[React] 상태 관리
전역 상태 관리
React가 상태 관리를 위한 라이브러리는 아닙니다. 그러나 상태 관리의 주요 원칙을 배우고 이를 따라간다면, 컴포넌트 간 서로 느슨하게 결합된(loose coupled), 구조적으로 아름다운 코드를 작성할 수 있습니다.
상태 : 변하는 데이터, UI에 동적으로 표현되는 데이터
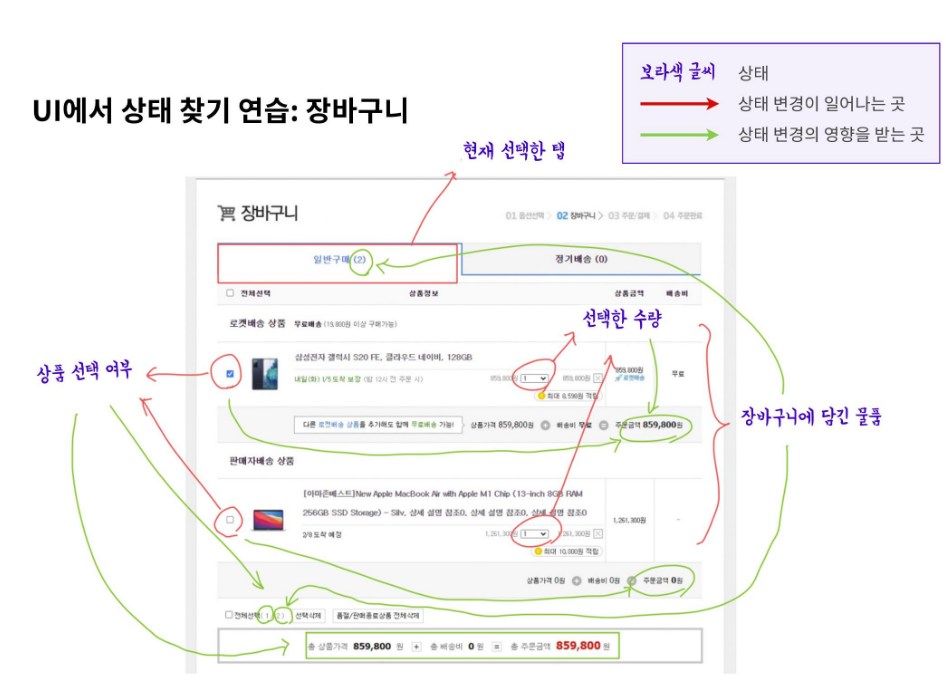
UI에서 상태찾기: 장바구니
프론트엔드 개발에서의 Side Effect
함수의 입력외에도 함수의 결과에 영향을 미치는 요인
대표적인 예) 네트워크요청, API호출
React의 주요 개발 원칙 중 하나는 UI를 페이지 단위가 아닌 컴포넌트 단위로 보는 것
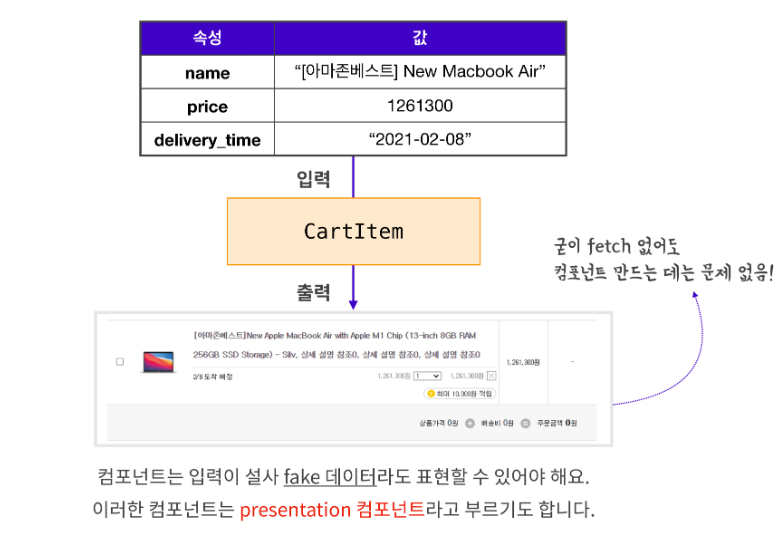
CartItem이라는 컴포넌트를 만든다면, fetch와 같은 API 요청이 없이도 이 컴포넌트는 작동되어야 합니다. 어떤 데이터가 들어오는지 상관하지 않고, 설사 데이터가 가짜 데이터라 할지라도 컴포넌트는 표현(presentation) 그 자체에 집중!
