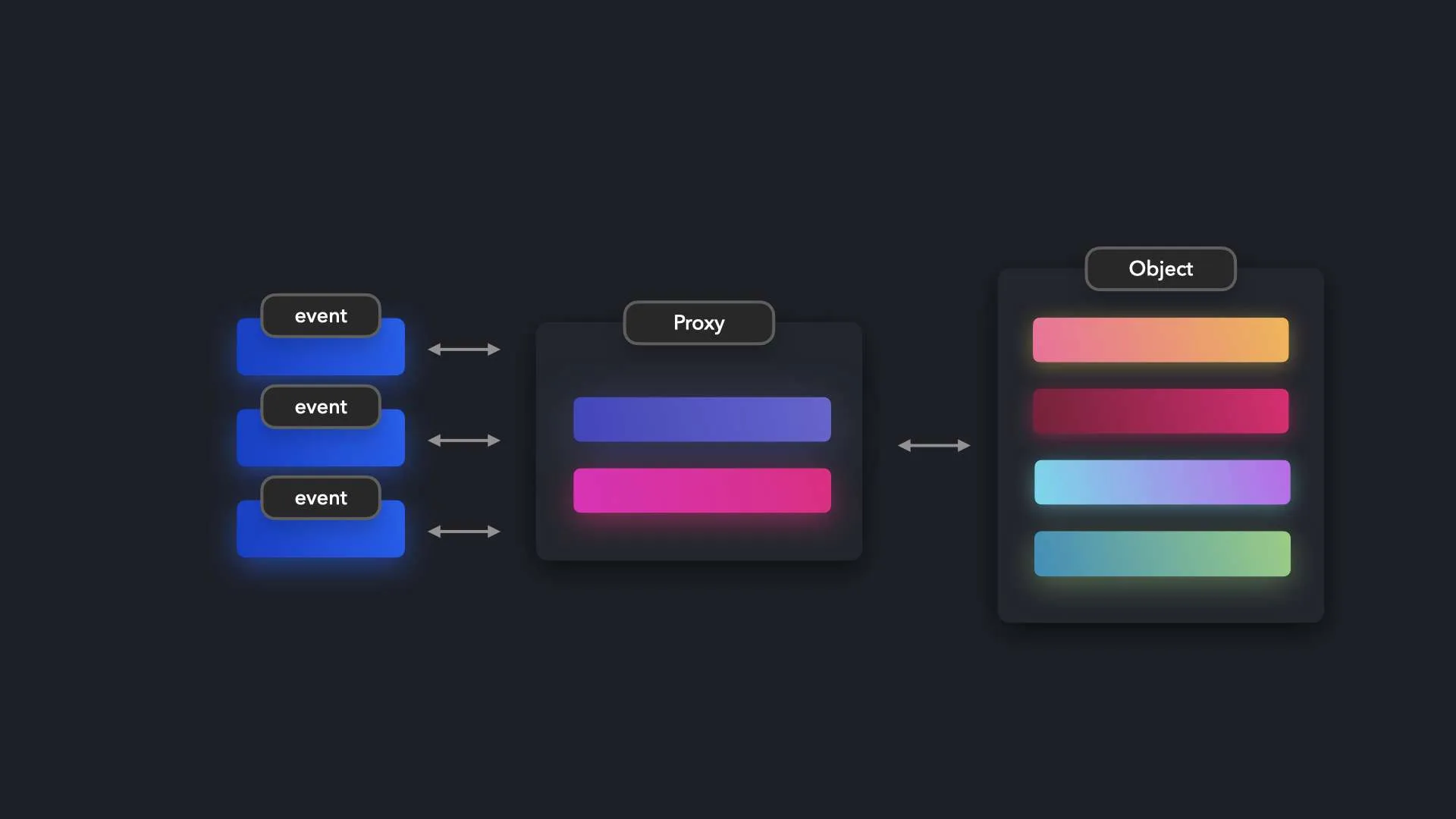
1. 패턴 정의: 정의와 핵심 요약
- 프록시 패턴은 실제 객체에 대한 접근을 제어하기 위해 그 앞에 대리 객체(프록시)를 두는 구조이다.
- 실제 객체를 직접 다루지 않고, 프록시 객체를 통해 제어, 로깅, 인증, 지연 로딩 등의 기능을 추가할 수 있다.
