기존 CPU 기반 LZW 압축은 스트립을 순차적으로 처리하므로 이미지가 클수록 시간이 급격히 증가합니다.
그래서 GPU 커널에 여러 스트립을 동시에 올려 병렬 압축을 수행하고, rowsPerStrip 파라미터를 최적화해 CPU 대비 75 %(7.1 s → 1.78 s) 빠른 결과를 얻었습니다.
1️⃣ 왜 GPU 가속이 필요한가?

| 구분 | CPU (RAM) | GPU (VRAM) |
|---|---|---|
| 메모리 대역폭 | ~50 GB/s | ~500 GB/s (10× 이상) |
| 연산 병렬성 | 코어 수에 제한 | 수천 개 CUDA 코어 |
| 데이터 이동 | CPU ↔ 메인 메모리 (1 회) | RAM → VRAM (2 회) → GPU 연산 |
| 병목 | 스트립 순차 처리 → 시간 선형 증가 | 다중 스트립 병렬 처리 → 시간 거의 상수 |
VRAM 은 GPU에 직접 장착된 메모리이며, RAM 은 CPU가 사용하는 메인 메모리입니다. 대역폭 차이 때문에 한 번에 더 많은 데이터를 전송·처리할 수 있어 전체 압축 시간이 크게 단축됩니다.
2️⃣ 스트립(rowsPerStrip) 개념

-
Strip – TIFF 파일에서 행(row) 단위로 나눈 조각.

-
rowsPerStrip - 한 스트립에 포함되는 행 수.
| rowsPerStrip 크기 | 장점 | 단점 |
|---|---|---|
| 작음 (예: 8) | 압축 단위가 작아 메모리 사용량 감소 | 스트립 수 증가 → GPU 커널 호출 오버헤드 증가 |
| 큼 (예: 24) | 한 번에 많은 데이터를 GPU에 전달 → 전송·연산 효율 증가 | 메모리 사용량 증가 (한 번에 처리해야 할 데이터 양 증가) |




저희 프로젝트에서는 세메스 장비에 맞춰 rowsPerStrip = 24 로 고정하고, 전체 1000개의 스트립으로 나누어 최적의 대역폭·연산 효율을 달성했습니다.
3️⃣ GPU‑가속 nvTIFF 코드 흐름
아래는 핵심 구현의 주요 단계와 설명입니다.
// ---------------------------------------------------
// 1) CUDA 초기화 + 비동기 스트림 생성
// ---------------------------------------------------
int devCount = 0;
