Distribution-Aware Coordinate Representation for Human Pose Estimation
Abstract
-
pose estimation을 위한 heat map은 기존 paper들에서 체계적으로 조사되지 않았다.
-
본 논문은 heat map에 특히 초점을 맞춘 좌표 표현(coordinate representation)을 연구함으로써이 격차를 메울 것이다.
-
흥미롭게도, 우리는 the process of decoding the predicted heatmaps into the final joint coordinates in the original image space가 성능에 있어서 매우 중요함을 알아 내었다.
-
우리는 현재 널리 사용하고있는 standard coordinate decoding method의 설계 한계를 조사하고 distribution-aware decoding method를 제안한다.
-
우리는 편향되지 않는 모델 training을 위해 the standard coordinate encoding process를 개선함으로써 정확한 heatmap분포를 생성할 것 이다.
- the standard coordinate encoding process: transforming ground-truth coordinates to heatmaps
-
DARK는 model-agnostic plugin(모델에 구애받지않는)이다. 즉, 모든 state-of-the-art pose estimation model들의 성능으르 크게 향상시킨다.
-
MPII and COCO에서 최고의 성능을 보여주었다.
Introduction
- 기존 pose estimation은 CNN 구조 설계에 중점을 두었다.
-
The standard label representation is a coordinate heatmap, generated as a 2-dimensional Gaussian distribution/kernel centered at the labeled coordinate of each join
-
이것은 coordinate encoding process로부터 얻어진다.
-
heat map의 장점
- 이러한 heat map은 공간적인 support를 한다.
- 맥락과 관련된 증거
- position에 대한 모호성
- overfitting risk를 줄여준다.
- smoothing regularisation
- HRNet은 현제 SOTA이며 heatmap coordinate representation을 사용한다.
- 이러한 heat map은 공간적인 support를 한다.
-
하지만 heat map도 계산해야 하므로 속도가 느리다.
-
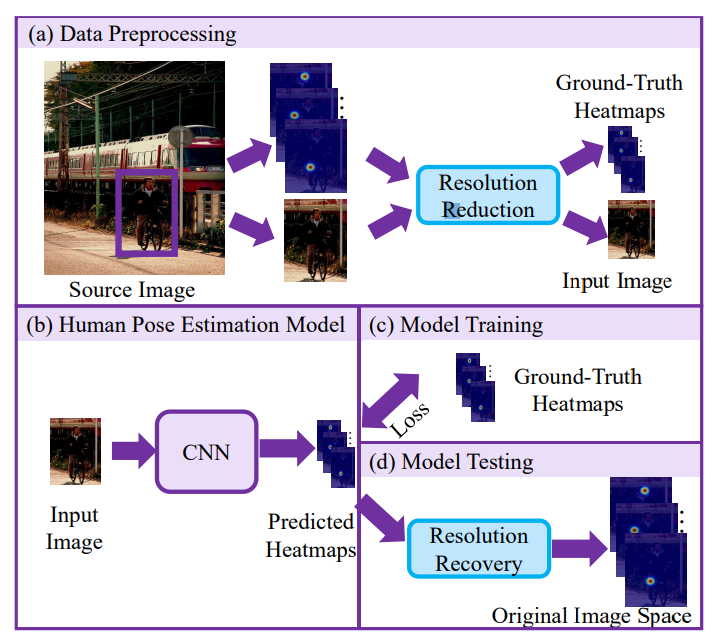
이러한 단점을 극복하기 위해 FIgure1과 같이 전처리로 해상도를 줄여준다. 그리고 predict를 위해 다시 해상도를 회복 시켜 주었다.
-
최종 예측은 최대 활성화가있는 위치로 간주된다. (We call this process coordinate decoding, from heatmap to coordinate.)
- coordinate encoding: 좌표를 heat map으로 만드는작업
- coordinate decoding: heat map을 좌표로 만드는작업
- 이때 quantization error(양자화잡음이 생길 수 있다.)
- 이러한 양자화 잡음을 줄이기 위해 shifting operation이 사용되는데 이는 성능에 굉장히 많은 영향을 끼친다.