2. 사용 목적: 이 패턴이 필요한 이유
- 리소스가 무겁거나 민감한 객체의 직접 접근을 차단하고, 대신 대리 객체를 통해 접근을 제어할 수 있다. (예: 생성 비용이 큰 이미지, 보안이 필요한 데이터 등)
- 클라이언트는 실제 객체와 동일한 인터페이스를 사용하되, 접근 전후에 로깅, 캐싱, 인증 등의 부가기능을 투명하게 삽입할 수 있다.
- 실제 객체를 필요할 때까지 지연 생성(Lazy Load) 하거나, 객체 생성을 아예 생략하고도 동일한 동작을 시뮬레이션할 수 있다.
3. 패턴 설명: 동작 방식과 구성 요소
프록시 패턴은 실제 객체(RealService)에 대한 접근을 제어하거나 기능을 확장하기 위해, 같은 인터페이스를 구현한 대리 객체(Proxy) 를 중간에 두는 구조이다. 클라이언트는 실제 객체가 아니라 프록시를 통해 접근하지만, 두 객체 모두 동일한 인터페이스를 구현하기 때문에 사용 방식은 동일하다.
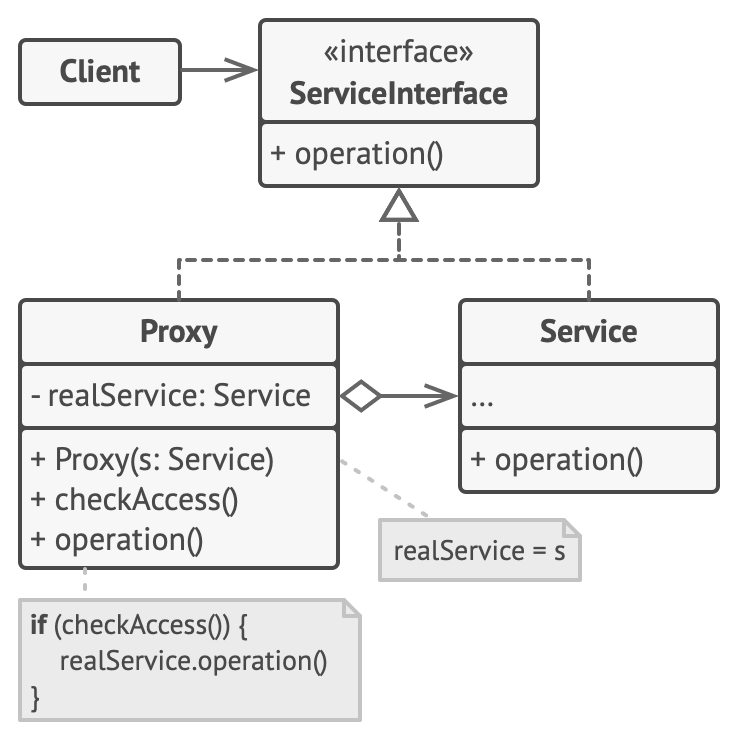
구성 요소
-
ServiceInterfaceRealService와Proxy가 모두 구현하는 공통 인터페이스- 클라이언트는 이 인터페이스만을 기준으로 서비스를 사용하므로, 실제 구현체가 어떤 것이든 관계없다.
-
RealService- 실질적인 비즈니스 로직을 수행하는 실제 서비스 객체
- 무겁거나, 민감하거나, 통제가 필요한 기능을 포함하고 있을 수 있다.
-
ProxyServiceInterface를 구현하고 내부에RealService에 대한 참조를 가진다.- 자체적으로 로깅, 인증, 접근 제한, 캐싱, 지연 초기화(lazy load) 등을 수행한 뒤, 필요한 경우
RealService에 작업을 위임한다.
-
ClientServiceInterface만 알고 있으며,Proxy와RealService를 구분하지 않고 사용한다.- 프록시를 통해 실제 객체와 동일한 방식으로 메서드를 호출한다.
동작 방식
-
클라이언트는
ServiceInterface타입을 통해 서비스에 접근하려고 한다. -
이때 프록시 객체가
ServiceInterface를 구현하고 있으므로, 클라이언트는 프록시를 서비스처럼 사용한다. -
프록시는 내부에서 요청을 가로채어, 접근 제어나 로깅, 캐싱 등의 부가 작업을 수행한다.
-
이후 실제 처리가 필요하면, 프록시가 내부에 가진
RealService객체를 호출하여 요청을 위임한다. -
클라이언트는 실제 서비스인지 프록시인지 알 필요 없이 동일한 방식으로 인터페이스를 통해 동작을 수행한다.