ck(cudaGetDeviceCount(&devCount), "cudaGetDeviceCount");
if (devCount <= 0) throw std::runtime_error("No CUDA device");
ck(cudaSetDevice(0), "cudaSetDevice(0)");
ck(cudaFree(0), "cuda warmup"); // 드라이버 초기화
ck(cudaStreamCreateWithFlags(&stream, cudaStreamNonBlocking), "cudaStreamCreate");
// ---------------------------------------------------
// 2) Host → Device (H2D) 전송 (pinned 메모리 + async)
// ---------------------------------------------------
ck(cudaMalloc(&d_img, expected), "cudaMalloc(d_img)");
if (!rgb.empty()) {
// 페이지‑잠금(pinned) 메모리 등록 → DMA 전송 가속
if (cudaHostRegister((void*)rgb.data(), rgb.size(),
cudaHostRegisterPortable) == cudaSuccess)
pinned = true;
}
ck(cudaMemcpyAsync(d_img, rgb.data(), expected,
cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, stream), "H2D async");
ck(cudaStreamSynchronize(stream), "sync after H2D");
if (pinned) { cudaHostUnregister((void*)rgb.data()); pinned = false; }
// ---------------------------------------------------
// 3) 성능 측정 시작 (CUDA 이벤트 + NVML 샘플러)
// ---------------------------------------------------
ck(cudaEventCreate(&evStart), "eventCreate start");
ck(cudaEventCreate(&evStop), "eventCreate stop");
