여러 인터페이스 구현
자바에서 다중상속 문제(Diamond Problem)
자바에서는 다중상속을 허용하지 않는다. 하지만 인터페이스를 통해 다중상속은 가능다.
다중상속을 지원하지 않는 자바
다중상속을 지원하지 않는 이유는 어떤 부모의 메서드를 호출해야할지 모호해지는 문제가 발생하기 때문이다.
Person classpublic abstract class Person { public abstract void watch(); }Father class
public class Father extends Person{ public void watch() { System.out.println("samsung watch"); } }Mother class
public class Mother extends Person{ @Override public void watch() { System.out.println("apple watch"); } }Child class 에러
public class Child extends Father, Mother{ public void test() { watch(); } }
- 위 코드들은 같은메소드인watch()를 가지고 있는 부, 모 가 있다.
- 하지만 Child class에서 extends Father, Mother 할 수 없다.
- 만약 상속을 받을 수 있다 하더라도 부, 모가 가지고 있는 watch()메소드의
samsung watch 또는 apple watch중 어느 메소드를 호출 할 지 모르기 때문이다.
다중상속을 지원하는 인터페이스
Sell interface
public interface Sell { void sell(); default void order() { System.out.println("sell order"); } }Buy interface
public interface Buy { void buy(); default void order() { System.out.println("buy order"); } }Customer class 인터페이스의 implements는 다중 상속 가능하다.
public class Customer implements Buy, Sell{ @Override public void sell() { System.out.println("customer sell"); } @Override public void buy() { System.out.println("customer buy"); } @Override public void order() { System.out.println("customer order"); } public void hello() { System.out.println("Hello"); } }CustomerTest class 에러 없이 잘 작동
public class CustomerTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Customer customer = new Customer(); // 재정의 customer.buy(); customer.sell(); customer.order(); customer.hello(); Buy buyer = customer; // 재정의 했기때문에 buyer.buy(); // buy order이 아니라 customer buy buyer.order(); Sell seller = customer; // 역시 재정의 했기 때문에 seller.sell(); // sell order가 아니라 customer sell seller.order(); } }
- 인터페이스가 다중 상속을 지원하는 이유는 실질적인 구현이 이루어지지 않고 메소드에 대한 정의만 하고 있기 때문이다.
- 메소드가 겹치더라도 최종 구현 부분은 구현 객체에서 이루어질 것이기 때문에 인터페이스에서 다중상속은 에러없이 진행된다.
인터페이스 상속
- 인터페이스 사이에도 상속을 사용할 수 있다.
- extends 키워드 사용
- 인터페이스는 다중 상속이 가능하고 구현 코드의 상속이 아니므로 타입 상속 이라고 한다.
X interface
public interface X {
void x();
}Y interface
public interface Y {
void y();
}MyInterface interface 상속 키워드 extends를 사용하여 X, Y interface를 상속받음
public interface MyInterface extends X, Y{
void myMethod();
}MyClass class에서 implements를 사용하여 MyInterface상속
- X, Y, myMethod()를 모두 구현해야함
public class MyClass implements MyInterface{
@Override
public void x() {
System.out.println("x()");
}
@Override
public void y() {
System.out.println("y()");
}
@Override
public void myMethod() {
System.out.println("myMethod()");
}
}MyClassTest class
public class MyClassTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyClass mClass = new MyClass();
X xClass = mClass;
xClass.x();
Y yClass = mClass;
yClass.y();
MyClass iClass = mClass; // x, y, myMethod까지 사용하려면 MyClass를 사용하여야 한다.
iClass.x();
iClass.y();
iClass.myMethod();
}
}클래스 상속과 인터페이스 구현 함께 사용하기
- 실무에서 프레임워크나 오픈소스와 함께 연동되는 구현을 하게되면 클래스 상속과 인터페이스의 구현을 같이 사용하는 경우가 많다.
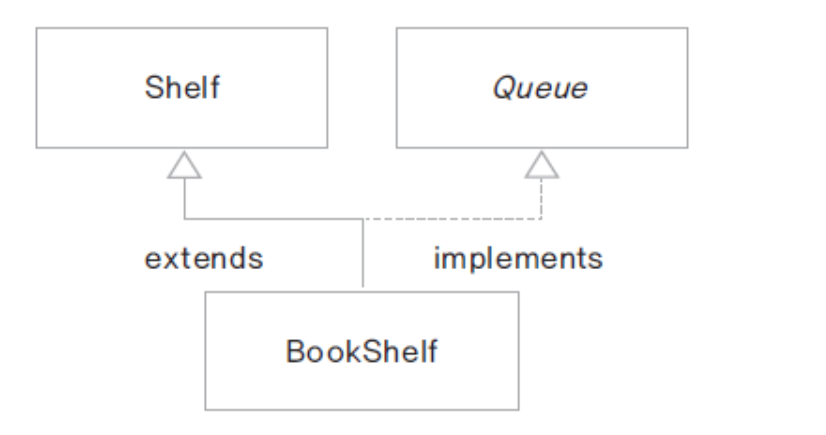
- 책이 순서대로 대여되는 도서관
- 책을 보관하는 자료 구조가 Shelf에 구현됨(ArrayList)
- Queue 인터페이스로 구현한다.
- Shelf클래스를 상속 받고 Queue를 구현한다.
Shelf class
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Shelf {
protected ArrayList<String> shelf; // protected를 사용하여 상속받을수있게 해준다.
public Shelf() {
shelf = new ArrayList<String>();
}
public ArrayList<String> getShelf(){
return shelf;
}
public int getCount() {
return shelf.size();
}
}Queue interface
public interface Queue {
void enQueue(String title); // 책 넣기
String deQueue();// 책 꺼내기
int getSize();
}BookShelf class는 extends와 implements를 사용하여 class상속과 interface 상속을 동시에 해준다.
- 자기보다 일반적인 클래스에서 상속받고
- 구현해야할 기능이 선언되어있는 인터페이스를 implements한다.
public class BookShelf extends Shelf implements Queue{
@Override
public void enQueue(String title) {
shelf.add(title);
}
@Override
public String deQueue() {
return shelf.remove(0);
}
@Override
public int getSize() {
return getCount();
}
}BookShelfTest
public class BookShelfTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue bookQueue = new BookShelf();
bookQueue.enQueue("삼국지1"); // 책 저장
bookQueue.enQueue("삼국지2");
bookQueue.enQueue("삼국지3");
bookQueue.enQueue("삼국지4");
bookQueue.enQueue("삼국지5");
System.out.println(bookQueue.getSize()+"권");
System.out.println(bookQueue.deQueue()); // 책 꺼내기
System.out.println(bookQueue.deQueue());
System.out.println(bookQueue.deQueue());
System.out.println(bookQueue.deQueue());
System.out.println(bookQueue.deQueue());
}
}
