Server Driven UI란?
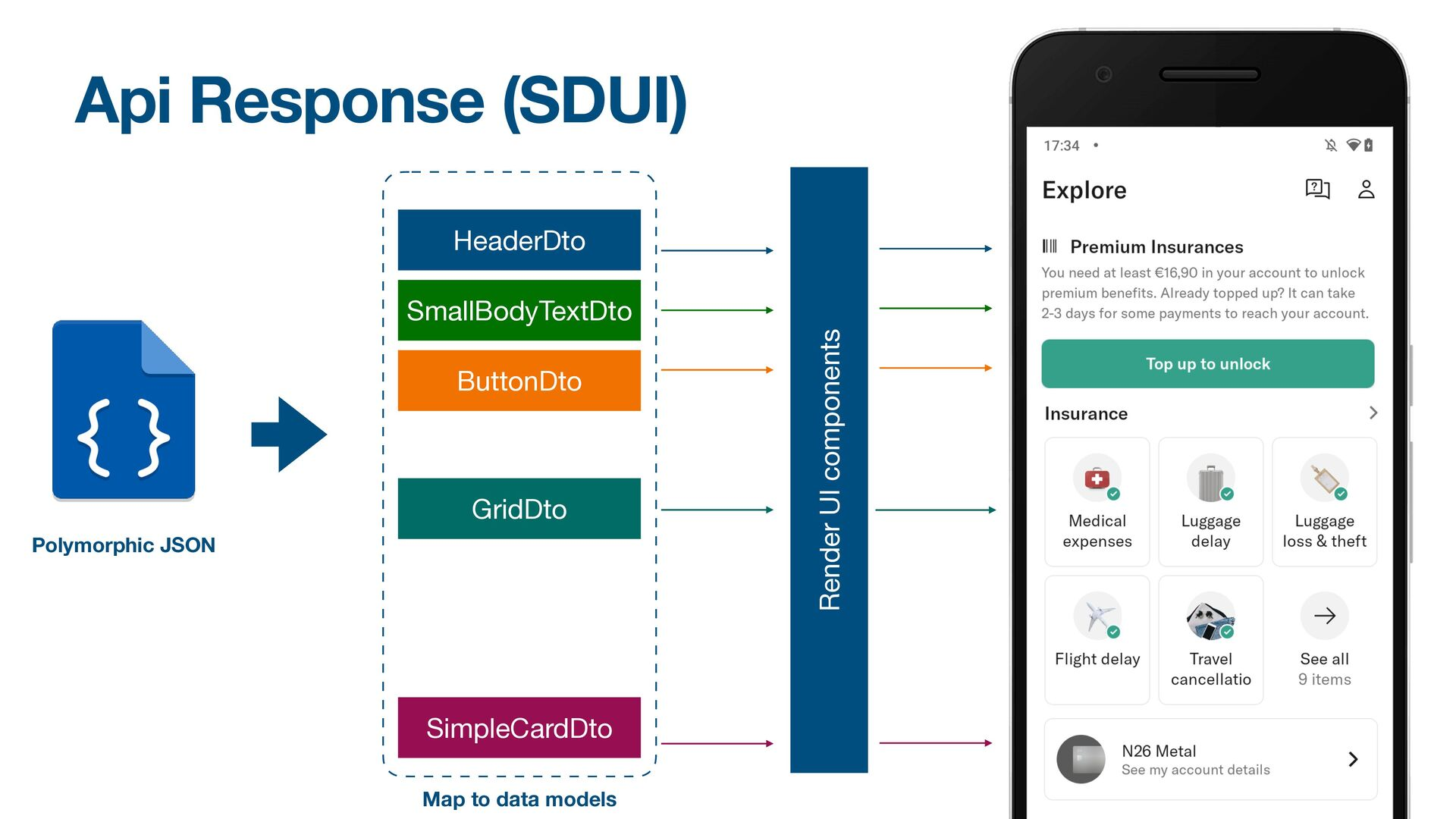
출처: Life is too short to develop only for Android
기존의 앱/웹에서는 서버가 도메인 객체를 JSON으로 인코딩하여 클라이언트에게 보내면, 클라이언트는 이 데이터를 UI로 그리는 방식을 주로 사용해왔다.
하지만 Server Driven UI(SDUI)는 서버에서 UI 구성과 레이아웃을 결정하고, 클라이언트는 이를 받아서 화면을 그린다. 클라이언트에서 하드 코딩된 UI 대신 서버가 레이아웃, 컴포넌트와 내부 데이터에 관련된 지시를 보내준다. 이를 통해 플랫폼 간 신속한 변경과 통합된 사용자 경험을 제공할 수 있게 된다.
