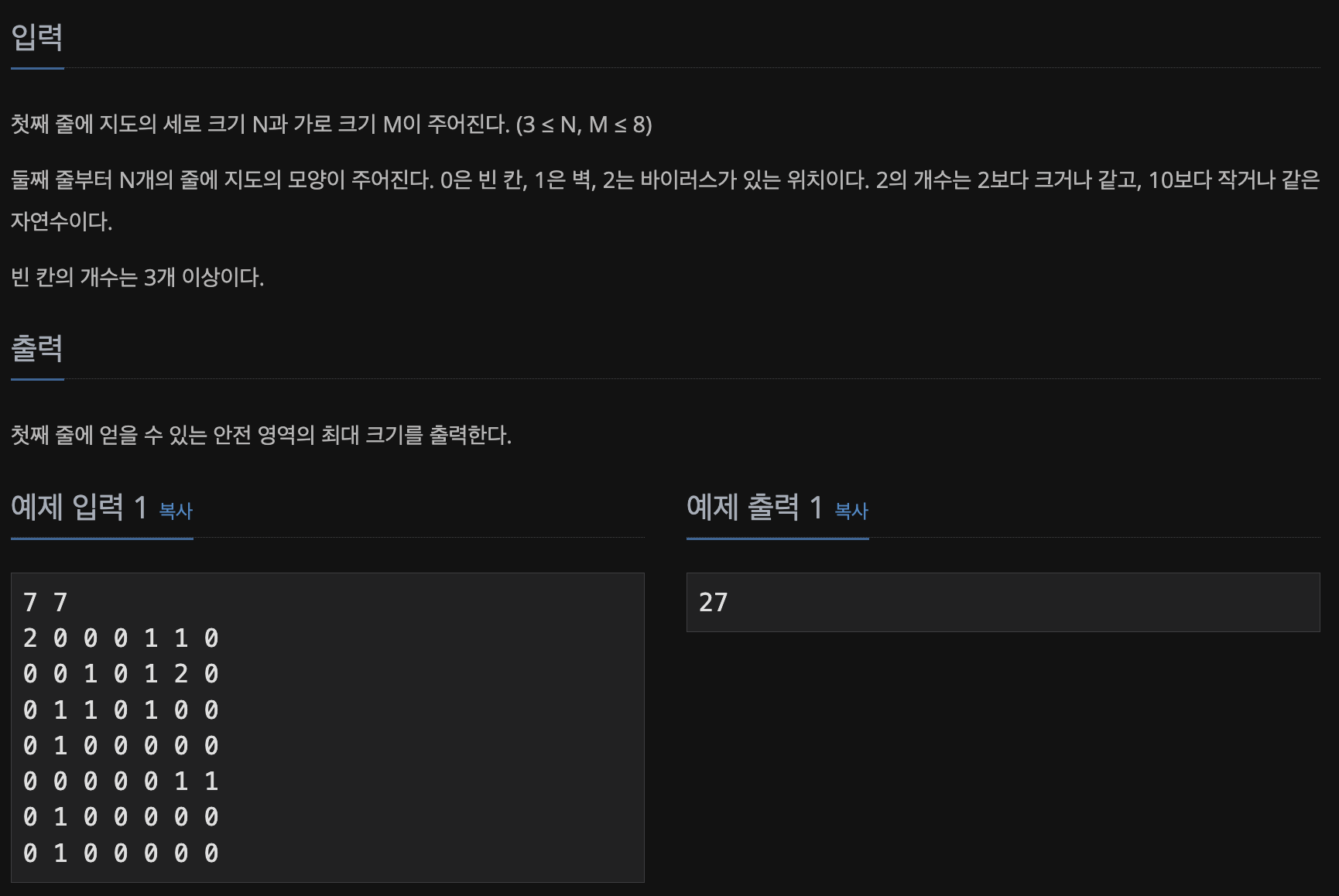
- 참고 사항
0 : 빈칸
1 : 벽
2 : 바이러스
📒 해결 과정
1️⃣ dfs(백트래킹)을 사용하여 벽을 세운다.
2️⃣ 만약 벽이 3개가 세워지면 BFS를 진행하여 세포들의 상하좌우 감염을 실시한다!
3️⃣ 마지막에 감염되지 않은(0) 곳들만 count한다. 필자는 애초에 bfs에서 큐에 넣을 때, +1을 진행하여 시간을 단축하였다.❗주의점
-
dfs를 사용하여 벽을 세울 때, vst를 사용할 필요가 없다. 왜냐하면 벽을 세우면서 해당 좌표값을 1로 변경하기 때문이다.
-
copy 라이브러리의 deepcopy를 사용하여 bfs할때마다 매번 매트릭스를 감염이되지 않고 벽만 세워진 매트릭스로 초기화한다.
tmp_mat = sys.deepcopy(mat)❗중요 -
que를 bfs밖에서 초기화 해버리면 매번 bfs할 때마다 (bfs를 dfs안에서 여러번 실행함) 공유하게 되므로 문제가 생긴다. 따라서 bfs안에서 큐를 초기화 하는 것이 중요!
💻 Code
import sys
from collections import deque
import copy
sys.setrecursionlimit(10**5)
# 가로 : N, 세로 : M
N, M = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split())
mat = [list(map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split())) for _ in range(N)]
res = 0
dx = [-1, 1, 0, 0]
dy = [0, 0, -1, 1]
def bfs():
que = deque([])
tmp_mat=copy.deepcopy(mat)
for i in range(N):
for j in range(M):
if mat[i][j] == 2:
que.append((i, j))
cnt=0
while que:
x, y = que.popleft()
for i in range(4):
nx, ny = x + dx[i], y + dy[i]
if nx>=0 and ny>=0 and nx<N and ny<M:
if tmp_mat[nx][ny] == 0:
que.append((nx,ny))
tmp_mat[nx][ny]=2
for i in tmp_mat:
for j in i:
if j==0:
cnt+=1
return cnt
def dfs(cnt):
global res
if cnt==3:
safe_zone_cnt = bfs()
if safe_zone_cnt>res:
res=safe_zone_cnt
return
for i in range(N):
for j in range(M):
if mat[i][j]==0:
mat[i][j]=1
dfs(cnt+1)
mat[i][j]=0
dfs(0)
print(res)🤔 느낀점
- 다 풀었는데 답이 이상하게 나오길래 확인해봤더니 큐를 bfs밖에서 초기화해서 문제가 발생했다. 디버깅을 문제 발생지점을 확인하고 해결하였다.
- 시간초과가 떠서 pypy3으로 했더니 성공하였다. python은 pypy3보다 입력받는 속도는 빠르지만 연산의 양이 많아지면 pypy3이 빨라진다고 한다.
