필자는 프로젝트 시 파이썬 버전 3.8과 amazon linux 2를 사용했습니다.
하지만 해당 파이썬 버전이 2024년 10월에 end of life가 됨에 따라 3.11버전과 함께 Elastic Beanstalk(이하 EB)의 플랫폼을 Amazon Linux 2023으로 미리 변경하게 되었습니다.
이 글을 쓰고 있는 현재, 파이썬 3.11은 아직 bug fix 단계이긴 하지만 EB의 플랫폼으로 지원한다는 것은 어느정도 stable한 상태에 접어들었다고 판단했기 때문입니다.
하지만 EB의 플랫폼을 변경했을 뿐인데, EB의 상태와 함께 제 기분이 severe해졌습니다...
Amazon Linux 2023이 나온 지 얼마 되지 않아 관련한 문서를 찾기가 꽤 어려웠고, 한글 문서는 더더욱 없었기에 해결법을 공유하고자 합니다.
feat. 내 코드 상태...
상태가 severe인 이유
AWS EB 콘솔에서 환경의 상태를 '원인 보기'로 본다면 대부분 health check 관련하여 이슈가 있을 겁니다.
Environment health has transitioned from Info to Severe. ELB processes are not healthy on all instances. ELB health is failing or not available for all instances.
솔루션을 알려드리기 전에 Health Check가 뭔지 알아야겠죠?
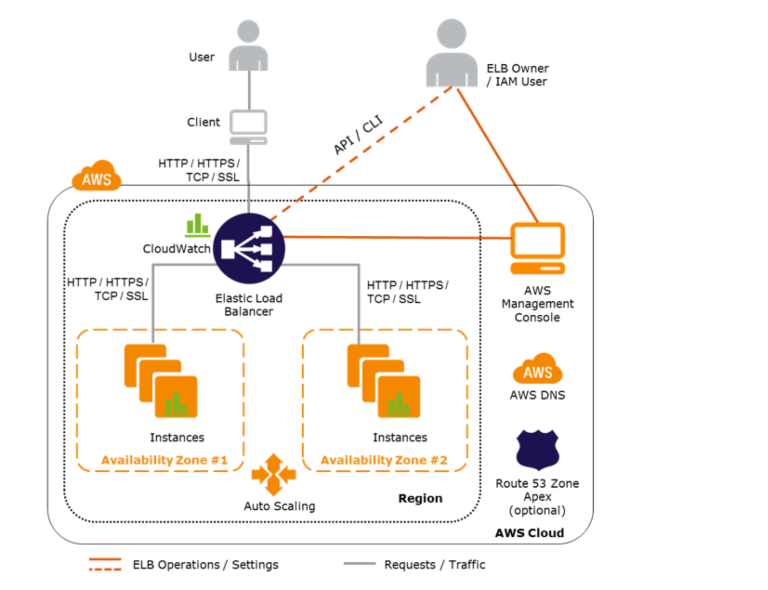
복잡해 보이지만 결국 중요한 건 Elastic Load Balancer(이하 ELB)입니다. ELB는 대상 그룹(target group)으로 지정된 인스턴스들에게 지속적으로 접근하여 인스턴스들의 상태를 확인하고, 상태가 정상이면 ELB로 접근한 트래픽들을 대상 그룹에 있는 인스턴스들에게 골고루 분산하여 Load를 Balancing합니다. 상태를 확인할 땐 상태확인할 대상의 relative url와 해당 경로로 접근했을 때, 정상일 경우 나와야 하는 HTTP status code를 명시적으로 설정해야 합니다.(기본값은 200)
이때, ELB와 EC2는 같은 VPC 내에 위치하기에 private ip로 통신하는데, health check 할 때 HTTP 프로토콜을 사용하고, 헤더에 해당 인스턴스의 private ip가 host이름으로 지정됩니다. 하지만 Django 어플리케이션은 settings.py에 있는 ALLOWED_HOSTS로 통신할 대상을 지정해줘야 하는데, Auto Scaling 되는 인스턴스들이라 그 private ip가 계속 동적으로 변경되기에 코드 레벨에서 정적으로 추가하는 건 사실상 불가능합니다.
솔루션
그래서 Amazon Linux 2를 사용할 당시엔 settings.py에 다음의 코드로 Auto Scaling에 대비했습니다.
if not DEBUG:
def is_ec2_linux():
if os.path.isfile("/sys/hypervisor/uuid"):
with open("/sys/hypervisor/uuid") as f:
uuid = f.read()
return uuid.startswith("ec2")
return False
def get_linux_ec2_private_ip():
"""Get the private IP Address of the machine if running on an EC2 linux server"""
from urllib.request import urlopen
if not is_ec2_linux():
return None
try:
response = urlopen("http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/local-ipv4")
ec2_ip = response.read().decode("utf-8")
if response:
response.close()
return ec2_ip
except Exception as e:
print(e)
return None
private_ip = get_linux_ec2_private_ip()
if private_ip:
ALLOWED_HOSTS.append(private_ip)하지만 Amazon Linux 2023으로 변경한 뒤론 /sys/hypervisor에는 아무것도 존재하지 않아 Django 어플리케이션이 EC2 시스템에서 동작하는 것인지 알기 위한 is_ec2_linux가 동작하지 않아 private ip를 얻을 수 없었습니다 ㅠㅠ...
좌절하던 중 다른 방법으로 EC2 인스턴스임을 확인할 수 있는 파일을 발견했읍니다..!
그래서 후다닥 코드를 다시 짰습니다.
def is_ec2():
if os.path.isfile("/sys/devices/virtual/dmi/id/board_asset_tag"):
with open("/sys/devices/virtual/dmi/id/board_asset_tag") as f:
uuid = f.read()
return uuid.startswith("i-")
return False인스턴스에 ssh로 접속하여 해당 경로에 접근하여 파일을 확인해 보시면 i-XXXXXX 어쩌고 저쩌고로 생긴 문자열이 있습니다. 'i-'로 시작할 경우 EC2 인스턴스입니다.
또한 기존에 urlopen으로 private ip를 얻으려고 했지만 기존의 방식으론 불가하여 검색해 보니 토큰이 필요했습니다.
def get_linux_ec2_private_ip():
import requests
token = requests.put(
"http://169.254.169.254/latest/api/token",
headers={"X-aws-ec2-metadata-token-ttl-seconds": "3600"},
)
if token.status_code != 200 or not is_ec2():
return None
private_ip = requests.get(
"http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/local-ipv4",
headers={"X-aws-ec2-metadata-token": token.text},
)
return private_ip.text if private_ip.status_code == 200 else None
private_ip = get_linux_ec2_private_ip()
if private_ip:
ALLOWED_HOSTS.append(private_ip)먼저 api로 토큰을 받아오고, 해당 토큰으로 private ip를 요청해야 정상적으로 값을 받아올 수 있습니다.
해당 ip를 ALLOWED_HOSTS에 추가해 주시면 여러분 혹은 기본값으로 지정된 경로의 HTTP status code에 따라 Health check가 의도한 대로 아주 잘 작동할 겁니다. ㅎㅎㅎㅎ
마치며
본 포스트는 Amazon Linux 2023을 위한 솔루션으로 다른 OS에선 정상적으로 동작하지 않을 수 있습니다! 읽어주셔서 감사합니다:)
출처
http://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/identify_ec2_instances.html
https://medium.com/@sumitkumar.it81/get-instance-metadata-in-amazon-linux-2023-al2023-e4bf0611d0ad
