Intro
: 필자의 경우, 공부를 하면 할 수록, 기본기에 대한 중요성을 많이 느끼게 되었다. 선형대수학적인 부분과 이에 대한 구현의 필요성을 많이 느꼈다. 그래서 작은 것부터 시작해보려고 한다. (블로그에 수식을 적고 싶은데 귀찮기 때문에 일단 생략)
References
Code
오늘의 실습코드
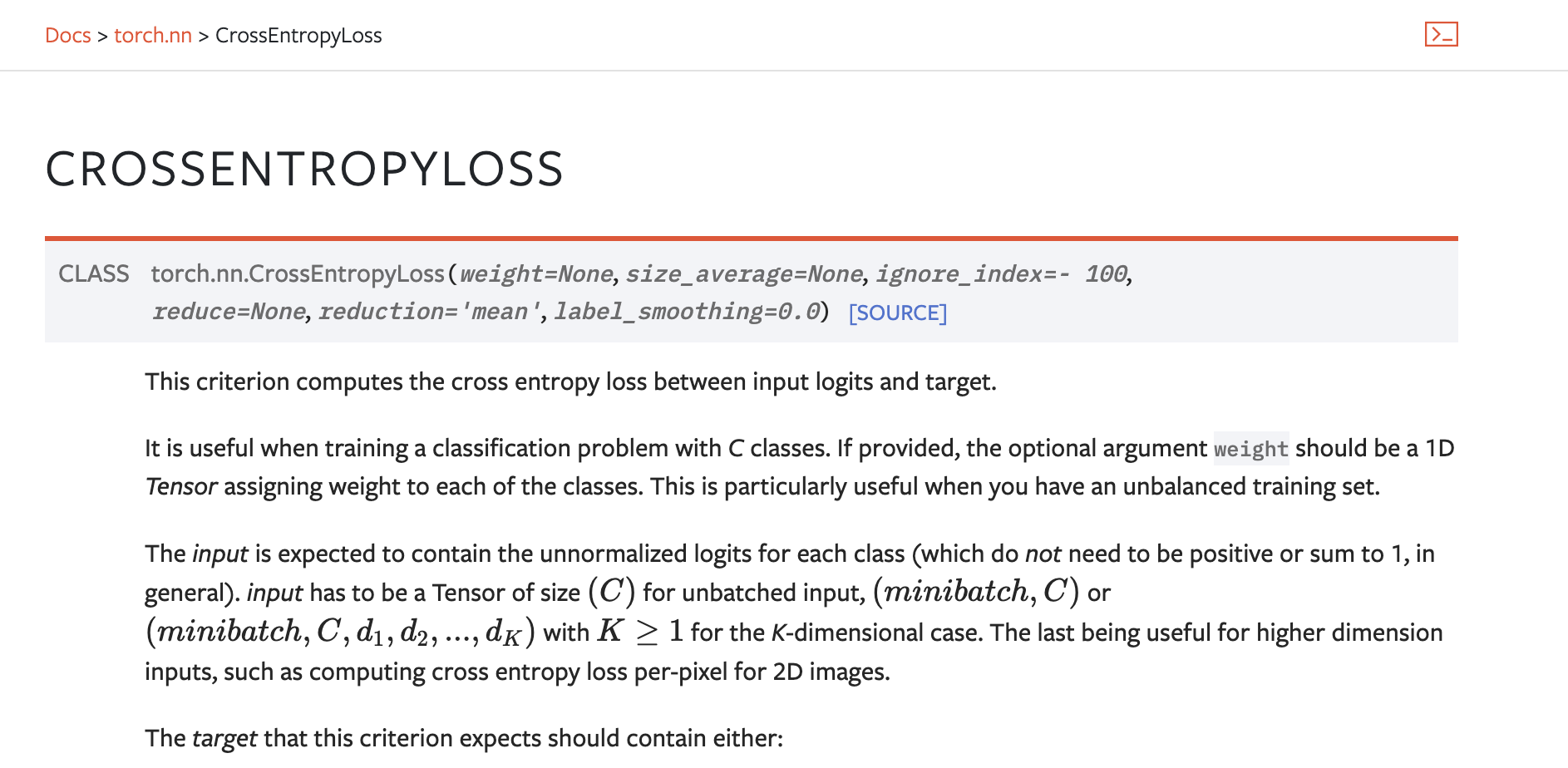
Cross Entropy Loss
: Cross Entropy Loss과 Pytorch Cross Entropy Loss를 많이 참고하였다.
class CELoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self, y_pred, y_true):
total_loss = 0
for index in range(y_pred.shape[0]):
total_loss += torch.log(torch.sum(torch.exp(y_pred[index]))) - y_pred[index, y_true[index].item()]
return total_loss / y_pred.shape[0]bs = 64
n_classes = 80
y_pred = torch.randn(bs, n_classes)
y_true = torch.arange(0, 64)
ChatGPT가 말하는 Cross Entropy Loss
import torch
class CrossEntropyLoss(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(CrossEntropyLoss, self).__init__()
def forward(self, predicted_labels, true_labels):
log_softmax = torch.nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1)
log_predictions = log_softmax(predicted_labels)
loss = -torch.sum(log_predictions[true_labels])
return loss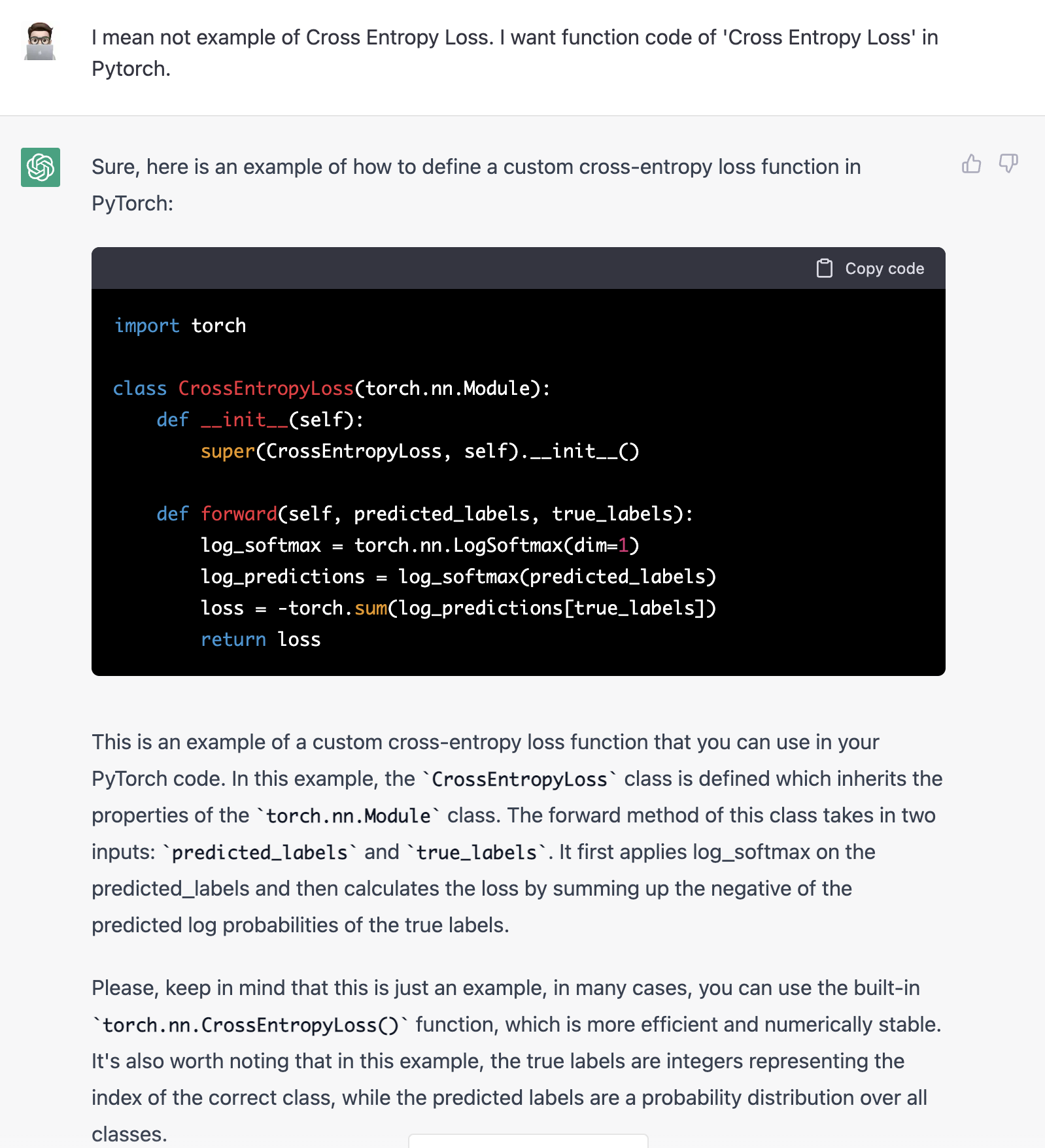
Softmax
1) 2차원 전용 Softmax
: Tensor가 2차원인 경우(엄밀히 말하면, '2차원 행렬'인 경우)에만 해당이 된다. 필자의 경우, 아직 수식이 약하기 떄문에 여기서부터 시작해보았다.
def soft_max(x):
bs = x.shape[0]
results = torch.zeros(bs, x.shape[1])
for index in range(bs):
logits = x[index]
results[index] = torch.exp(logits) / torch.sum(torch.exp(logits))
return results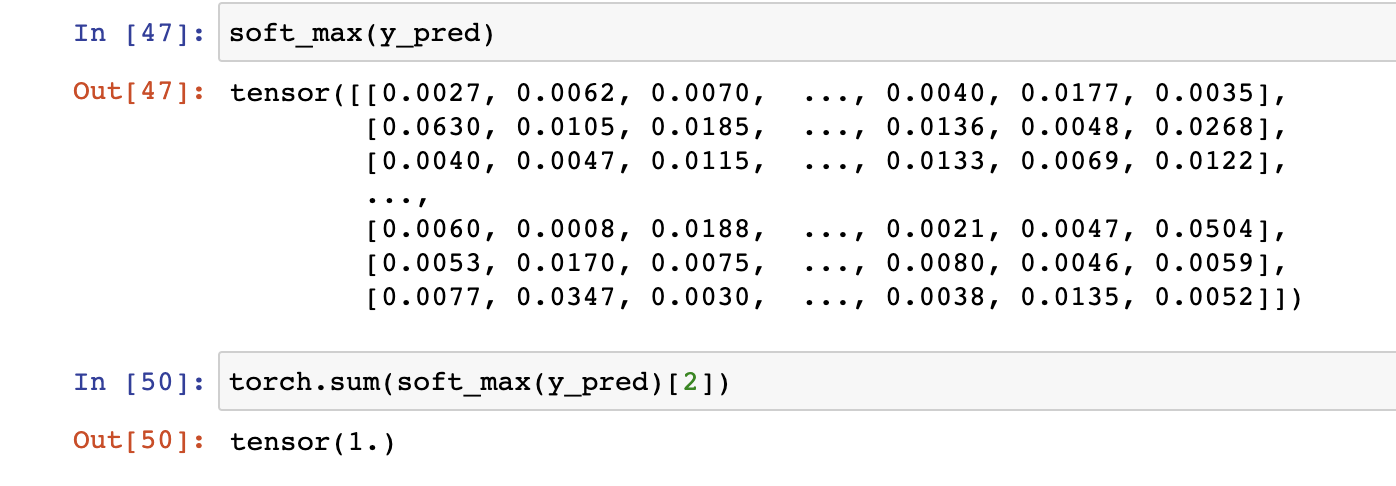
2) 3차원 이상의 텐서 - dim=-1인 경우
: 3차원 이상의 텐서에서도 적용가능하게끔 코드를 다시 작성해봤다. 단, 마지막 차원에 대해서만 Softmax를 진행하는 경우이다.
