167. Two Sum II - Input Array Is Sorted
Problem
Given a 1-indexed array of integers numbers that is already sorted in non-decreasing order, find two numbers such that they add up to a specific target number. Let these two numbers be numbers[index1] and numbers[index2] where 1 <= index1 < index2 <= numbers.length.
Return the indices of the two numbers, index1 and index2, added by one as an integer array [index1, index2] of length 2.
The tests are generated such that there is exactly one solution. You may not use the same element twice.
Example 1:
Input: numbers = [2,7,11,15], target = 9
Output: [1,2]
Explanation: The sum of 2 and 7 is 9. Therefore, index1 = 1, index2 = 2. We return [1, 2].
Example 2:
Input: numbers = [2,3,4], target = 6
Output: [1,3]
Explanation: The sum of 2 and 4 is 6. Therefore index1 = 1, index2 = 3. We return [1, 3].
Example 3:
Input: numbers = [-1,0], target = -1
Output: [1,2]
Explanation: The sum of -1 and 0 is -1. Therefore index1 = 1, index2 = 2. We return [1, 2].
Constraints:
2 <= numbers.length <= 3 * 104-1000 <= numbers[i] <= 1000numbersis sorted in non-decreasing order.-1000 <= target <= 1000- The tests are generated such that there is exactly one solution.
풀이
Two Point를 사용해 풀 수 있다.
-
주어진 배열이 정렬되어 있으며, 두 개의 수를 이용해 target을 구한다는 점에 유의하자.
-
가장 작은 수(index 0)와가장 큰 수(index -1)를 더한 결과 값을sum이라 할 때,sum이target보다 작으면 어떻게 해야 할까?sum에는 더 큰 수를 더해줄 필요가 있다. 따라서가장 작은 수(index 0)보다다음으로 작은 수(index 1)을가장 큰 수(index -1)과 더해주면sum은target에 더 가까이 갈 수 있을 것이다. -
반대로,
sum이target보다 클 경우에는 어떻게 해야 할까?sum에는가장 큰수 (index -1)보다 작은 수를 더해줄 필요가 있으므로,index -1다음으로 큰 수인index -2와가장 작은 수(index 0)를 더해주면sum은target에 더 가까워질 수 있다. -
따라서, 아래와 같으 구현할 수 있다.
left, right = 0, len(nums) - 1 sum = nums[left] + nums[right] if sum == 0 : return elif sum < 0 : left++ else : right-- -
Ex) numbers = [2,7,11,15], target = 9
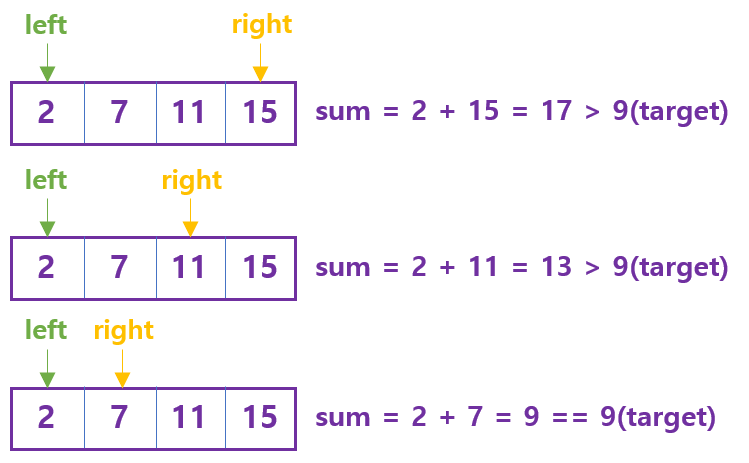
코드
class Solution(object):
def twoSum(self, numbers, target):
"""
:type numbers: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
left = 0
right = len(numbers) - 1
while left < right :
sum = numbers[left] + numbers[right]
if sum == target :
return [left+1,right+1]
elif sum < target :
left += 1
else :
right -= 1