ck(cudaEventRecord(evStart, stream), "eventRecord start");
sampler.start(0 /*deviceIndex*/, 100 /*ms*/); // 100 ms 간격 GPU 이용률 수집
// ---------------------------------------------------
// 4) rowsPerStrip 자동 결정 (24 행 고정)
// ---------------------------------------------------
unsigned int rowsPerStrip = opt.rowsPerStrip.has_value() && opt.rowsPerStrip.value() > 0
? static_cast<unsigned int>(opt.rowsPerStrip.value())
: pickRowsPerStrip(info.width, info.height);
rowsPerStrip = std::max(1u, std::min(rowsPerStrip, height));
LOGI("[nvTIFF] rowsPerStrip=" << rowsPerStrip);
// ---------------------------------------------------
// 5) 인코딩 루프 – 최대 4번 재시도 (rowsPerStrip 절반 감소)
// ---------------------------------------------------
const int kMaxAttempts = 4;
bool encoded = false;
std::string lastErr;
for (int attempt = 0; attempt < kMaxAttempts && !encoded; ++attempt) {
// ① 기존 객체 해제
if (params) { nvtiffEncodeParamsDestroy(params, stream); params = nullptr; }
if (encoder){ nvtiffEncoderDestroy(encoder, stream); encoder = nullptr; }
// ② Encoder / Params 생성
auto st = nvtiffEncoderCreate(&encoder, nullptr, nullptr, stream);
if (st != NVTIFF_STATUS_SUCCESS) { lastErr = "nvtiffEncoderCreate failed"; continue; }