-
본 논문에서는 다른 논문들과달리 encoding, decoding을 포함한 joint coordinate representation에 중점을 두었다.
-
또한, heatmap resolution은 속도를 위해 더 작은 input을 넣지 못하게하는 장애물이다.
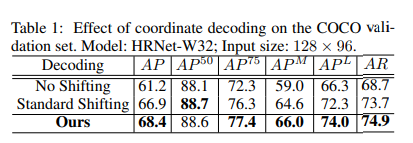
- When decreasing the input resolution from 256×192 to 128×96, the model performance of HRNet-W32 drops significantly from 74.4% to 66.9% on the COCO validation set.
-
이에 우리는 Taylor-expansion-based distribution approximation를 통한 heatmap 추출 방법을 제안한다.
-
Besides, we observe that the standard method for generating the ground-truth heatmaps suffers from quantization errors.
-
이 문제를 해결하기 위해 우리는 Gaussian kernel이 하위 픽셀 위치에 집중 될 수 있도록 편향되지 않은 heat map 생성을 제안합니다.
contribution
- propose a novel Distribution-Aware coordinate Representation of Keypoint(DARK) method with two key components
- ) Taylor-expansion based coordinate decoding
- ) Unbiased sub-pixel centred coordinate encoding
- 해당 방법은 어느 heat map 모델에도 사용 될 수 있으며, 좋은 performance를 보여 주었다.
Methodology
- 이미지에서 출력 좌표로 회귀 모델을 학습해야하며 heat map은 종종 model training 및 test 중에 좌표 표현으로 활용된다.
- 모델 학습을 용이하게하기 위해 레이블이 지정된 관절의 실측 좌표를 heat map으로 encoding한다.
- 테스트 중에는 예측 된 heat map을 원래 이미지 좌표 공간의 좌표로 decoding해야한다.
-
) In the following we first describe the decoding process, focusing on the limitation analysis of the existing standard method and the development of a novel solution.
-
) Then, we further discuss and address the limitations of the encoding process.
-
) Lastly, we describe the integration of existing human pose estimation models with the proposed method.
1) Coordinate Decoding
-
a predicted heatmap of each individual joint을 a coordinate in the original image space로 옮기는 것을 말한다.
-
heat map이 원본 이미지와 동일한 공간 크기를 갖는다 고 가정하면, 관절 좌표 예측과 같이 최대 활성화 위치를 찾기 만하면 된다.
The standard coordinate decoding method
-
The standard coordinate decoding method은 모델 성능에 따라 경험을 기반으로 으로 설계되었다.
-
훈련 된 모델에 의해 예측 된 heat map h가 주어지면 먼저 최대 (m) 및 두 번째 최대 (s) 활성화의 좌표를 식별한다.
-
The joint location is then predicted as
- 는 벡터의 크기를 정의한다.
- 위 공식은 예측된 heat map 공간에서의 최대 activation에서 두 번째 최대 activation쪽으로 0.25 pixel(i.e. sub-pixel) 이동하는 최대 activation을 뜻 한다.
- 이는 양자화잡음을 최소화시키기 위함이다.
-
The final coordinate prediction in the original image is computed as:
- λ는 해상도 축소 비율이다.
-
즉, 예측 된 heat map의 최대 활성화는 원래 좌표 공간에서 관절의 정확한 위치와 일치하지 않고 대략적인 위치에만 해당한다. (성능이 좋지 않은이유)
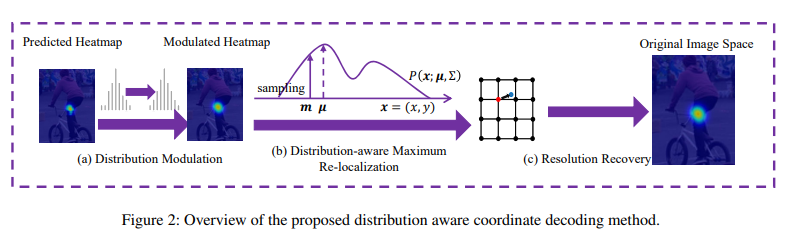
The proposed coordinate decoding method
-
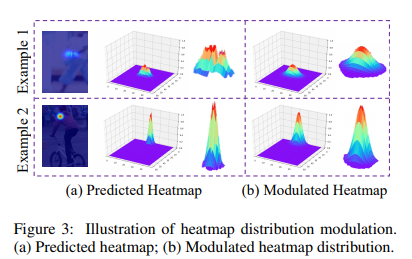
he proposed coordinate decoding method는 예측 된 heat map의 분포 구조를 탐색하여 기본 최대 활성화를 추론한다.