🤔 왜 사용할까?
기존의 문제
UI를 자주 바꿔야하는 애플리케이션이 있다고 가정해보자. 애플리케이션 개발에 있어서 새로운 가설을 검증하기 위해 빠르게 신기능을 도입하고, 여러 UI로 A/B 테스트를 진행해보는 것은 중요하다.
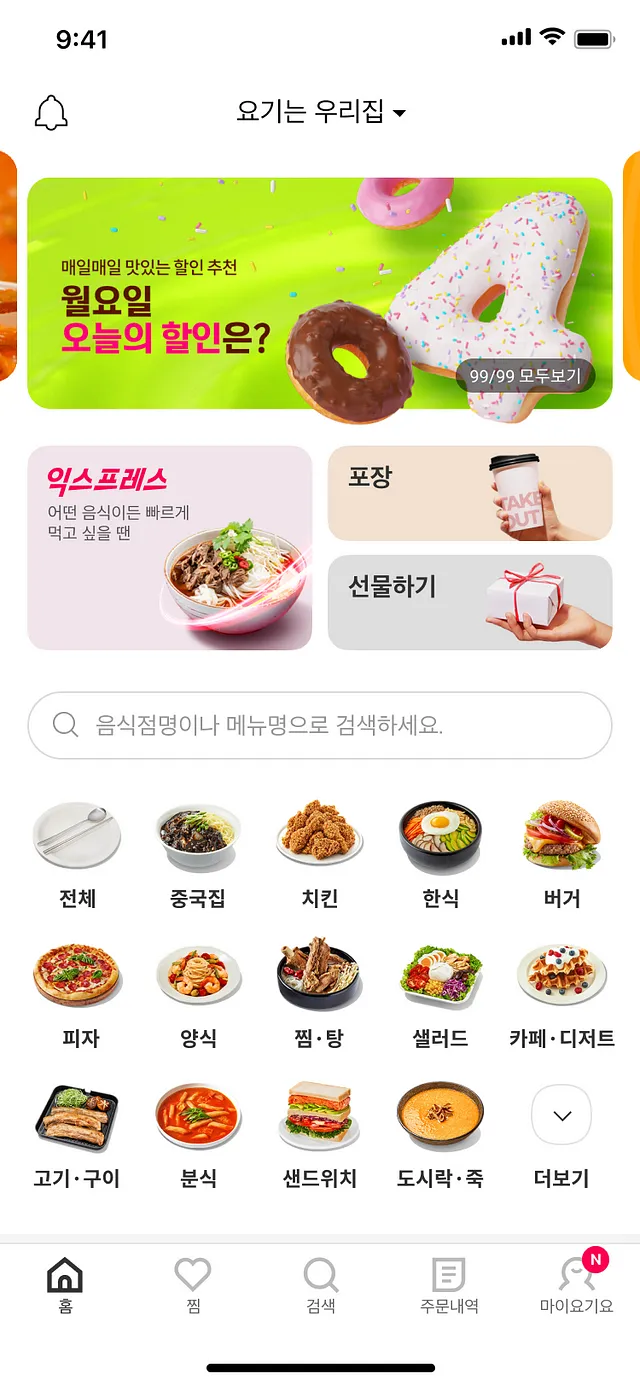
이러한 상황에서 클라이언트 개발자들은 매번 새로운 UI를 개발하고, 서버 개발자들은 이전 버전과의 호환성을 고려하며(또는 버전 분기 처리를 하며) 새로운 기능을 위한 API를 개발해야 한다.
🧐 무슨 문제가 있는거죠?
- 구버전 사용자에게는 변경된 UI가 적용되지 않는다.
- WebView로 구현된 앱이 아니라는 가정 하에, 사용자가 새로운 버전을 직접 다운로드 받지 않는 이상 계속 구버전을 사용해야 한다.
- 강제 업데이트 또는 CodePush는 사용자 경험에 좋지 않을 수 있으므로 매 업데이트마다 해당 방식을 채택하는 것도 무리가 있다.
- 구버전 호환을 위한 서버 측 버전 분기가 계속해서 늘어날 수 있다.
- 이전 버전을 사용하는 사용자도 문제 없이 프로그램을 사용할 수 있게 하기 위해서는 이전 코드를 전면 수정할 수 없고, 분기 처리를 통해 조건적으로 대응해야 한다.
- 이로 인해 if 문이 계속 늘어나고, 코드 가독성이 저하될 수 있다.
- 비정형 데이터에 대해 처리하는 것이 복잡하다.
