- 클래스 , 변수, 메소드 등등 이름 한번에 고치기
- Ctrl + 1 -> Rename in workspace -> 이름 수정 -> Enter
2021.04.16
클래스 파일
- 자바파일(*.java) 1개당 클래스는 1개만 정의한다.(AAA,BBB -> CCC처럼 따로 만드는 것이 좋다.)
- 하나의 파일에 여러 개의 클래스를 정의
- 모든 클래스 중 딱 1개만이 public 키워드를 가질 수 있다.
- public 키워드를 가진 클래스가 해당 파일의 대표 클래스이다.
- 대표 클래스(public)의 이름이 파일 이름이 된다.
//자바 파일의 이름은 반드시 class명과 동일해야한다.(★★★)
//에러 메세지 : The public type Ex30_Class2 must be defined in its own file
//main 메소드를 소유한 클래스 > 스스로 실행을 할 수있는 클래스
public class Ex30_Class {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AAA a1 = new AAA();
a1.a =10;
System.out.println(a1.a);
BBB b1 = new BBB();
b1.b = 20;
System.out.println(b1.b);
//따로 만든 클래스 파일
CCC c1 = new CCC();
c1.c = 30;
System.out.println(c1.c);
}
}//class
//파일(*.java) 1개 안에 2개의 클래스를 선언했음.
//파일(*.java) 1개 안에 N개의 클래스를 선언할 수 있음.
//하나의 파일에 여러개의 클래스를 정의
// -> 모든 클래스 중 딱 1개만이 public 키워드를 가질 수 있다.
// -> public 키워드를 가진 클래스가 해당 파일의 대표 클래스이다.
// -> 대표 클래스(public)의 이름이 파일 이름이 된다.
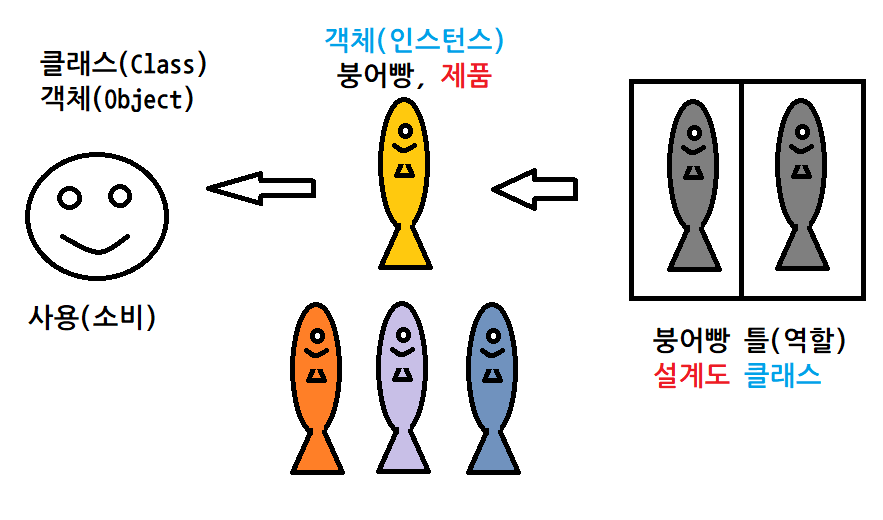
//클래스 선언(붕어빵 틀 만들기)
class AAA{
public int a;
}
class BBB{
public int b;
}
클래스
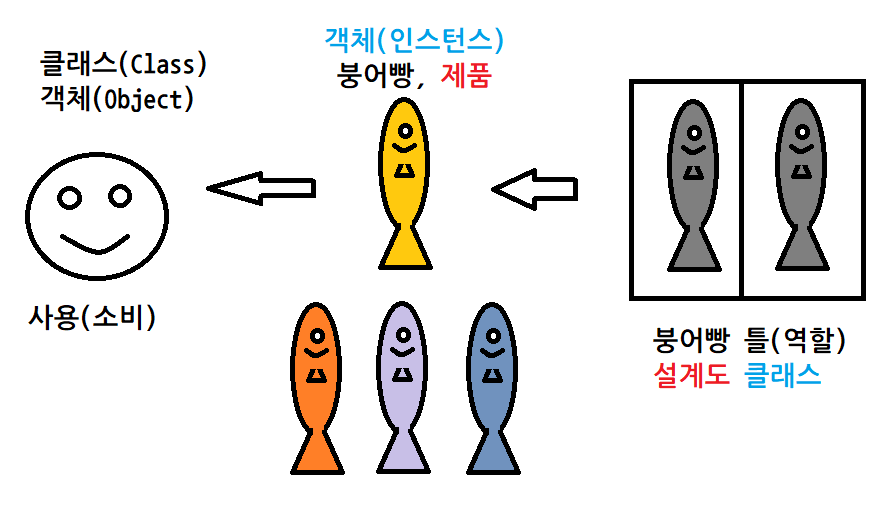
- 클래스 선언하기(정의) -> int 정의(사람x, 이미 정의되어 있음)
- 객체 생성하기(인스턴스 생성하기) -> 변수 생성하기
- 객체 사용하기(주 목적) -> 변수 사용하기
객체가 가진 데이터(상태)
- 객체는 유일하다. > 객체는 유일성을 보장받는다. ★★★
- 객체의 상태: 객체 자신만이 가지고 있는 데이터
public class Ex30_Class {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//책상 크기
Size s1 = new Size();
s1.name = "책상"; // 객체의 상태(State), 특성(Property), 특징, 속성(Attribute)
s1.width =1000;
s1.height = 500;
//노트 크기
Size s2 = new Size();
s2.name = "노트";
s2.width = 30;
s2.height = 25;
//휴대폰 크기
Size s3 = new Size();
s3.name = "휴대폰(s21)";
s3.width = 25;
s3.height = 12;
Size s4 = new Size();
s4.name = "휴대폰(s21)";
s4.width = 25;
s4.height = 12;
// s3와 s4는 같은 휴대폰(객체)인가?
