
Deep High-Resolution Representation Learning for Human Pose Estimation
Abstract
- high-resolution representations를 pose estimation problem에 적용하였다.
- 대부분의 방법들은 high-resolution representations을 low-resolution representations로 부터 복구한다. 왜냐하면, 이런 모델들은 high-to-low resolution network이기 때문이다.
- 하지만 우리는 high-resolution representations를 전체 process동안 유지 하였다.
- 먼저 high-resolution subnetwork를 첫번째 stage로써 시작한다. 그리고 점차적으로 high-to-low resolution subnetworks를 하나씩 추가한다. 이는 더 많은 stages를 만들기 위해서가 첫번째 그리고 multi-resolution subnetworks를 병렬로 연결하기 위해서다.
- 우리는 multi-scale fusions을 반복한다. 이는 high-to-low resolution representation가 other parallel representations로부터 정보를 계속 받는것이다
- 그 결과 keypoint heatmap을 예측하는 문제에서 좋은 accuracy를 얻을 수 있었다. 그리고 이러한 결과는 경험적으로 증명 되었다.
1. Introduction
-
pose estimation은 including human action recognition, human-computer interaction, animation등 많은 applications에서 쓰인다.
-
이 논문은 single-person pose estimation에 집중한다.
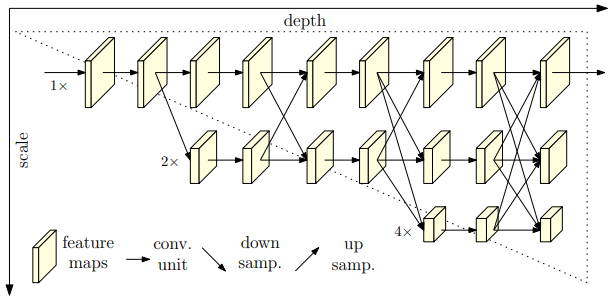
-
기존 방법들은 직렬로 서로 연결하여 해상도를 높인다.
-
또한 팽창된 convolutions들을 사용하는데 이는 the later layers of a high-to-low resolution network를 확장시키기 위해 사용된다. (e.g., VGGNet or ResNet)
- 우리는 HRNet를 사용하였는데 이는 high-resolution representations 를 전체 과정동안 유지해준다.
- 먼저 high-resolution subnetwork를 첫번째 stage로써 시작한다. 그리고 점차적으로 high-to-low resolution subnetworks를 하나씩 추가한다. 이는 더 많은 stages를 만들기 위해서가 첫번째 그리고 multi-resolution subnetworks를 병렬로 연결하기 위해서다.
- 우리는 multi-scale fusions을 반복한다. 이는 high-to-low resolution representation가 other parallel representations로부터 정보를 계속 받는것이다
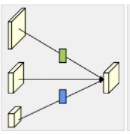
- The resulting network is illustrated in Figure 1.
1) Our network has two benefits
- high-to-low resolution subnetworks는 기존의 방법처럼 직렬이 아닌 병렬로 연결되어있다.
-
-
대부분의 기존 fusion scheme들은 low-level and high-level representations로 통합 되었다.
-
하지만 우리는 그 대신에, multi-scale fusions을 반복하였다. 이는 high-resolution representation들을 low-resolution representations of the same depth and similar level와 함께 증폭시켜주며 그 반대도 마찮가지이다.
-
-
우리는 경험적으로 해당 모델이 아래의 모델에서 좋은 성적을 보여줌을 알 수 있었다.
- COCO keypoint detection dataset
- MPII Human Pose dataset
- PoseTrack dataset
3. Approach
-
The state-of-the-art methods는 pose estimation 문제를 heatmap들의 위치를 찾는것으로 변형시키는 것 이다.
** K heatmaps of size W ' ×H', {} -
우리는 기존 pose estimation model들 처럼 input과 output resolution을 맞추었고, heatmaps regressor을 사용 하였다.
-
우리는 main body인 HRNet에 집중 하였다. (Figure 1.)
1) Sequential multi-resolution subnetworks.
-
기존 pose estimation은 high-to-low resolution subnetworks을 직렬로 사용한다. 그리고 해당 모델들은 down-sample layer(Pooling layer)가 있어 resolution을 반으로 줄인다.
-
r: resolution index
-
s: stage
-
-
-
Its resolution is of the resolution of the first subnetwork
2) Parallel multi-resolution subnetworks.