- 역할은 동일하나 개별 페이지마다 다른 데이터 구조 및 레이아웃을 가지는 페이지가 있다고 할 때, 이를 클라이언트 측에서 일일이 하드코딩하기에는 무리가 있다.
- **유사한 형태의 컴포넌트들을 재사용하지 못하고
🤠 Server Driven UI로 해결하기
Server Driven UI 구조라고 가정하고, 위 예시 이미지 상단의 배너, Grid Layout과 검색 컴포넌트를 아래와 같이 JSON 데이터로 표현해보았다.
[
{
"type": "bannerCarousel",
"props": {
'items": [
// ...
{
"id": 99,
"image": "https://example.com/banner.png",
"url": "https://somewhere.com"
}
]
},
},
{
"type": "category",
"props": {
"categories": [
{
"title": "익스프레스",
"description": "어떤 음식이든 빠르게 먹고 싶을 땐",
"image": "https://example.com/express.png"
},
{
"title": "포장",
"description": null,
"image": "https://example.com/takeout.png"
},
{
"title": "선물하기",
"description": null,
"image": "https://example.com/gift.png"
}
]
},
"design": {
"grid": {
"row": 2,
"col": 2
},
// ...
}
},
{
"type": "searchBar",
"props": {
"placeholder": "음식점명이나 메뉴명으로 검색하세요.",
"onChange": () => {}
},
"design": {
// ...
}
},
{
"type": "menu",
"props": {
"items": [
{ "title": "전체", "image": "https://example.com/all.png" },
{ "title": "중국집", "image": "https://example.com/chinese.png" },
// ...
{ "title": "더보기", "image": "https://example.com/more.png" }
]
},
"design": {
"grid": {
"row": 3,
"col": 5
},
// ...
}
},
]- 이런 방식으로 UI를 구현하면 위에서 언급한 문제들을 아래처럼 해결할 수 있다.
- 서버에서 위와 같이 보내주던 레이아웃 데이터의 순서나 스타일, 내부 데이터를 수정해 내려준다면 사용자는 앱을 업데이트하지 않고도 변경된 구조를 확인할 수 있게 된다.