// 같은 종류의 휴대폰인가? 같다.(s21이니까)
// 같은 휴대폰(객체)인가? (= 동일한 객체인가?) -> 다르다.
//★★★ 객체는 유일하다. > 객체는 유일성을 보장받는다.
//사람(= 클래스)
// -> 홍길동(= 객체, 실체화된 사람)
// -> 아무개 (= 객체)
//사람마다 구분되는 특징
// -> 유재석(객체) -> 말랐다. 얼굴이 작다. 60kg
// -> 강호동(객체) -> 뚱뚱하다. 얼굴이 크다. 90kg
// -> 특징 -> 특성 -> 객체의 상태(State★★) : 객체 자신만이 가지고 있는 데이터 -> 데이터의 차이가 객체와 객체를 구분할 수 있는 요소가 된다.
}//main
}
//대상의 크기를 저장하기 위한 단위
class Size{
public String name;
public int width;
public int height;
}
객체(object)
-
철학 용어
-
데이터 + 행동(Behavior)
-
데이터(변수) + 행동(메소드)
클래스의 용도
-
데이터의 집합 : 멤버 변수들의 집합
-
행동 집합 : 멤버 메소드들의 집합
public class Ex31_Class {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ex31_Class.divide(10, 2); //(소속.메소드) 정석
divide(10, 2); //같은 동네 안이면 생략가능, 같은 클래스의 메소드
add(10, 20); // (우리집생략) 아빠
Ex31_Class.add(10,20); //우리집 아빠
MyMath.add(10, 20); //다른집 아빠
} //main
public static void add(int a, int b) {
System.out.println(a + b);
}
public static void divide(int a, int b) {
System.out.println(a / b);
}
} //Ex31 (같은 동네)
//행동의 집합
class MyMath{ //다른 동네
//MyMath클래스 소속 멤버 메소드
public static void add(int a, int b) {
System.out.println(a + b);
}
public static void substract(int a, int b) {
System.out.println(a - b);
}
public static void multiply(int a, int b) {
System.out.println(a * b);
}
}- 데이터 + 행동 집합 : 멤버 변수 + 멤버 메소드들의 집합 (★★★가장 자주 쓰임★★★)
- 메서드를 가치있게 만들려면 자신이 가지고 있는 데이터를 활용하게 만들어야한다.
public class Ex32_Class {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student();
s1.name = "홍길동";
s1.eng = 90;
s1.kor = 100;
s1.math = 80;
s1.hello();
Student s2 = new Student();
s2.name = "아무개";
s2.eng = 99;
s2.kor = 87;
s2.math = 60;
s2.hello();
}//main
} //Ex32
//The type Student is already defined
//파일이 달라도 클래스 이름이 같으면 에러가 생긴다.
class Student{
//멤버 변수 -> 객체 상태(를 저장하는 공간)
public String name; //학생명
public int kor; //국어
public int eng; //영어
public int math; //수학
//멤버 메소드
// a.잘못 만든 메소드 > 효용가치가 전혀 없는 메소드 ->
// b.잘 만든 메소드 > 자신이 가지고 있는 데이터를 활용하는 행동을 구현한다.(★★★★★★)
public void hello() {
//System.out.println("안녕하세요."); //a.
System.out.printf("안녕하세요 저는 %s입니다.\n", name); //b.