- high-resolution subnetwork을 처음 stage로 시작한다.
- high-to-low resolution subnetworks을 하나씩 추가한다.
- multi-resolution subnetworks을 병렬로 연결시킨다.
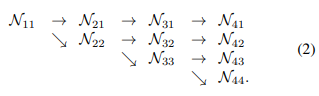
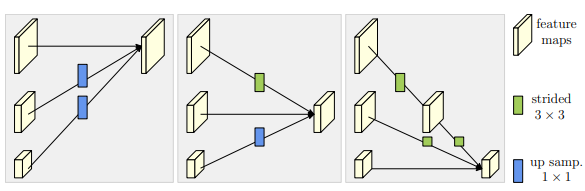
- 1*1filter로 channel개수를 정할 수 있으며 upsampling의 경우 Nearest Neighbor upsampling을 사용 하였다.
3) Repeated multi-scale fusion.
-
위의 방식(Parallel multi-resolution subnetworks)으로 인해 병렬적으로 각 subnetwork들이 정보를 받을 수 있다.
-
r: resolution
-
s: stage
-
b: block
-
* exchange blocks
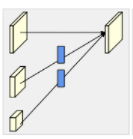
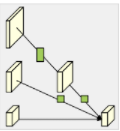
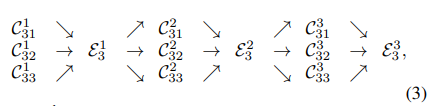
-
설명의 편의를 위해서 에서 s,b를 제거하고 r만 남겨놓아보자
-
input response maps: {}
-
output response maps: {} resolutions
and widths are the same to the input. -
Each output is an aggregation of the input maps
-
extra output map(마지막으로 다 계산된 값에 한번 더 넣어준다.)
- down sampling: 3×3 convolution with the stride 2
- upsampling: nearest neighbor sampling following a 1 × 1 convolution for aligning the number of channels.
4) Heatmap estimation.
-
heatmap regress를 위해 high-resolution representations output을 사용하였다.
-
loss function: mean squared error (heatmaps을 예측하기위해)
-
heatmap은 표준편차가 1pixel인 2d 가우시안분포에 의해 생성 되었다.
5) Network 인스턴트화
-
ResNet의 설계 규칙에 따라 각 단계에 깊이를 분배하고 각 해상도에 채널 수를 분배하여 키포인트 히트 맵 추정을 위해 네트워크를 인스턴스화 한다.
-
HRNet, contains four stages with four parallel subnetworks, whose resolution is gradually decreased to a half, and accordingly, the width (the number of channels) is increased to double.

-
first stage는 4개의 residual unit을 포함하고 있다. 이는 bottleneck 구조 64채널의 ResNet-50와 같다. 또한 3x3 conv를 해상도를 줄이기위해 사용한다.
-
본논문의 HRNet은 The 2nd, 3rd, 4th stages는 각각 1, 4, 3 exchange blocks을 포함한다.
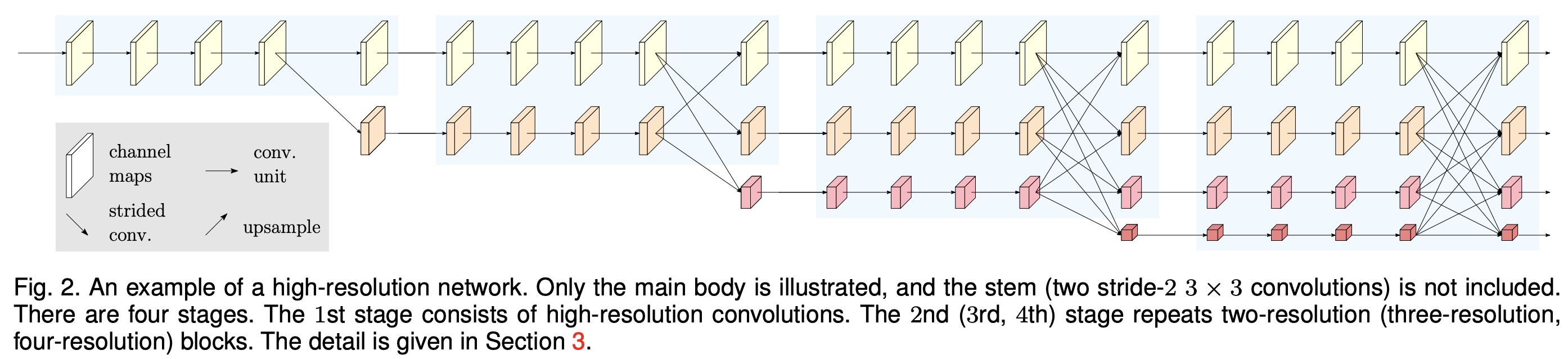
- 본연구에서는 small net(HRNent-W32)과 big net(HRNet-W48)을 사용했으며 WN은 the widths (C) of the high-resolution subnetworks in last three stages을 뜻한다.