st = nvtiffEncodeParamsCreate(¶ms);
if (st != NVTIFF_STATUS_SUCCESS) { lastErr = "nvtiffEncodeParamsCreate failed"; continue; }
// ③ 이미지 메타데이터 설정
nvtiffImageInfo_t img{};
img.image_width = width;
img.image_height = height;
img.samples_per_pixel = 3; // RGB24
img.bits_per_sample[0] = img.bits_per_sample[1] = img.bits_per_sample[2] = 8;
img.photometric_int = NVTIFF_PHOTOMETRIC_RGB;
img.compression = NVTIFF_COMPRESSION_LZW; // LZW 고정
if (nvtiffEncodeParamsSetImageInfo(params, &img) != NVTIFF_STATUS_SUCCESS) {
lastErr = "nvtiffEncodeParamsSetImageInfo failed"; continue;
}
// ④ 스트립 크기 지정
nvtiffImageGeometry_t geom{};
geom.strile_height = rowsPerStrip;
if (nvtiffEncodeParamsSetImageGeometry(params, &geom) != NVTIFF_STATUS_SUCCESS) {
lastErr = "nvtiffEncodeParamsSetImageGeometry failed"; continue;
}
// ⑤ 입력 이미지 포인터 (GPU 메모리) 지정
unsigned char* images_d[1] = { d_img };
if (nvtiffEncodeParamsSetInputs(params, images_d, 1) != NVTIFF_STATUS_SUCCESS) {
lastErr = "nvtiffEncodeParamsSetInputs failed"; continue;
}
// ⑥ 실제 압축 실행
if (nvtiffEncode(encoder, ¶ms, 1, stream) != NVTIFF_STATUS_SUCCESS) {
lastErr = "nvtiffEncode failed"; continue;
