참고
https://gmlwjd9405.github.io/2018/05/10/data-structure-heap.html
https://devmjun.github.io/archive/Heap
https://github.com/raywenderlich/swift-algorithm-club/tree/master/Heap
https://babbab2.tistory.com/109
Heap
힙의 정의 및 특징
- Heap이란
완전 이진 트리의 일종이다. - 우선 순위 큐를 만들 때 사용하는 자료구조이다.
- Heap Sort에서도 사용된다.
- 여러 개의 값들 중 최댓값 혹은 최솟값을 빠르게 찾아내도록 만들어졌다.
- 힙은 반정렬 상태를 유지한다.
- MaxHeap의 경우 큰 값이 상위 레벨에 있고, 작은 값이 하위 레벨에 있음
- 부모 노드의 키 값이 자식 노드의 키 값보다 항상 큰(혹은 작은) 상태
- 힙 트리는 중복값을 허용한다.(이진 탐색 트리는 중복 값을 허용하지 않음)
인덱스
parent(i) = floor((i - 1)/2)
left(i) = 2i + 1
right(i) = 2i + 2
힙의 종류
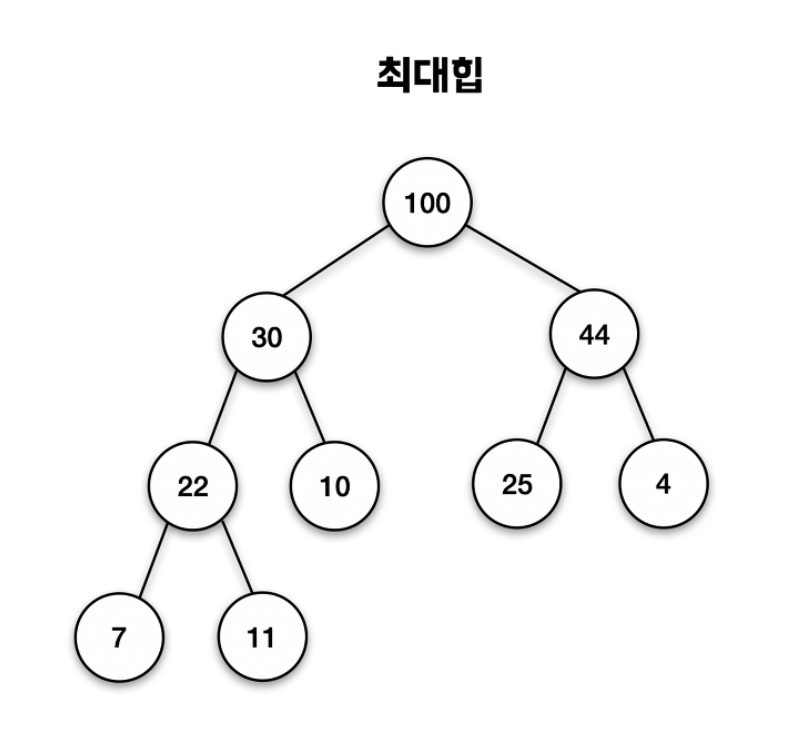
최대 힙(Max Heap)
자식의 노드 값이 부모의 노드 값보다 작거나 같은 힙
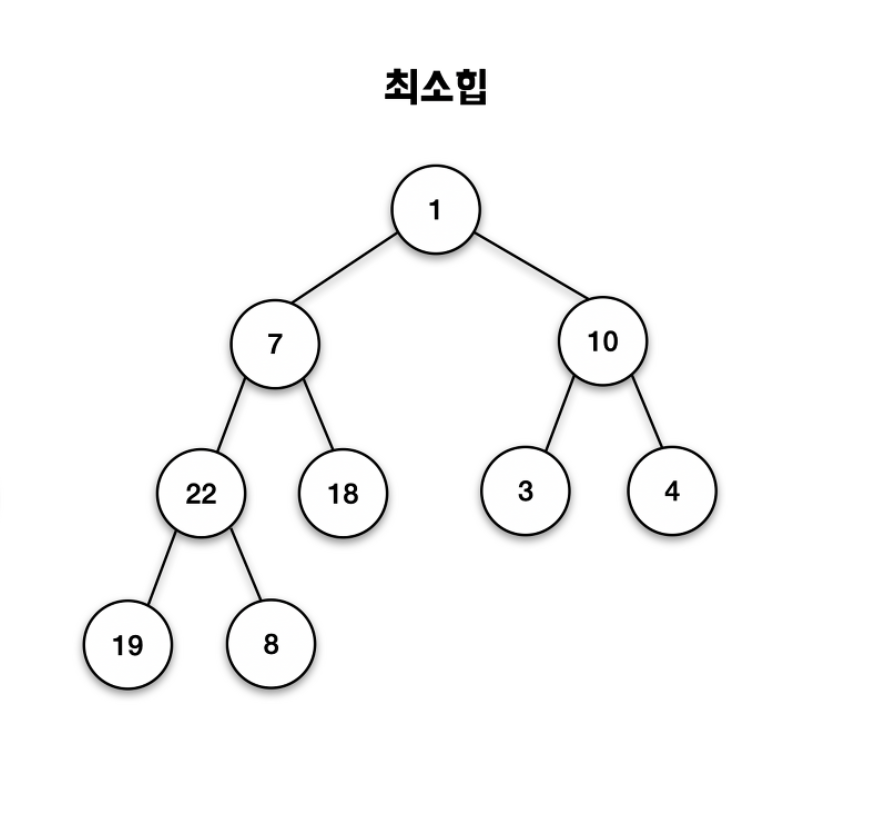
최소 힙(Min Heap)
자식의 노드 값이 부모의 노드 값보다 크거나 같은 힙
힙의 구현
import Foundation
// T는 비교 가능해야 하기 때문에 Comparable을 준수해야함
struct Heap<T: Comparable> {
// 실제 힙을 저장하는 장소
var nodes: [T] = []
private let sort: (T, T) -> Bool
init(sort: @escaping (T, T) -> Bool) {
self.sort = sort
}
// MARK: Insert, Delete
// struct이기 때문에 data를 insert하면 현재 값타입을
// 새로운 값타입으로 다시 그리기 때문에 mutating 키워드를 써야한다.
