설계
main
if __name__ == '__main__':
answer = 0
N = int(input())
graph = []
for _ in range(N):
graph.append(list(map(int,input().split())))
while check(graph):
visited = [[False]*N for _ in range(N)]
for i in range(N):
for j in range(N):
if graph[i][j] == 0 and not visited[i][j]:
graph,visited = bfs(graph,i,j,visited)
graph = color(graph)
answer += 1
print(answer)- 그래프가 전부 0이 될 때까지
- 전부 물든 단풍 나무(0)를 기준으로 그래프 탐색을 진행한다.
- 그래프에서 물들일 나무를 음수로 처리한다.
- 음수로 처리한 나무들을 0으로 바꾼다 (단풍을 물들인다.)
- 시간을 경과시킨다.
bfs
오류 BFS
def bfs(graph,sx,sy,visited):
q = deque([(sx,sy)])
dx = [1,-1,0,0]
dy = [0,0,1,-1]
visited[sx][sy] = True
while q:
x,y = q.popleft()
for i in range(4):
nx = x+dx[i]
ny = y+dy[i]
if 0<=nx<N and 0<=ny<N and not visited[nx][ny]:
if graph[nx][ny] == 0:
q.append((nx,ny))
visited[nx][ny] = True
else:
graph[nx][ny] -= 1
if graph[nx][ny] == 0:
graph[nx][ny] = -1
return graph,visited여기서 중요한 점은 그래프 탐색을 진행할 때 양수면(덜 물든 나무) 1씩 깎는데 0이면 -1로 변환시켜준다는 점이다.
왜 굳이 음수로 처리하는가?
그냥 0이 되면 0으로 두면 될 것이지 왜 굳이 후처리를 해주는가에 대한 의문이 생길 수 있다.
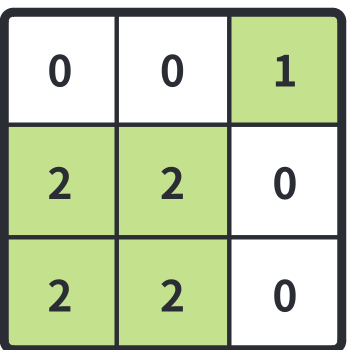
예제 #1을 보자.
0 묶음이 2세트 있으므로 (0,0)과 (1,2) 위치에서 BFS를 돌릴 것이다.
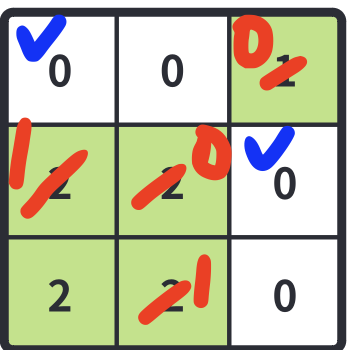
(1,1) 위치에서 0이 발생했다.
이 0 은 초기 (1,0)과 (2,1)에 영향을 미치면 안 된다.
왜냐하면, 현재 1사이클에서 (1,1)이 다 물들었으므로 이 단풍나무는 2사이클부터 다른 나무들을 물들일 수 있기 때문이다.
그런데 내가 기존에 작성했던 코드는 나무들을 표시해놨다가 한번에 0으로 바꾸는 로직이 아닌 다이렉트로 그때그때 0으로 바꾸는 로직이므로 위와 같은 문제가 생기는 것이다.
cycle: 0 [[0, 0, 0], [1, 1, 0], [2, 2, 0]]
cycle: 0 [[0, 0, 0], [1, 0, 0], [2, 1, 0]]
cycle: 0 [[0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0], [2, 0, 0]]
cycle: 0 [[0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0], [1, 0, 0]]
cycle: 1 [[0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0]]
콘솔 출력을 확인해보면
한 사이클에 위 과정이 다 돌았음을 알 수 있다.
정답 BFS
def bfs(graph,sx,sy,visited):
q = deque([(sx,sy)])
dx = [1,-1,0,0]
dy = [0,0,1,-1]
visited[sx][sy] = True
while q:
x,y = q.popleft()
for i in range(4):
nx = x+dx[i]
ny = y+dy[i]
if 0<=nx<N and 0<=ny<N and not visited[nx][ny]:
if graph[nx][ny] == 0:
q.append((nx,ny))
visited[nx][ny] = True
else:
graph[nx][ny] -= 1
if graph[nx][ny] == 0:
graph[nx][ny] = -1
return graph,visitedcheck
def check(graph):
for i in range(N):
for j in range(N):
if graph[i][j]:
return True
return False그래프의 양수인 원소가 1개라도 존재하는지 확인해주는 함수
양수가 1개라도 있으면 True
전부 0이면 False를 return한다.
color
def color(graph):
for i in range(N):
for j in range(N):
if graph[i][j] < 0:
graph[i][j] = 0
return graph물들이기로 체크한 나무들을 단풍나무로 바꿔주는 함수
다시 말해, 음수인 노드들을 전부 0으로 바꿔주는 함수다.
전체 코드
from collections import deque
def bfs(graph,sx,sy,visited):
q = deque([(sx,sy)])
dx = [1,-1,0,0]
dy = [0,0,1,-1]
visited[sx][sy] = True
while q:
x,y = q.popleft()
for i in range(4):
nx = x+dx[i]
ny = y+dy[i]
if 0<=nx<N and 0<=ny<N and not visited[nx][ny]:
if graph[nx][ny] == 0:
q.append((nx,ny))
visited[nx][ny] = True
else:
graph[nx][ny] -= 1
if graph[nx][ny] == 0:
graph[nx][ny] = -1
return graph,visited
def check(graph):
for i in range(N):
for j in range(N):
if graph[i][j]:
return True
return False
def color(graph):
for i in range(N):
for j in range(N):
if graph[i][j] < 0:
graph[i][j] = 0
return graph
if __name__ == '__main__':
answer = 0
N = int(input())
graph = []
for _ in range(N):
graph.append(list(map(int,input().split())))
while check(graph):
visited = [[False]*N for _ in range(N)]
for i in range(N):
for j in range(N):
if graph[i][j] == 0 and not visited[i][j]:
graph,visited = bfs(graph,i,j,visited)
graph = color(graph)
answer += 1
print(answer)