- 해당 부분은 온전히 서버가 주도하여 UI를 그리게 되므로 버전에 따른 호환성을 고려하여 분기를 생성할 필요 없이, 버전에 맞춰 서버 측 데이터만 수정하면 된다.
- 클라이언트 측에서는 서버에서 데이터로 보내준 UI가 들어갈 자리만
Slot으로 만들어두면 되기 때문에 예측 불가능한 데이터 구조에도 대응하기 용이하다.
💫 Slot이란?
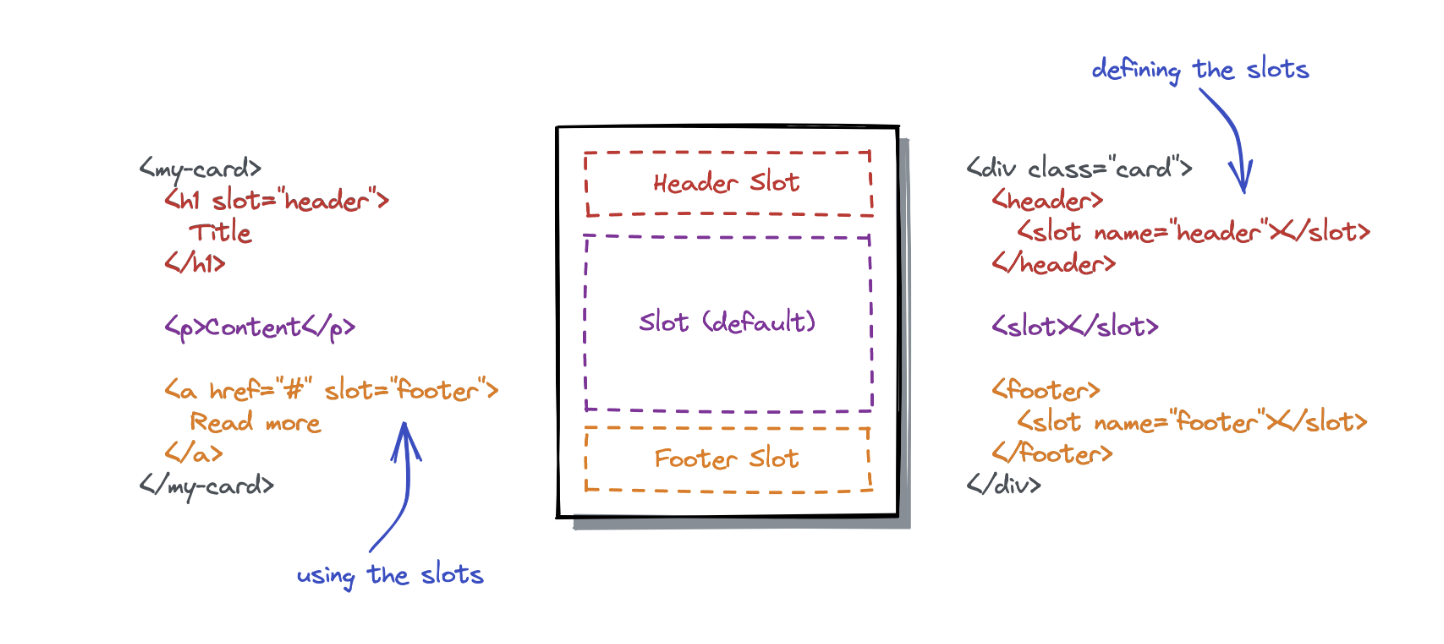
출처: React에서 Slot 패턴과 Coumpound Component 패턴 사용
컴포넌트 내부 특정 위치에 자식 콘텐츠를 삽입할 수 있도록 자리를 미리 지정하고, 이후에 자식 컴포넌트를 동적으로 삽입할 수 있게 하는 컴포넌트 디자인 구조이다.
💫 장점
- 실시간으로 UI 업데이트가 가능하기 때문에 주로 앱 환경에서 유용하다.
- 새로운 디자인이나 기능이 필요할 때 앱의 새 버전 출시 없이도 서버에서 UI를 업데이트 하기만 하면 된다.
- 일반적인 데이터 갱신과 유사하게 동작하므로 강제 업데이트, CodePush 없이 서버 변경만으로 UI를 즉시 업데이트 할 수 있어 UX에 부정적인 영향을 최소화할 수 있다.
- A/B 테스트
- 불필요하게 실험군/대조군 별 UI를 각각 작업하여 배포하는 대신 유연한 설계를 가진 컴포넌트 구조를 구현할 수 있다.
- 컴포넌트에 필요한 속성을 내려받고 이를 조합하여 원하는 형태로 렌더링하도록 구현할 수 있다. 예측 불가능한 비정형 데이터에 대해 각각의 컴포넌트를 생성하는 대신 하나의 컴포넌트 내부에서 데이터에 따른 컴포넌트를 렌더링할 수 있어 반복되고, 불필요한 코드를 최소화할 수 있다.
- 유사한 UI를 가지고 동일한 API를 호출하는 컴포넌트가 있다고 할 때, 사소한 디자인 차이를 서버에서 속성으로 받아 렌더링함으로써 반복되는 코드를 줄이고 UI의 유연성을 높일 수 있다.
- 예를 들어, 아래와 같은 두 컴포넌트가 있다면 구좌별로 여러 개의 컴포넌트를 생성할 필요 없이
border-radius정도의 속성만 서버에서 받아서 그려줄 수 있게 되는 것이다.
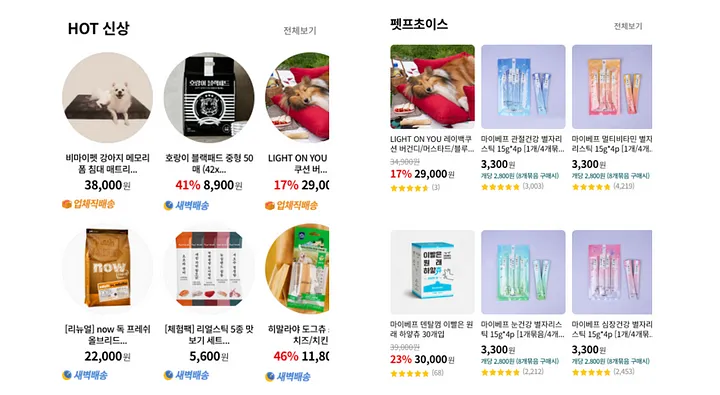
출처: 펫프렌즈 기술블로그
🎯 Airbnb의 Ghost Platform

Airbnb는 이러한 SDUI의 장점을 적극 활용하여 그들만의 시스템인 Ghost Platform(GP) 을 만들었다. 이를 통해 Airbnb는 백엔드에서 데이터를 제어하고 모든 클라이언트에서 동시에 데이터가 표시되는 방식을 제어할 수 있게 되었다. 화면 레이아웃, 섹션의 배열 방식, 내부에 표시되는 데이터와 사용자와의 interaction 작업까지 웹, iOS, Android 환경에서 모두 단일 백엔드 응답으로 제어되도록 GraphQL의 universal 스키마를 사용할 수 있게 구현되었다고 한다.