mutating func shiftUp(child: Int) {
var child = child
var parent = parentIndex(of: child)
// 노드의 제일 위까지 올라가거나, 부모의 노드 값과 비교했을 때 자기 자리일 때
while child > 0 && sort(nodes[child], nodes[parent]) {
nodes.swapAt(child, parent)
child = parent
parent = parentIndex(of: child)
}
}
mutating func shiftDown(parent: Int) {
var parent = parent
while true {
let left = leftChildIndex(of: parent)
let right = rightChildIndex(of: parent)
var candidate = parent
if left < nodes.count && sort(nodes[left], nodes[candidate]) {
candidate = left
}
if right < nodes.count && sort(nodes[right], nodes[candidate]) {
candidate = right
}
if candidate == parent {
return
}
nodes.swapAt(parent, candidate)
parent = candidate
}
}
mutating func insert(_ data: T) {
nodes.append(data)
let lastIndex = nodes.count - 1
shiftUp(child: lastIndex)
}
mutating func remove() -> T? {
guard !nodes.isEmpty else { return nil }
nodes.swapAt(0, nodes.count - 1)
defer { shiftDown(parent: 0) }
return nodes.removeLast()
}
mutating func remove(at index: Int) -> T? {
guard index < nodes.count else { return nil }
if index == nodes.count - 1 {
return nodes.removeLast()
} else {
nodes.swapAt(index, nodes.count - 1)
defer {
shiftUp(child: index)
shiftDown(parent: index)
}
return nodes.removeLast()
}
}
public func peek() -> T? {
return nodes.first
}
// MARK: Private Methods
private func parentIndex(of child: Int) -> Int {
return (child - 1) / 2
}
private func leftChildIndex(of parent: Int) -> Int {
return (parent * 2) + 1
}
private func rightChildIndex(of parent: Int) -> Int {
return parent * 2
}
}
var heap = Heap<Int>(sort: >)
heap.insert(10)
heap.insert(100)
heap.insert(50)
heap.insert(60)
heap.insert(110)
print(heap.nodes)
heap.remove()
print(heap.nodes)
// [110, 100, 50, 10, 60]
// [100, 60, 50, 10]
우선순위 큐
- 자료에 우선도를 가지고, 우선순위가 높은 자료가 먼저 나간다.
- MaxPriority: 가장 큰 요소가 맨 앞에 있음
- MinPriority: 가장 작은 요소가 맨 앞에 있음
- 힙, 배열, 연결리스트로 구현이 가능하다.
- 힙으로 구현하는 것이 O(logn)의 시간 복잡도를 가지므로 가장 효율적이다.
우선순위 큐의 활용
다익스트라 알고리즘에서 우선 순위 큐를 활용하여 최소 비용을 계산한다.- 우선순위 큐를 사용하여
Heap Sort를 구현 가능 Huffman Coding압축트리를 만든다.
위에서 구현한 Heap을 사용하여 Priority Queue를 만들 수 있다.
public struct PriorityQueue<T> {
fileprivate var heap: Heap<T>
/*
To create a max-priority queue, supply a > sort function. For a min-priority
queue, use <.
*/
public init(sort: @escaping (T, T) -> Bool) {
heap = Heap(sort: sort)
}
public var isEmpty: Bool {
return heap.isEmpty
}
public var count: Int {
return heap.count
}
public func peek() -> T? {
return heap.peek()
}
public mutating func enqueue(_ element: T) {
heap.insert(element)
}
public mutating func dequeue() -> T? {
return heap.remove()
}
}
extension PriorityQueue where T: Equatable {
public func index(of element: T) -> Int? {
return heap.index(of: element)
}
}