}
if (nvtiffEncodeFinalize(encoder, ¶ms, 1, stream) != NVTIFF_STATUS_SUCCESS) {
lastErr = "nvtiffEncodeFinalize failed"; continue;
}
ck(cudaStreamSynchronize(stream), "sync after finalize");
// ⑦ 파일 쓰기
if (nvtiffWriteTiffFile(encoder, ¶ms, 1,
outPath.c_str(), stream) != NVTIFF_STATUS_SUCCESS) {
lastErr = "nvtiffWriteTiffFile failed"; continue;
}
// 성공 → 루프 탈출
encoded = true;
break;
// 실패 시 rowsPerStrip 절반 감소 후 재시도
if (attempt < kMaxAttempts - 1) {
unsigned int next = std::max(1u, rowsPerStrip / 2);
LOGW("[nvTIFF] retry with smaller rowsPerStrip: " << rowsPerStrip
<< " -> " << next);
rowsPerStrip = next;
}
}
if (!encoded) throw std::runtime_error("nvTIFF encoding failed: " + lastErr);
// ---------------------------------------------------
// 6) 성능 측정 종료 & 결과 계산
// ---------------------------------------------------
ck(cudaEventRecord(evStop, stream), "eventRecord stop");
ck(cudaEventSynchronize(evStop), "eventSync stop");
double avgUtil = sampler.stopAndAverage(); // GPU 평균 이용률 (%)
float ms = 0.0f;
ck(cudaEventElapsedTime(&ms, evStart, evStop), "eventElapsed");
double encodeSec = static_cast<double>(ms) / 1000.0;