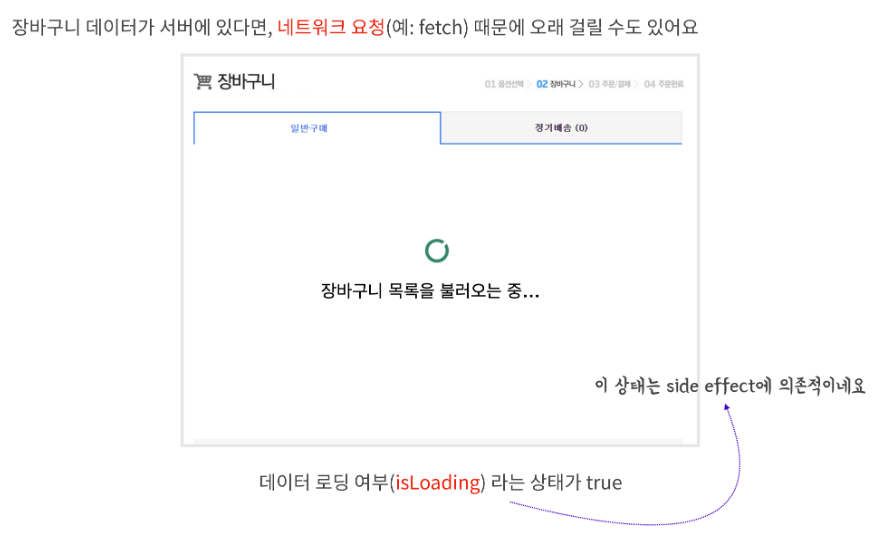
하지만, 앱을 만들다 보면 분명 API 호출도 해야 하고, side effect는 불가피하게 생겨 side effect에 의존적인 상태도 있을 수 있습니다.
예를 들어 그림과 같이 "로딩 중"을 나타낼 것인지 아닌지 여부는 데이터 전송 여부에 따라 달려 있습니다. 앱을 만들고, UI를 구성할 때에는 항상 이러한 로딩 중 상태도 고려하여야 합니다.
React로 사고하기 (공부하고 넘어가기)
상태의 2가지 구분
상태를 구분하는 데에는 절대적인 기준이나 법칙이 있는 것은 아니지만,
로컬 상태 : 특정 컴포넌트 안에서만 관리되는 상태
전역 상태 : 프로덕트 전체 혹은 여러 가지 컴포넌트가 동시에 관리하는 상태
로컬상태
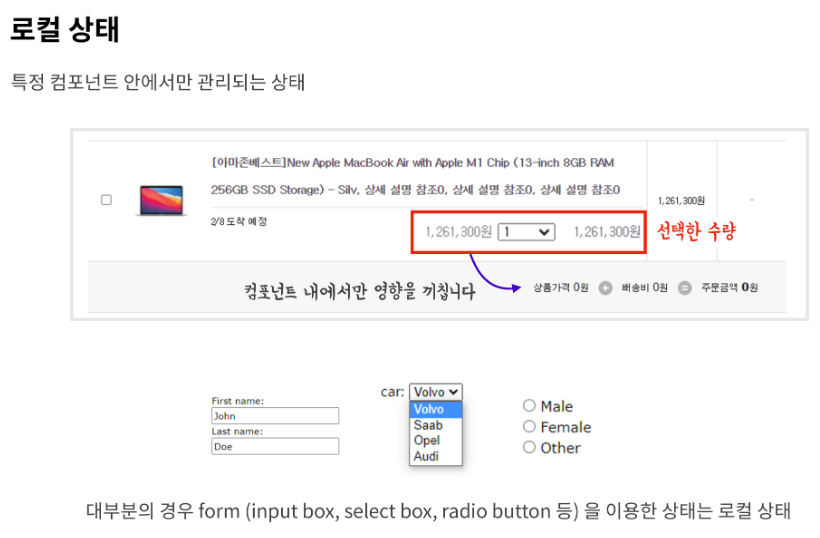
보통 컴포넌트 내에서만 영향을 끼치는 상태는 로컬 상태입니다. CartItem 컴포넌트의 경우, '선택한 수량'이 되겠습니다. 원래 가격에 상태를 곱해 컴포넌트 내에 표시되는 주문 금액을 업데이트하면 됩니다.
다른 컴포넌트와 데이터를 공유하지 않는 폼(form) 데이터는 대부분 로컬 상태입니다. input box, select box 등과 같이 입력값을 받는 경우가 이에 해당합니다.
