189. Rotate Array(Easy)
Problem
Given an array, rotate the arrya to the right by k steps, where k is non-negative.
Example 1
Input : nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], k = 3
Output : [5,6,7,1,2,3,4]
Explanation :
rotate 1 steps to the right : [7,1,2,3,4,5,6]
rotate 2 steps to the right : [6,7,1,2,3,4,5]
rotate 3 steps to the right : [5,6,7,1,2,3,4]
Example 2
Input : nums = [-1,-100,3,99], k = 2
Output : [3,99,-1,-100]
Explanation :
rotate 1 steps to the right : [99,-1,-100,3]
rotate 2 steps to the right : [3,99,-1,-100]
Constraints
1<= nums.length <= 10^5-2^31 <= nums[i] <= 2^31 - 10 <= k <= 10^5
Follow up
- Try to come up with as many solutions as you can. There are at least three different ways to solve this problem.
- Could you do it in-place with O(1) extra space?
풀이
이번에도 주어진 입력 nums에 새로운 값을 할당하면 안된다.
1. Two Pointer
2. 배열 인덱싱
- 파이썬 인덱싱을 이용해 값들의 위치만 바꿔보자.
-
nums=[1,2,3,4,5,6,7], k=3일 때를 예제로 들어보면 아래 그림과 같이 자리가 이동한다.
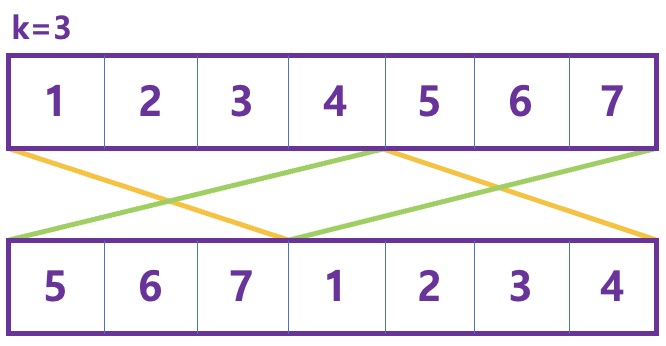
-
자리가 이동하는 곳을 배열 인덱싱으로 표현하면 아래 그림과 같다.
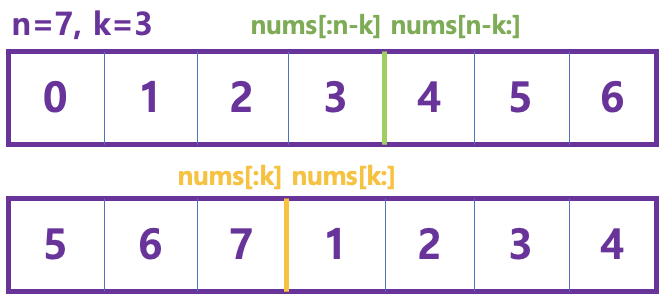
따라서,nums[:k],nums[k:] = nums[n-k:],nums[:n-k]이다. -
k가 n(배열의 길이)보다 크게 주어질 경우도 있기 때문에 이를 처리해줄 필요가 있다.
- n번 오른쪽으로 이동하면 결국 처음의 배열과 동일하다는 것을 알 수 있다.
- 그러므로,
k = k % n을 하고 연산을 수행해도 같은 결과를 얻을 수 있다.
코드
class Solution(object):
def rotate(self, nums, k):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type k: int
:rtype: None Do not return anything, modify nums in-place instead.
"""
n = len(nums)
k = k % n
nums[k:],nums[:k] = nums[:n-k], nums[n-k:]