def soft_max2(x):
x_ = x.reshape(-1, x.shape[-1])
results = torch.zeros_like(x_)
for index in range(x_.shape[0]):
logits = x_[index]
results[index] = (torch.exp(logits) / torch.sum(torch.exp(logits)))
return results.view(x.shape)2차원 텐서(행렬) 테스트

3차원 텐서 테스트
a = torch.randn(2, 3, 4)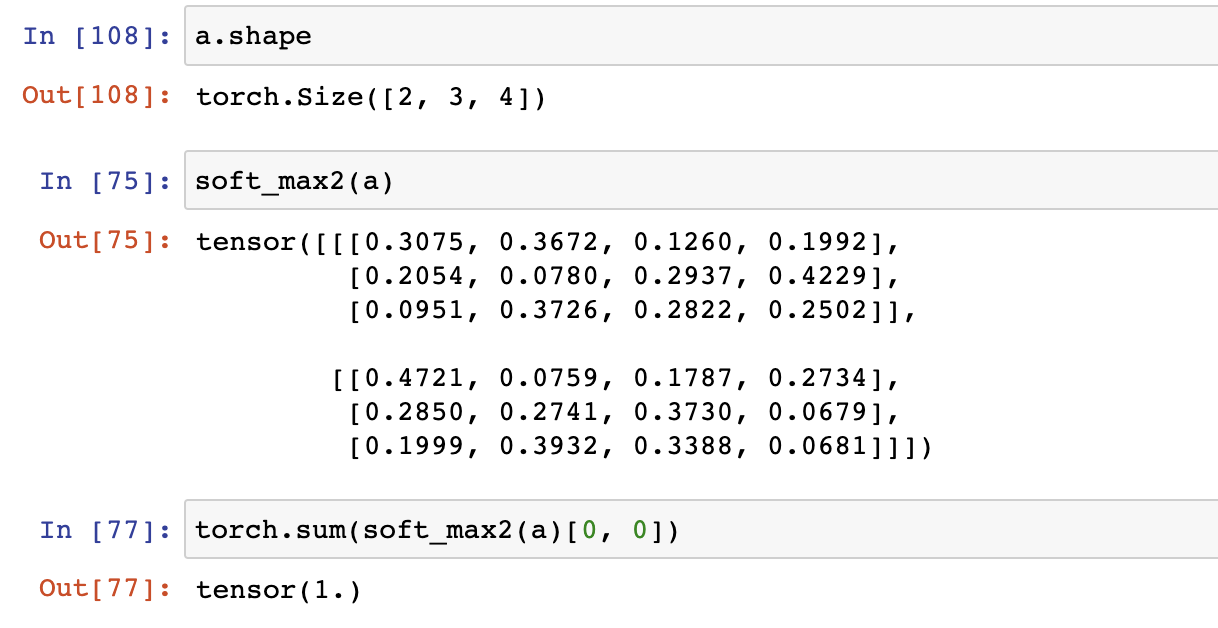
3) 3차원 이상의 텐서 - dim= N인 경우
: 3차원 이상의 텐서에 대해서 원하는 dim에 대하여 Softmax를 적용할 수 있도록 코드를 작성해보았다.
def soft_max3(x, dim):
dim_ = x.shape[dim]
x_ = x.transpose(dim, -1)
x__ = x_.reshape(-1, dim_)
results = torch.zeros_like(x__)
for index in range(x__.shape[0]):
logits = x__[index]
results[index] = (torch.exp(logits) / torch.sum(torch.exp(logits)))
return results.view(x_.shape).transpose(dim, -1)테스트

End
아직 부족한 점이 많다. 그렇기 때문에 잘못된 부분이 있다면 꼭 알려주길 바란다.