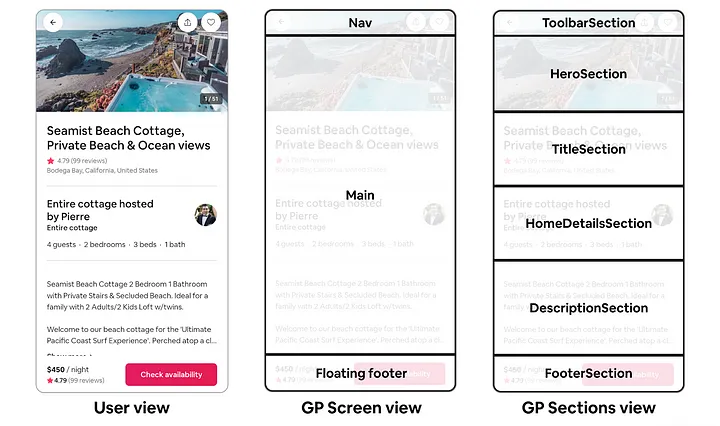
출처: Airbnb 기술 블로그
Section과 Screen
GP Response의 GraphQL 스키마는 아래와 같이 구현되어 있다.
interface GPResponse {
sections: [SectionContainer]
screens: [ScreenContainer]
# ... Other metadata, logging data or feature-specific logic
}- Section
- GP의 가장 기본적인 구성 요소로, UI 컴포넌트를 표현하는 데이터와 어떤 데이터가 표현될지를 포함한다.
- 서버에서 응답할 때 데이터를 미리 처리해서 주는데, 번역을 해야 하는 데이터의 경우 번역 후 i18n 처리를 완료하고 formatting을 거쳐 클라이언트 측에 내려준다. 클라이언트는 이 값을 단순하게 렌더링하기만 하면 된다.
- 플랫폼별 native language(TypeScript, Swift, Kotlin)으로 구현되어 있어 플랫폼별로 구현만 해두면 네이티브 환경에 맞게 렌더링하고 테스트할 수 있다.
- Screen
- n개의 화면은 각 화면의 레이아웃을 설명하고
section배열 내의 배치를 설명하는 데이터이다. - 또한 popover, modal, full-screen 또는 log data 등의 metadata를 정의한다.
- n개의 화면은 각 화면의 레이아웃을 설명하고
- Action
- 단순히 화면에서 보여지는 부분에서 더 나아가 사용자와 상호작용하는 UI의 event handling도 제어할 수 있다.
- 예: 버튼 클릭 액션, 카드 넘기는 동작
미래에는,,,
추후 Airbnb는 Nested Section 관련 기능을 추가하고, Figma 또는 WISYWIG 기능을 통해 no-code로 UI를 수정할 수 있는 형태로의 확장을 목표하고 있다고 한다. 더 자세한 GP에 대한 내용이 궁금하다면 원문을 참조할 수 있다.
🧐 어떻게 사용할까?
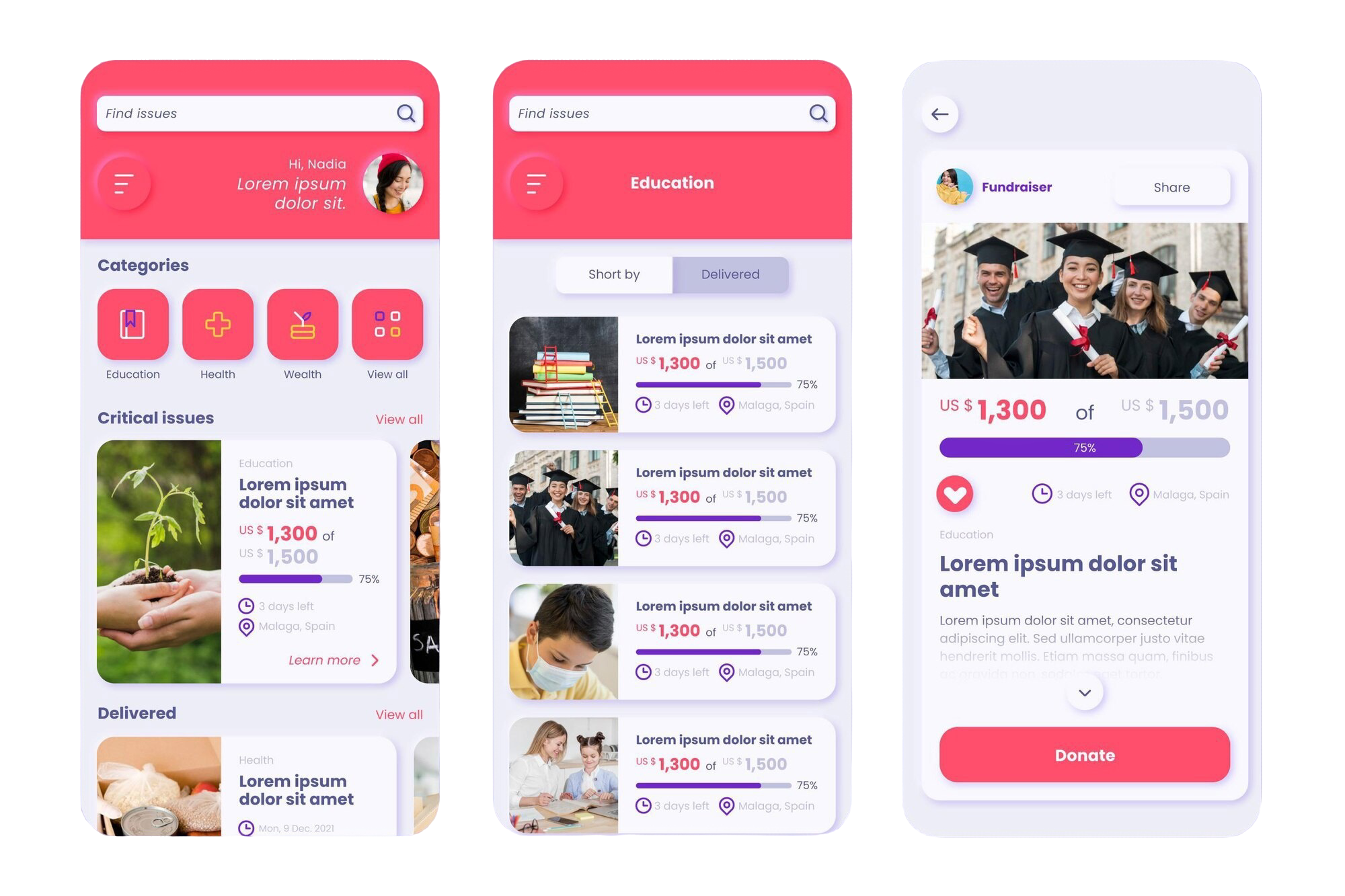
위 이미지는 Freepik에서 가져온 Mockup Asset이다. 이 중 첫 번째 화면인 Main Screen을 기준으로 코드를 작성해보자.
기존 데이터 기반 UI로 구현하기
const data = {
user: {
name: "Jacob",
profileImage: "https://example.com/profile.jpg",
subtext: "Find causes you care about and make an impact.",
},
categories: [
{ name: "Health" },
{ name: "Education" },
{ name: "Environment" },
{ name: "Animals" },
{ name: "Community" },
],