-
이방법은 설계 정당성과 근거가 거의없이 수작업으로 설계 한 오프셋 예측에 의존하는 위의 The standard coordinate decoding method와 크게 다르다.
-
구체적으로 sub-pixel의 정확한 위치를 얻기 위해, 예측 된 heat map이 ground-truth heat map과 같은 2D Gaussian 분포를 따른다고 가정한다
-
따라서 예측 된 heat map을 다음과 같이 표현한다.
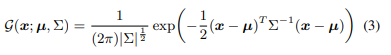
-
여기서 x는 예측 된 heat map의 pixel의 위치이고 µ는 추정 될 관절 위치에 해당하는 가우스 평균(중심)이다.
-
공분산 Σ는 좌표 인코딩에 사용 된 것과 동일한 대각 행렬이다.

-
여기서 σ는 양방향에 대해 동일한 표준 편차이다.
-
log-likelihood optimization principle에서 최대 활성화의 원래 위치를 다음과 같이 유지하면서 추론을 용이하게하기 위해 G를 대수로 변환한다.
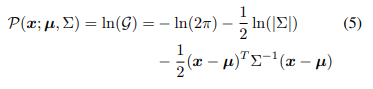
2) Coordinate Encoding
-
the standard coordinate encoding method은 원본 인물 이미지를 모델 입력 크기로 다운 샘플링하는 것으로 시작된다.
-
따라서 heat map을 생성하기 전에 Ground-Truth Joint 좌표를 적절히 변환해야 한다.
-
Formally, we denote by g = (u, v) the ground-truth coordinate of a joint.
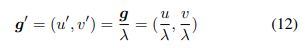
- 여기서 λ는 다운 샘플링 비율이다. 일반적으로 kernel generation을 용이하게하기 위해 종종 을 양자화(quantise)한다.
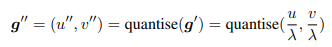
-
여기서 quantise ()는 floor, ceil 및 round를 포함한 일반적인 선택과 함께 양자화 함수를 지정한다.
-
그 후, 양자화 된 좌표 을 중심으로하는 heat map은 다음을 통해 합성 할 수 있다.
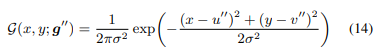
-
여기서 (x, y)는 heat map의 pixel 위치를 지정하고 σ는 고정 된 공간 분산을 나타낸다.
-
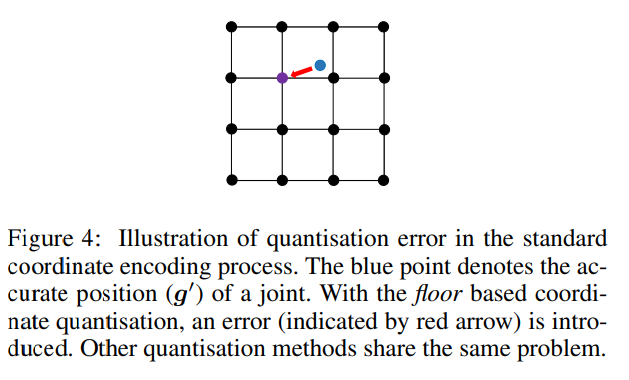
분명히 위의 방식으로 생성 된 heat map은 부정확하고 양자화 오류로 인해 편향되어 있었다.
-
이 문제를 해결하기 위해 heat map 중심을 정확한 실제 좌표를 나타내는 비 양자화 위치 에 배치 하였다.
-
여전히 (14)을 적용하지만 을 으로 대체하였다.
Reference
https://github.com/ilovepose/DarkPose (github)
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1910.06278.pdf (논문)
https://linecard.tistory.com/59 (양자화 잡음)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XhlfVtGb19c (log-likelihood)