}
}//Student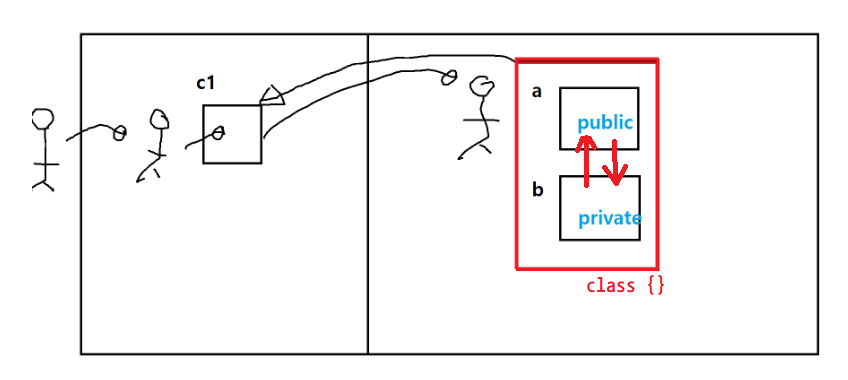
public class Ex32_Class {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Rectangle r1 = new Rectangle();
r1.name = "노트";
r1.width = 35;
r1.height = 23;
Rectangle r2 = new Rectangle();
r2.name = "아파트";
r2.width = 5000;
r2.height = 2800;
//호출
r1.getArea();
r2.getArea();
}//main
}//Ex32
class Rectangle {
//멤버변수
public String name;
public int width;
public int height;
//멤버 메소드
public void getArea() {
//면적 = 자신의 데이터를 활용
System.out.printf("[%s] %,d㎠\n", name, width * height);
}
}//Rectangle접근 지정자(제어자), Access Modifier
- public, private / protected, default(friendly)
-
public
- 클래스(객체)의 울타리를 기준으로 외부에 100% 공개한다.
-
private
-
클래스(객체)의 울타리를 기준으로 외부에 100% 비공개한다.
-
가이드 라인★★★
-
멤버 변수의 접근 지정자는 무조건 private한다.
- 잘못된 값을 제어할 방법이 없기 때문에
-
private 멤버 변수 제어를 위한 Setter와 Getter를 구현한다.
- 제어가 가능하기 때문에 안전하다.
-
-
멤버변수 -> private
-
멤버 메소드 -> private or public
public class Ex33_Accsess {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Circle c1 = new Circle();
c1.a = 10;
//The field Circle.b is not visible, 접근 불가능 or 사용 불가능
//c1.b = 20;
}//main
}//Ex33
class Circle {
//멤버변수, 필드(field)
public int a;
private int b;
}< public을 사용했을 경우 > - 값이 잘못될 위험이 높음.
public class Ex33_Accsess {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//값이 바뀔 위험이 있음..
Keyboard k1 = new Keyboard();
k1.model = "K810";
k1.weight = 500;
k1.color = "Black";
k1.price = 140000;
System.out.println("model: " + k1.model);
System.out.println("weight: " + k1.weight);
System.out.println("color: " + k1.color);
System.out.println("price: " + k1.price);
System.out.println();
//말도 안되는 데이터...
Keyboard k2 = new Keyboard();
k2.model = "G3000";
k2.weight = 30000000;
k2.color = "홍길동";
k2.price = - 21000;
System.out.println("model: " + k2.model);
System.out.println("weight: " + k2.weight);
System.out.println("color: " + k2.color);
System.out.println("price: " + k2.price);
}//main
}//Ex33
class Keyboard {
public String model;
public int weight;
public String color;
public int price;
}Setter & Getter
- 본질은 일반 멤버 메소드
- 역할이 있다.
- 주로 private 변수를 입출력하기 위한 역할을 한다.
- public 변수를 사용하는 것과 다른 점은 내부에서 통제를 할 수 있다는 것이다.★★★
< private으로 사용했을 경우 >
- 같은 클래스 내부에서는 서로 접근 지정자가 동작하지 않는다. (public이든 private이든 상관 없음)
public class Ex33_Accsess {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Keyboard k3 = new Keyboard();
//k3.weight //not visible
k3.setWeight(30000); //쓰기 작업
//System.out.println(k3.weight); //not visible
System.out.println(k3.getWeight()); // 읽기 작업
}
}//Ex33
class Keyboard {
private String model;
private int weight;
private String color;
private int price;
//Setter, Getter
//쓰기 작업 메소드
// - Setter
// - setOOO -> set멤버변수명 -> "set" + "weight" -> setweight -> 캐멀 표기법 -> setWeight
public void setWeight(int weight) throws Exception {
//지역변수와 멤버변수의 충돌 -> 같은 이름
// - 무조건 지역변수가 이긴다.
//절대 규칙!!!★★★★★
// 큰 지역과 작은 지역이 충돌이 나면 작은 지역이 이긴다.
// 두리뭉실한 것과 자세한 것이 충돌나면 자세한 것이 이긴다.