4. 코드 및 활용 예시: 기본 구현과 프론트엔드 적용
기본 구현 (Proxy 객체 활용 X)
// 1. ServiceInterface
interface Service {
request(): void;
}
// 2. RealService
class RealService implements Service {
request() {
console.log("RealService: 요청 처리");
}
}
// 3. Proxy
class LoggingProxy implements Service {
private realService: RealService;
constructor(realService: RealService) {
this.realService = realService;
}
request() {
console.log("Proxy: 요청 전 로깅");
this.realService.request();
console.log("Proxy: 요청 후 로깅");
}
}
// 4. Client
const service: Service = new LoggingProxy(new RealService());
service.request();사용 예시: Fetch 로직 Logging (Proxy 객체 활용)
// 원래의 fetch API를 감싼 프록시 함수
function createFetchProxy(originalFetch: typeof fetch): typeof fetch {
return new Proxy(originalFetch, {
apply(target, thisArg, args) {
const [url, options] = args;
console.log(`[API 요청] ${options?.method || "GET"} ${url}`);
const start = Date.now();
return Reflect.apply(target, thisArg, args).then((res) => {
const duration = Date.now() - start;
console.log(`[응답 시간] ${url} - ${duration}ms`);
return res;
});
},
});
}
// 프록시 적용
const fetchWithLog = createFetchProxy(fetch);
// 사용
fetchWithLog("/api/user", { method: "GET" });5. 정리와 확장: 학습 포인트와 추가 학습거리
학습 포인트
- 프록시 패턴은 실제 객체에 대한 접근을 제어하거나 감싸는 중간 객체를 두는 구조적 설계 패턴이다.
- 접근 제어, 부가기능 삽입, 지연 로딩, 원격 통신 등 다양한 목적으로 활용되며, 실제 객체와 동일한 인터페이스를 유지하는 것이 핵심이다.
- JavaScript에서는 Proxy 객체를 사용해 객체의 속성 접근/메서드 호출을 동적으로 가로채고 조작할 수 있으며, Reflect 객체와 함께 쓰면 더 안정적이고 일관된 구현이 가능하다.
- 프론트엔드에서는 API 래퍼, 설정 객체, 컴포넌트 접근 제어, 글로벌 로깅 등 다양한 상황에서 유용하게 응용할 수 있다.
추가학습: Javascript의 Proxy, Reflect 객체
Proxy
-
Proxy는 객체의 속성 접근, 설정, 삭제, 함수 호출 등 모든 동작을 가로채고 제어할 수 있는JavaScript의 내장 객체이다. -
핸들러 객체를 통해
get,set,apply,has,construct등 다양한 트랩(trap)을 정의하여 대상 객체의 동작을 조작할 수 있다.
const personProxy = new Proxy(person, {
get: (obj, prop) => {
if (!obj[prop]) {
console.log(
`Hmm.. this property doesn't seem to exist on the target object`
);
} else {
console.log(`The value of ${prop} is ${obj[prop]}`);
}
},
set: (obj, prop, value) => {
if (prop === "age" && typeof value !== "number") {
console.log(`Sorry, you can only pass numeric values for age.`);
} else if (prop === "name" && value.length < 2) {
console.log(`You need to provide a valid name.`);
} else {
console.log(`Changed ${prop} from ${obj[prop]} to ${value}.`);
obj[prop] = value;
}
},
});Reflect
-
Reflect는Proxy핸들러 내부에서 기존 객체의 기본 동작을 호출할 때 사용하는 표준 API 모음이다. -
Reflect.get,Reflect.set,Reflect.apply등은 해당 동작을 원래 방식대로 수행하며, 코드의 일관성과 가독성을 높이는 데 유용하다.
const personProxy = new Proxy(person, {
get: (obj, prop) => {
console.log(`The value of ${prop} is ${Reflect.get(obj, prop)}`);
},
set: (obj, prop, value) => {
console.log(`Changed ${prop} from ${obj[prop]} to ${value}`);
Reflect.set(obj, prop, value);
},
});-
Reflect는Proxy가 기본 동작을 "직접 구현"하는 대신, 안정적으로 "위임"할 수 있게 해준다. -
예를 들어
target[prop]처럼 직접 접근하면 예상치 못한 오류나 사이드 이펙트가 생길 수 있는데,Reflect.get(target, prop, receiver)는 이 과정을 일관되고 안전한 방식으로 수행해준다.