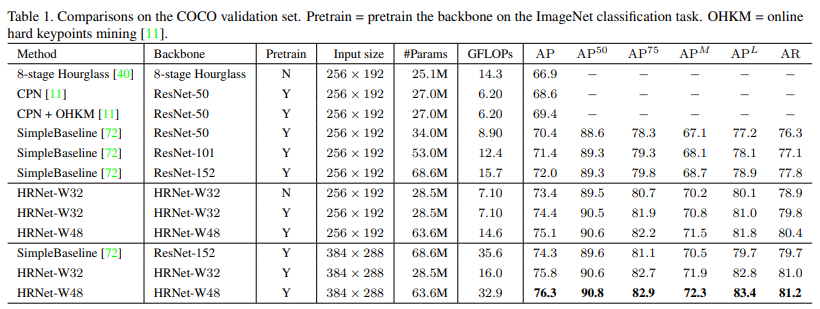
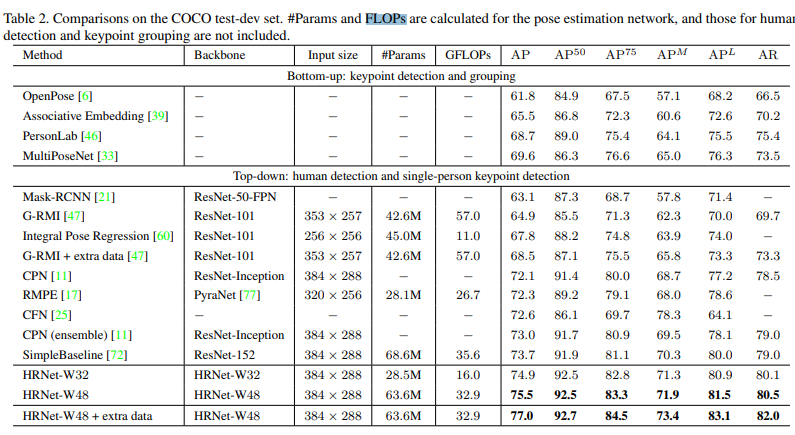
4. Experiments
1) Dataset
-
The COCO dataset contains over 200, 000 images and 250, 000 person instances labeled with 17 key points.
-
We train our model on COCO train2017 dataset, including 57K images and 150K person instances.
-
We evaluate our approach on the val2017 set and test-dev2017 set, containing 5000 images and 20K images, respectively.
2) Evaluation metric
-
The standard evaluation metric is
based on Object Keypoint Similarity (OKS) -
-
is the Euclidean distance between the detected keypoint and the corresponding ground truth
-
is the visibility flag of the ground truth
-
s is the object scale
-
: 하락을 제어하는 per-keypoint 상수
- (AP at OKS = 0.50)
- (AP at OKS = 0.75)
- (the mean of AP scores at 10 positions, OKS = 0.50, 0.55, . . . , 0.90, 0.95)
- (for medium objects)
- (for large objects)
- (OKS = 0.50, 0.55, . . . , 0.90, 0.955)
4) Training
- height: width = 4 : 3 비율로 image를 맞췄다.
- 256 × 192 or 384 × 288 size
- The data augmentation
- random rotation ()
- andom scale (0.65, 1.35)
- flipping
- half-body data augmentation is also involved.
5) Testing
-
detect the person instance using a person detector, and then predict detection keypoints.
-
We use the same person detectors provided by SimpleBaseline
Reference
- 논문
- Simple Baselines for Human Pose Estimation
and Tracking- Nearest Neighbor upsampling
- Bottle Neck
- HRNet

깔끔한 정리 감사합니다~