전역상태
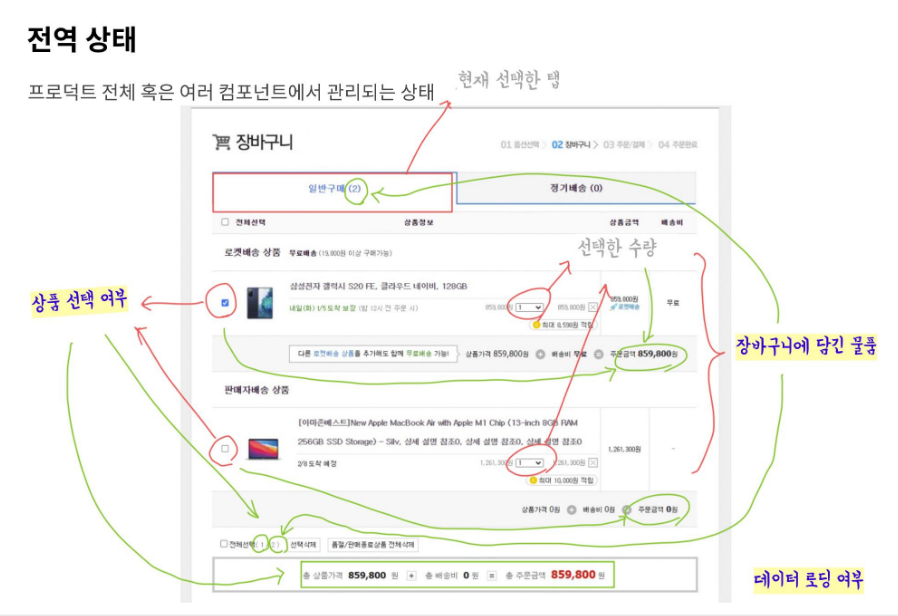
전역 상태는 다른 컴포넌트와 상태를 공유하고 영향을 끼치는 상태입니다.
장바구니에 담긴 물품의 경우, 상품 선택 여부에 따라 총 주문 금액을 업데이트해야 합니다. 장바구니에 담긴 물품은 그 갯수 등을 다른 컴포넌트에 전달해 주어야 합니다.
아까 언급한 데이터 로딩 여부(로딩 중) 상태 역시, 앱 전반에 영향을 미칩니다.
JavaScript에서는 전역 변수를 남용하는 것은 좋지 않다고 하지만, 경우에 따라 전역 상태가 필요합니다.
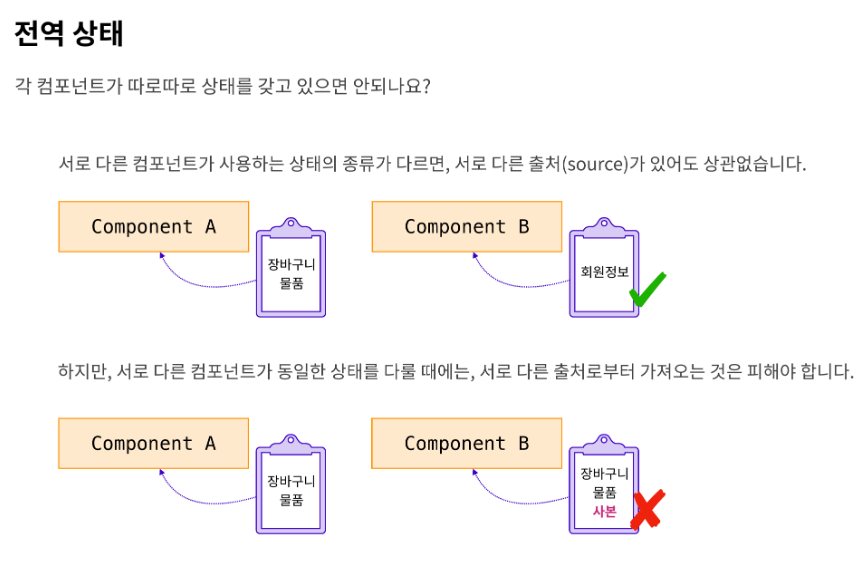
서로 다른 컴포넌트가 사용하는 상태의 종류가 다르면, 꼭 전역 상태일 필요는 없습니다.
출처(source)가 달라도 됩니다.
그러나, 서로 다른 컴포넌트가 동일한 상태를 다룬다면, 이 출처는 오직 한 곳이어야 합니다.