// 부모와 자식이 출돌하면 자식이 이긴다.
//this -> 객체 접근 연산자(객체 지정 연산자) -> 객체 자신을 참조한다.
//this.weight = weight;
//통제(유효검사)
if(weight > 0 && weight < 10000) {
this.weight = weight;
} else {
//무게로서 올바르지 않은 수치이다. -> 잘못됨 -> 복사X
throw new Exception("잘못된 무게입니다.");
}
}
// 읽기 작업 메소드
// -> Getter
// -> "get" + 멤버변수명
public int getWeight() {
return weight;
}
}Setter & Getter의 목적
- 유효성 검사
- 읽기 전용, 쓰기 전용 멤버 구현
- b1.getName() -> private String name 반환
- b1.getWeight() -> private int weight 반환
- b1.getAge() -> private int age 반환? (실제로 존재하지 않는 멤버, 계산으로 만들어진 멤버) -> 계산된 멤버(가상의 멤버)
public class Ex34_Class {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Setter, Getter의 목적
//1. 유효성 검사
//2. 읽기 전용, 쓰기 전용 멤버 구현
Baby b1 = new Baby();
//읽기, 쓰기 멤버
b1.setName("홍길동");
System.out.println(b1.getName());
//쓰기 전용 멤버
b1.setHeight(50);
//System.out.println(b1.getHeight());
//읽기 전용 멤버
System.out.println(b1.getWeight());
//a. 부모 -> 엄마, 아빠 따로 작업
b1.setFather("홍아빠");
b1.setMother("김엄마");
System.out.println(b1.getFather());
System.out.println(b1.getMother());
//b. 부모 -> 엄마, 아빠 같이 작업
//배열을 노출시키는 방법
String[] parent = new String[] { "홍파더", "김마더" };
b1.setParent(parent);
b1.setParent(new String[] { "홍파더", "김마더" });
String[] temp = b1.getParent();
System.out.println(temp[0] + "," + temp[1]);
System.out.println(b1.getParent()[0]);
System.out.println(b1.getParent()[1]);
//c. 겉으로 배열을 드러나지 않게 배열을 사용. - 간결함
b1.setFather2("홍가가");
b1.setMother2("김나나");
System.out.println(b1.getFather2());
System.out.println(b1.getMother2());
//a. 생일
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
c.set(2021, 0, 10);
b1.setBirthday(c);
System.out.printf("%tF\n", b1.getBirthday());
//b. 생일
b1.setBirthday2(2021, 1, 20);
//나이
System.out.println("나이: " + b1.getAge());
//b1.getName() -> private String name 반환
//b1.getWeight() -> private int weight 반환
//b1.getAge() -> private int age 반환 -> 계산된 멤버(가상의 멤버)
}//main
}//Ex34
class Baby{
//이름, 키, 몸무게, 부모(엄마, 아빠), 생일
private String name;
private int height;
private int weight = 5;
//부모
private String father;
private String mother;
//c. 부모
private String[] parent = new String[2];
//생일
private Calendar birthday;
//Setter(O), Getter(O) - 읽기, 쓰기
public void setName(String name) {
//+ 유효성 검사(한글, 글자수 기타 등등..)
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
//Setter(O), Getter(X) - 쓰기만
public void setHeight (int height) {
this.height = height;
}
// Setter(X), Getter(O) - 읽기만
public int getWeight() {
return this.weight;
}
//a. 부모
public void setFather(String father) {
this.father = father;
}
public String getFather() {
return this.father;
}
public void setMother(String mother) {
this.mother = mother;
}
public String getMother() {
return this.mother;
}
//b. 부모 - 배열
public void setParent(String[] parent) {
//String[] = String[]
this.parent = parent;
}
public String[] getParent() {
return this.parent;
}
//c. 부모 - 배열을 노출 시키지 않고 내부에서만 사용.
public void setFather2(String father) {
this.parent[0] = father;
}
public void setMother2(String mother) {
this.parent[1] = mother;
}
public String getFather2() {
return this.parent[0];
}
public String getMother2() {
return this.parent[1];
}
//a. 생일 Calendar를 외부에서 처리
public void setBirthday(Calendar birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public Calendar getBirthday() {
return this.birthday;
}
//b. 생일 Calendar를 내부에서 처리
public void setBirthday2(int year, int month, int date) {
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
c.set(year, month-1, date);
this.birthday = c;
}
//나이
//Setter(X), Getter(O)
public int getAge() {
Calendar now = Calendar.getInstance();
long gap = now.getTimeInMillis() - this.birthday.getTimeInMillis(); //현재시간 - 태어난 날짜
gap = gap / 1000 / 60 / 60 / 24 / 365; //단위 환산
return (int)gap; //다운 캐스팅(long -> int)
}
}//Baby