issues: [
{
id: 1,
title: "Save the Rainforest",
image: "https://example.com/rainforest.jpg",
raised: 5000,
goal: 10000,
progress: 50,
highlight: true,
},
{
id: 2,
title: "Support Local Schools",
image: "https://example.com/schools.jpg",
raised: 800,
goal: 5000,
progress: 16,
highlight: false,
},
{
id: 3,
title: "Help Stray Animals",
image: "https://example.com/animals.jpg",
raised: 2000,
goal: 3000,
progress: 66,
highlight: true,
},
],
};이러한 데이터를 클라이언트 측에서 UI 상에 표현하면 아래와 같을 것이다. (스타일은 별도로 CSS를 통해 구현될 것이다.)
import React from "react";
const Home: React.FC = () => {
// 데이터 바인딩
const { user, categories, issues } = data;
return (
<div>
{/* Header Section */}
<div>
<h2>{`Welcome, ${user.name}`}</h2>
<p>{user.subtext}</p>
<img
src={user.profileImage}
alt="Profile"
/>
</div>
{/* Category Section */}
<div>
<h3>Categories</h3>
{categories.map((category, index) => (
<button
key={index}
onClick={() => navigate(`/${category.name}`)}
>
{category.name}
</button>
))}
</div>
{/* Issues Section */}
<div>
<h3 style={styles.sectionTitle}>Trending Causes</h3>
{issues.map((issue) => (
<div
key={issue.id}
>
<img
src={issue.image}
alt={issue.title}
/>
<h4>{issue.title}</h4>
<p>
Raised: ${issue.raised} / ${issue.goal}
</p>
<div>
<div
/>
</div>
</div>
))}
</div>
</div>
);
};
// 스타일 정의
const styles = {
header: {
backgroundColor: "#4f46e5",
padding: "16px",
color: "#ffffff",
textAlign: "center",
},
// ...