size_t inputBytes = static_cast<size_t>(info.width) *
static_cast<size_t>(info.height) * 3ull;
double mb = static_cast<double>(inputBytes) / (1024.0 * 1024.0);
double avgMBps = (encodeSec > 0.0) ? (mb / encodeSec) : 0.0;
// ---------------------------------------------------
// 7) 정리 & 결과 반환
// ---------------------------------------------------
cleanup(); // 모든 CUDA/NVML 리소스 해제
EncodeResult r{};
r.gpu.avgUtil = avgUtil;
r.speed.avgMBps = avgMBps;
r.speed.minMBps = avgMBps;
r.speed.maxMBps = avgMBps;
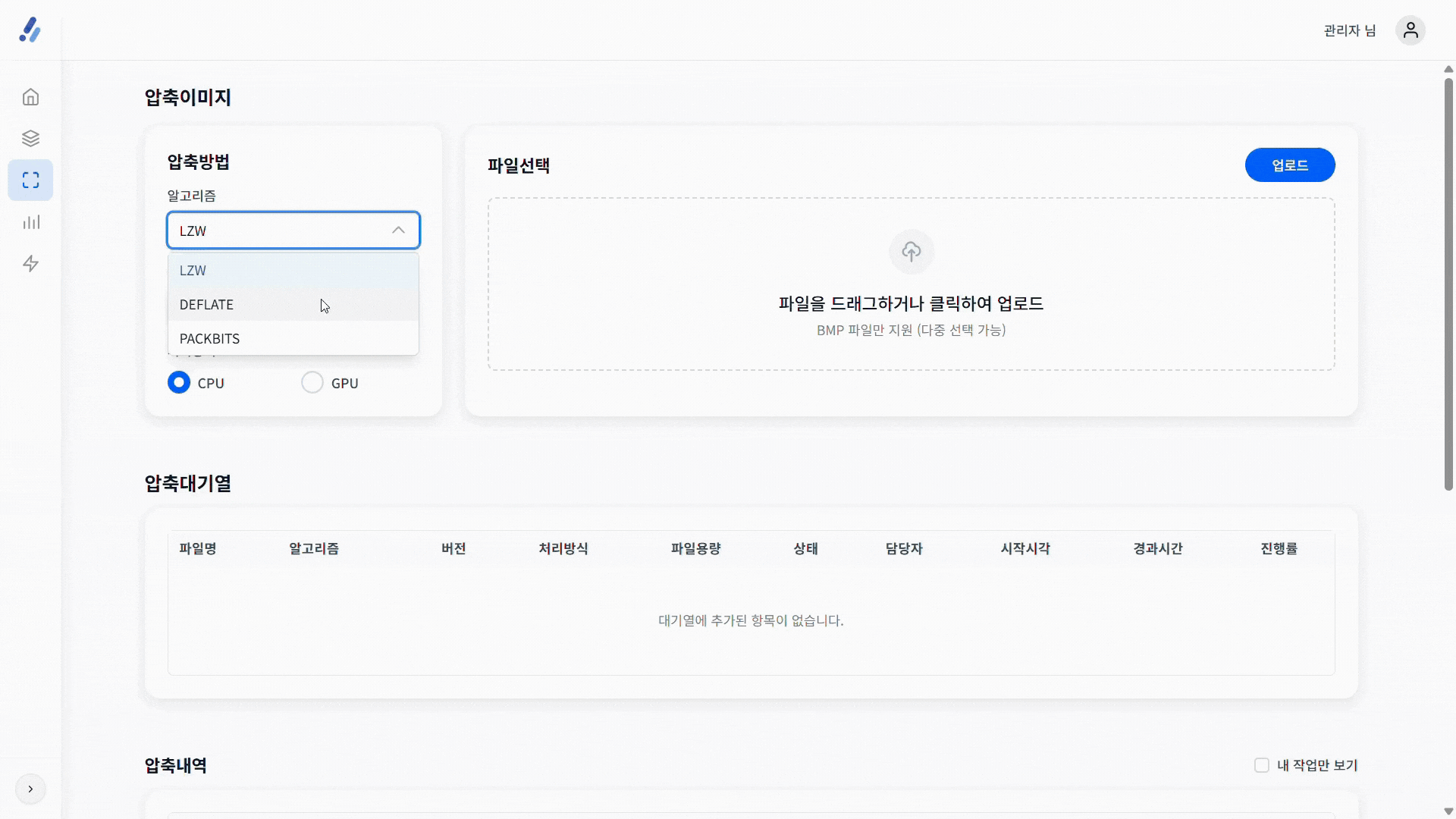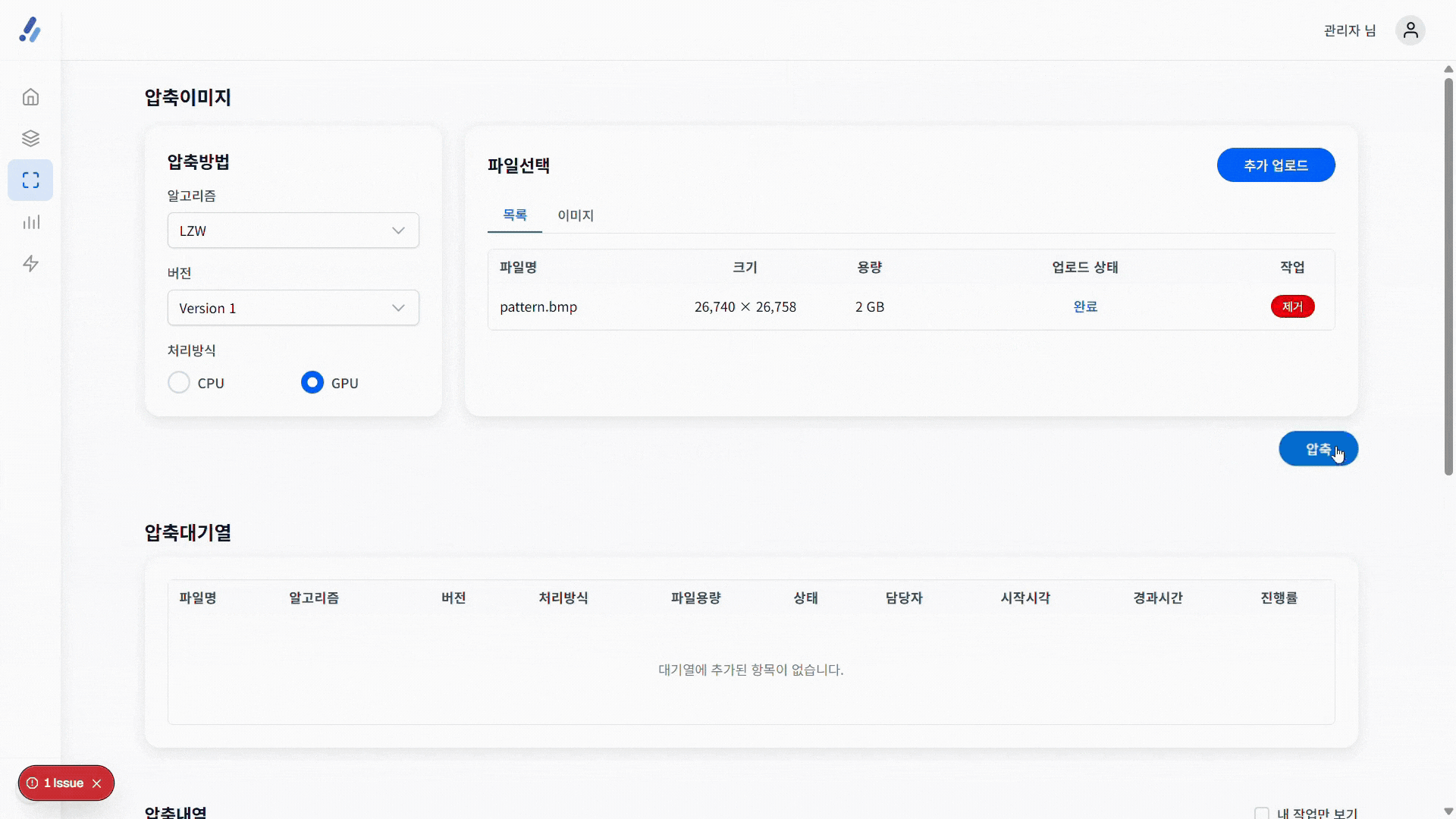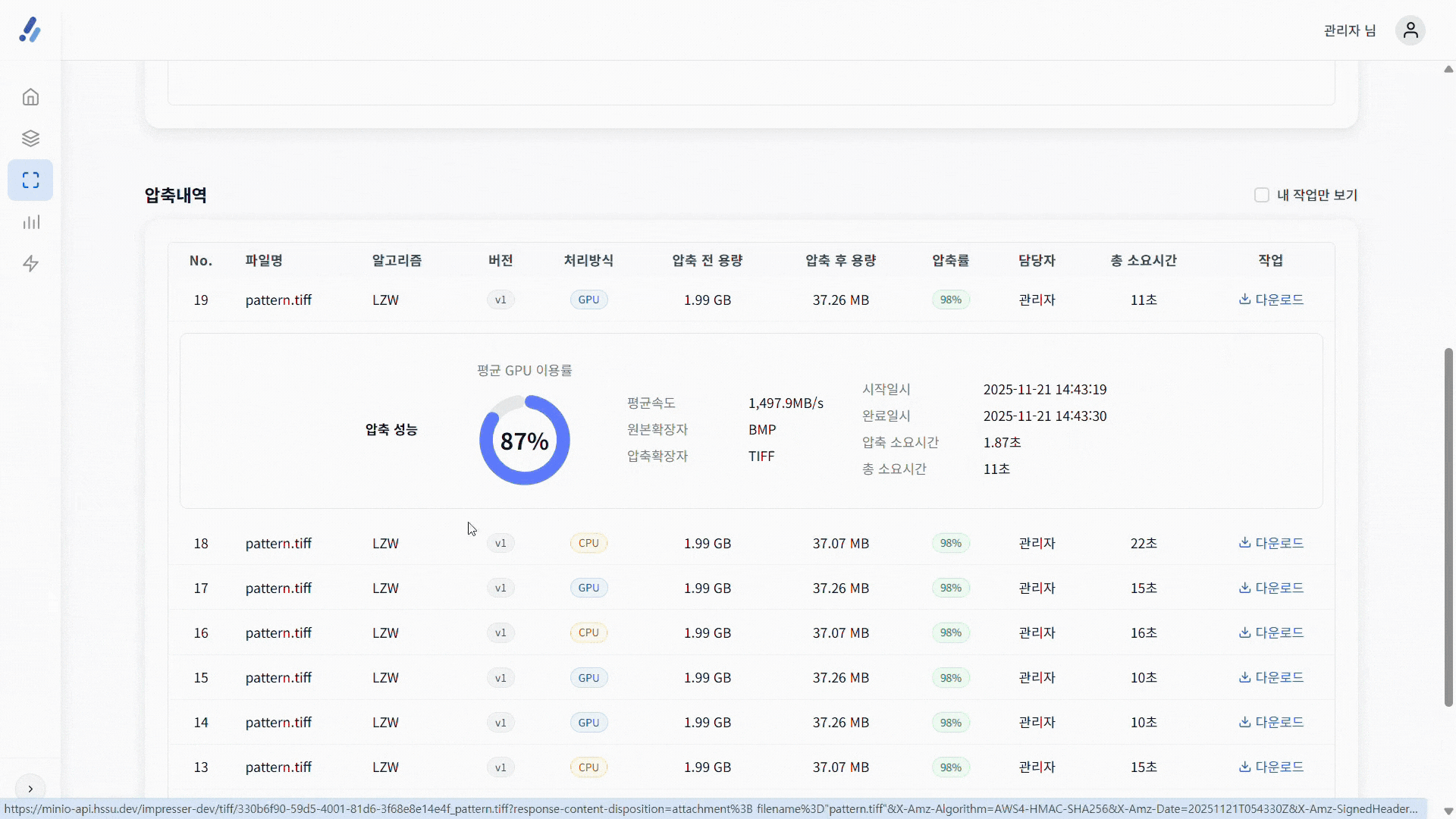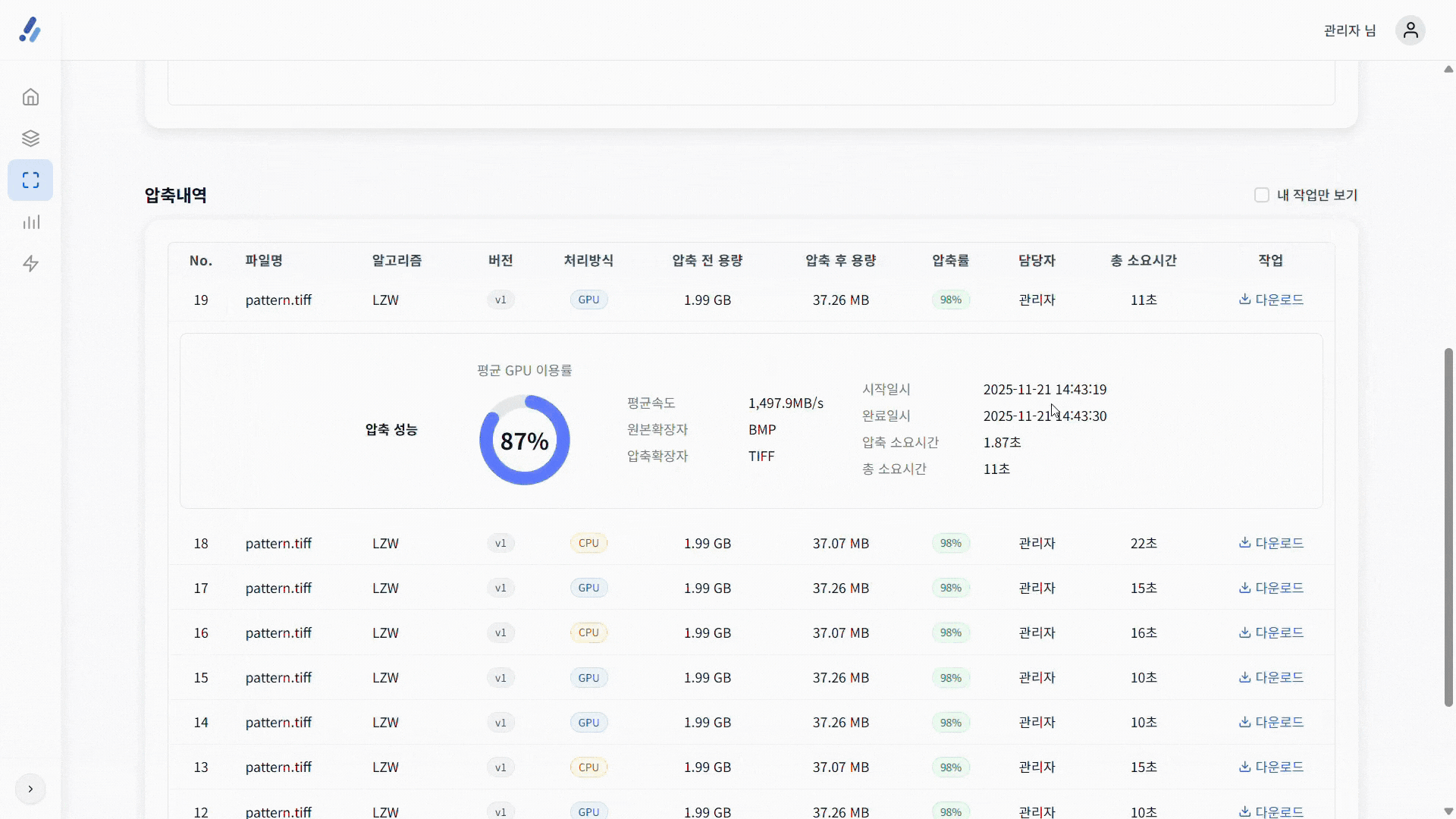
return r;4️⃣ 실험 결과 (세메스 장비 기준)
| 이미지 크기 | 압축 방식 | 압축 비율 | 실행 시간 | 속도 향상 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 GB (RGB24) | CPU-LZW (단일 스트립 순차) | 38 MB (≈ 1.9 %) | 7.1 s | – |
| 2 GB (RGB24) | GPU-nvTIFF (다중 스트립 병렬) | 38 MB (≈ 1.9 %) | 1.78 s | ≈ 75 % 감소 |
정리 – 동일 LZW 알고리즘을 GPU에서 실행했음에도 압축 비율은 동일하지만 처리 시간이 4배 이상 빨라졌습니다.
이는 스트립 병렬 처리와 VRAM 대역폭 덕분입니다.
5️⃣ 압축 화면
참고
https://developer.nvidia.com/nvtiFF#section-more-resources
https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-runtime-api/