만일 사본이 있을 경우, 두 데이터는 서로 동기화(sync)하는 과정이 필요한데, 이는 문제를 어렵게 만듭니다. 한 곳에서만 상태를 저장하고 접근해야 합니다.
여기서 '하나의 출처'는 다른 말로 이야기하면 '전역 공간'이라고 볼 수 있습니다.

즉, 데이터 무결성을 위해, 동일한 데이터는 항상 같은 곳에서 데이터를 가지고 오도록 해야 합니다.
Single source of truth(신뢰할 수 있는 단일 출처) 원칙은 프론트엔드 뿐만 아니라 다양한 곳에서 언급되는 원칙입니다.
전역으로 상태를 관리해야 하는 경우
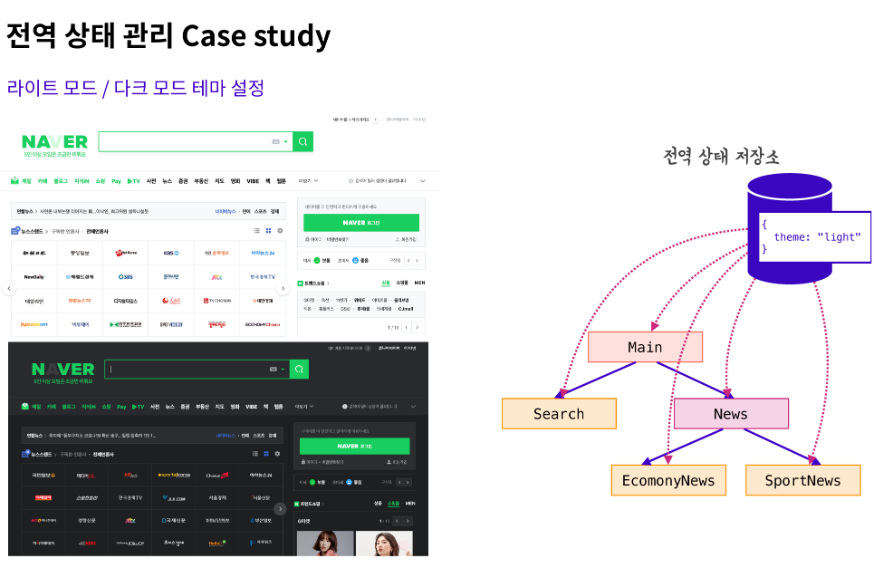
네이버를 비롯한 여러 사이트에서 다크 모드 기능을 이용하는 경우 모든 페이지, 모든 컴포넌트에 다크 모드 혹은 라이트 모드가 적용이 되어야 하기 때문에 이러한 테마 설정을 전역으로 관리한다.
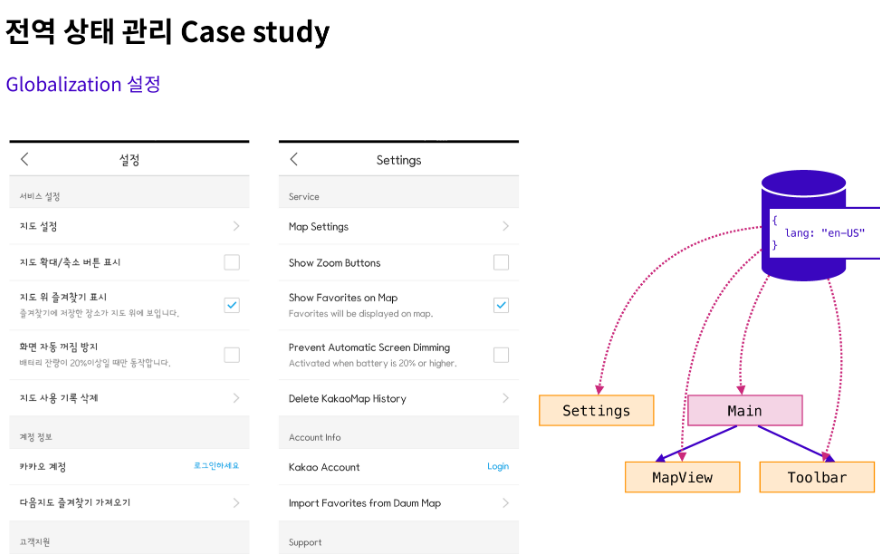
국제화(Globalization) 설정
사용자가 사용하는 브라우저나, 운영체제가 특정 언어를 사용하고 있음을 알아내서, UI에 필요한 텍스트 리소스를 따로 저장한 후, 전역 상태로 관리한다.
모든 컴포넌트에서 사용자 언어로 표현이 되어야 하기 때문에 전역에서 상태 관리가 필요하다.