};
export default Home;이렇게 구현할 경우 UI 레이아웃과 스타일이 컴포넌트 자체에 하드코딩 되기 때문에 데이터를 바탕으로 UI가 렌더링 되고, 각 컴포넌트의 구조와 스타일을 변경하려면 별도의 작업이 필요하다.
만약 위의 이미지에서 메인 페이지의 컴포넌트 배치 순서를 바꾼다거나 UI의 스타일을 수정하려 한다면 클라이언트 코드를 수정하고 해당 어플리케이션을 다시 배포하는 과정을 거쳐야 한다.
🤔 SDUI 없는 개발 프로세스는 어떻게 진행됐나요
- 프론트엔드는 디자이너가 작성한 UX를 기반으로 페이지를 퍼블리싱한다.
- 백엔드는 기능적 요구사항을 수용하기 위해 API를 개발한다.
- 프론트엔드는 API를 통합해 사용자에게 데이터와 기능을 제공할 수 있도록 구현한다.
- 코드를 테스트하고 배포한 뒤 새로운 릴리즈 버전을 파이프라인에 제공한다.
- 앱 사용자는 최신 빌드를 다운로드(스토어에서 업데이트)하고, 웹 사용자는 새로고침을 통해 새로운 버전을 사용하게 된다.
- 변경 사항이 생긴다.
- 1 - 5의 과정을 반복한다....
앞에서도 언급했듯, 빠른 테스트와 검증이 필요한 환경에서는 이러한 과정이 비효율적일 수 있다.Server Driven UI로 구현하기
Server Driven UI에서는 위에서처럼 전체 UI를 하드코딩하는 대신 클라이언트가 서버에 UI를 요청하고, 서버는 UI 구조를 포함하는 payload(JSON, XML 등)로 응답한다. 아래는 서버가 전송하는 데이터를 예상하여 작성해본 JSON 데이터이다.
{
"components": [
{
"type": "searchBar",
"placeholder": "Search for causes or categories...",
"style": {
"backgroundColor": "#f9fafb",
"textColor": "#333333",
"borderRadius": "8px",
"padding": "12px",
"fontSize": "14px"
}
},
{
"type": "header",
"text": "Welcome, Jacob",
"subtext": "Find causes you care about and make an impact.",
"profileImage": "https://example.com/profile.jpg",
"style": {
"backgroundColor": "#4f46e5",
"textColor": "#ffffff",
"profileImageBorderRadius": "50%",
"padding": "16px",
"textFontSize": "20px",
"subtextFontSize": "14px"
}
},
{
"type": "categorySection",
"title": "Categories",
"categories": [
{ "name": "Health", "highlight": true },
{ "name": "Education", "highlight": false },
{ "name": "Environment", "highlight": false },
{ "name": "Animals", "highlight": true },
{ "name": "Community", "highlight": false }
],
"style": {
"titleColor": "#1f2937",
"categoryButton": {
"highlightBackgroundColor": "#f87171",
"defaultBackgroundColor": "#e5e7eb",
"textColor": "#ffffff",
"borderRadius": "12px",
"padding": "10px"
}
}
},
{
"type": "issueSection",
"title": "Trending Causes",
"issues": [
{
"id": 1,
"title": "Save the Rainforest",
"image": "https://example.com/rainforest.jpg",
"raised": 5000,
"goal": 10000,
"progress": 50,
"highlight": true
},
{
"id": 2,
"title": "Support Local Schools",
"image": "https://example.com/schools.jpg",
"raised": 800,
"goal": 5000,
"progress": 16,
"highlight": false
},
{
"id": 3,
"title": "Help Stray Animals",
"image": "https://example.com/animals.jpg",
"raised": 2000,
"goal": 3000,
"progress": 66,
"highlight": true
}
],
"style": {
"titleColor": "#111827",
"issueCard": {
"highlightBackgroundColor": "#fbbf24",
"defaultBackgroundColor": "#ffffff",
"borderColor": "#d1d5db",
"padding": "16px",
"borderRadius": "8px",
"titleColor": "#374151",
"progressBarColor": "#4ade80"
}
}
}
]
}클라이언트 측에서는 위와 같은 JSON/XML 데이터를 서버로부터 전송받은 뒤 아래처럼 렌더링할 수 있다.
ComponentMapper는 서버에서 전달받은 데이터에 따라 UI를 동적으로 렌더링하기 위해 미리 클라이언트 측에서 특정 컴포넌트 타입과 React 함수형 컴포넌트를 매핑해둔 객체이다.
const ComponentMapper: Record<ComponentType, React.FC<any>> = {
searchBar: ({ placeholder }) => <input placeholder={placeholder} className="search-bar" />,
header: ({ text, subtext, profileImage }) => (
<div className="header">
<h2>{text}</h2>
<p>{subtext}</p>
<img src={profileImage} alt="Profile" />
</div>
),
categorySection: ({ title, categories }) => (
<div className="category-section">
<h3>{title}</h3>
{categories.map((cat: any, index: number) => (
<button key={index} className={cat.highlight ? 'highlight' : ''}>
{cat.name}
</button>
))}
</div>
),
issueSection: ({ title, issues }) => (
<div className="issue-section">
<h3>{title}</h3>
{issues.map((issue: any) => (
<div key={issue.id} className={issue.highlight ? 'issue-card highlight' : 'issue-card'}>
<img src={issue.image} alt={issue.title} />
<h4>{issue.title}</h4>
<p>{`Raised: $${issue.raised} / $${issue.goal}`}</p>
<div className="progress-bar">
<div style={{ width: `${issue.progress}%` }} className="progress" />
</div>
</div>
))}
</div>
),
};위와 같이 정의해두고 실제 UI가 렌더링 되어야 하는 Slot에서는 배열을 순회하면서 각 요소의 type 속성에 따라 적절한 컴포넌트를 보여줄 수 있다
const App: React.FC<{ components: any[] }> = ({ components }) => {
return (
<div>
{components.map((component, index) => {
const Component = ComponentMapper[component.type];
return Component ? <Component key={index} {...component.props} /> : null;
})}
</div>
);
};물론 SDUI가 모든 상황에서 최적의 방식이라는 것은 아니다.
- SDUI 상에서는 UI 변경 사항이 백엔드에서 관리되므로 디자인 변경이 잦다면 단순한 스타일 변경을 위해서 백엔드 배포 과정을 거쳐야 하는 상황이 발생할 수도 있다.
- Drag&Drop이나 애니메이션 같은 복잡한 형태의 UX가 요구되는 경우에는 UI를 프론트엔드 상에서 관리하는 것이 더 효율적일 수 있다.
- UI가 자주 바뀌지 않고 정적 콘텐츠가 주를 이루는 환경에서는 백엔드 중심의 유연한 UI가 필요하지 않으므로 오히려 개발 복잡성만 추가할 수 있다.
- 네트워크 연결 없이 오프라인에서 작동해야 하는 애플리케이션의 경우 서버 의존적인 SDUI의 구조가 오히려 한계가 될 수 있다.
그러므로 SDUI의 도입을 위해서는 팀 내에서 현재 상황을 파악하고 적합하다고 판단할 때에 도입하는 것이 중요해 보인다.
결론적으로, 디자인 변경이 빈번하지 않고, 복잡한 사용자 경험(UX)보다는 데이터 중심의 화면 구성이 중요한 경우, 그리고 프론트엔드의 개발 효율성과 유지보수를 최적화하고자 하는 상황에서는 SDUI 도입을 고려해볼 만 하다. 특히, SDUI에 대해 정리하면서 백엔드와 프론트엔드 간의 명확한 역할 분리를 통해 협업이 원활해지고, 새로운 페이지나 뷰를 빠르게 확장할 수 있는 환경이라면 SDUI는 강력한 선택지가 될 수 있겠다고 느꼈다.
🔎 References
- Server Driven UI
- 🚀 Server-Driven UI Design Patterns: A Professional Guide with Examples
- A Deep Dive into Airbnb’s Server-Driven UI System
- Server Driven UI
- Server-Driven UI — Concepts and Building Blocks
- Why Server-Driven UI Is Key to the Longevity of Web Software Architecture Platforms
- Server Driven UI: How to Start.
- Server-Driven UI — A Brief Introduction
- 네이버 검색의 Server Driven UI
- 우당탕탕 Server Driven UI 개발기
- Next.js로 이전하고 Server Driven UI로 변화하다
- 토스ㅣSLASH 23 - Server-driven UI로 다이나믹한 서비스 효율화하기
- 토스ㅣSLASH 23 - Server-driven UI로 토스의 마지막 어드민 만들기
- Introducing LiquidUI – PhonePe’s Server-Driven UI Framework – Part 1
- Server Driven UI (Feat.Flutter)