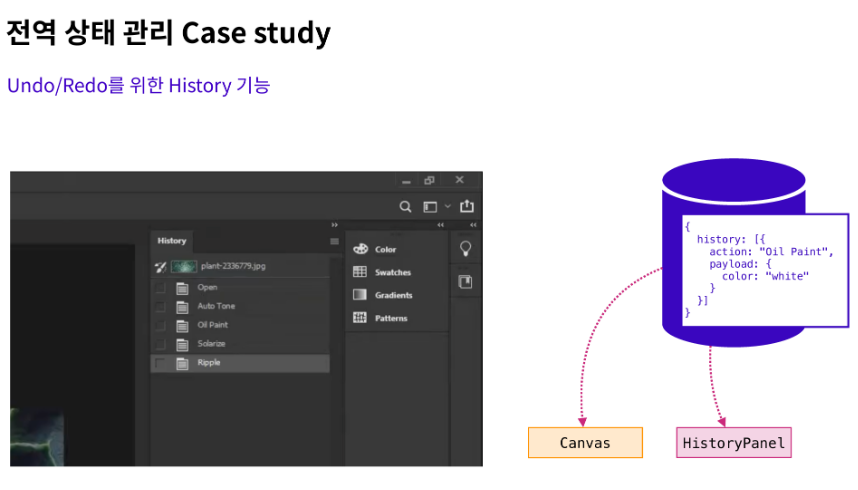
포토샵이나 일러스트레이터에는 히스토리 기능과 Undo/Redo를 지원합니다. 화면에 표시되는 모든 내용을 전부 상태 객체로 만들어서 저장해버린다면, 원하는 특정 상태를 바탕으로 컴포넌트를 표현할 수도 있습니다. 이것이 Undo/Redo, 히스토리 기능의 작동 원리입니다.
상태관리를 위한 각종 툴
React Context
Redux
MobX
상태관리 툴이 해결해주는 문제
전역상태 저장소 제공
props drilling 이슈 해결
props drilling
Props Drilling은 상위 컴포넌트의 state를 props를 통해 전달하고자 하는 컴포넌트로 전달하기 위해 그 사이는 props를 전달하는 용도로만 쓰이는 컴포넌트들을 거치면서 데이터를 전달하는 현상을 의미합니다.
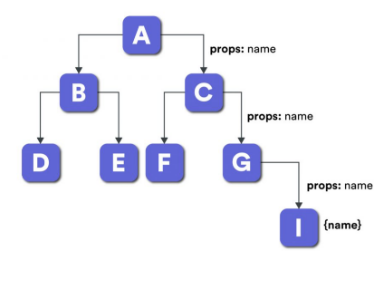
예를 들어, A라는 컴포넌트에 상태가 있고, I라는 컴포넌트가 해당 상태를 사용한다고 하면, 그 중간에 존재하는 C, G 등은 굳이 name이라는 상태가 필요하지 않음에도, 컴포넌트에 props를 만들어 자식 컴포넌트에 넘겨주어야 했습니다. 이를 props drilling(프로퍼티 내려꽂기) 문제라고 부릅니다.
상태관리 툴이 반드시 필요한 것은 아니며 없이도 충분히 규모 있는 애플리케이션을 만들 수 있다.
대부분의 경우 "React 사고하기"를 통해 문제 해결 가능
Props Drilling의 문제점
Props의 전달 횟수가 5회 이내로 많지 않다면 Props Drilling 은 큰 문제가 되지 않습니다. 하지만 규모가 커지고 구조가 복잡해지면서 Props의 전달 과정이 늘어난다면 아래와 같은 문제가 발생합니다.
코드의 가독성이 매우 나빠지게 됩니다.
코드의 유지보수 또한 힘들어지게 됩니다.
state 변경시 Props 전달 과정에서 불필요하게 관여된 컴포넌트들 또한 리렌더링이 발생합니다.
따라서, 웹성능에 악영향을 줄 수 있습니다.
해결 방법
과도한 Props Drilling을 방지하기 위한 방법으로는 컴포넌트와 관련있는 state는 될 수 있으면 가까이 유지하는 방법과 상태관리 라이브러리를 사용하는 방법이 있습니다. 상태관리 라이브러리를 사용하게 되면 전역으로 관리하는 저장소에서 직접 state를 꺼내쓸 수 있기 때문에 Props Drilling을 방지하기에 매우 효과적입니다. 이번 유닛에서는 다양한 상태관리 라이브러리(Redux, Context api, Mobx, Recoil 등) 중 Redux를 다룰 예정입니다.
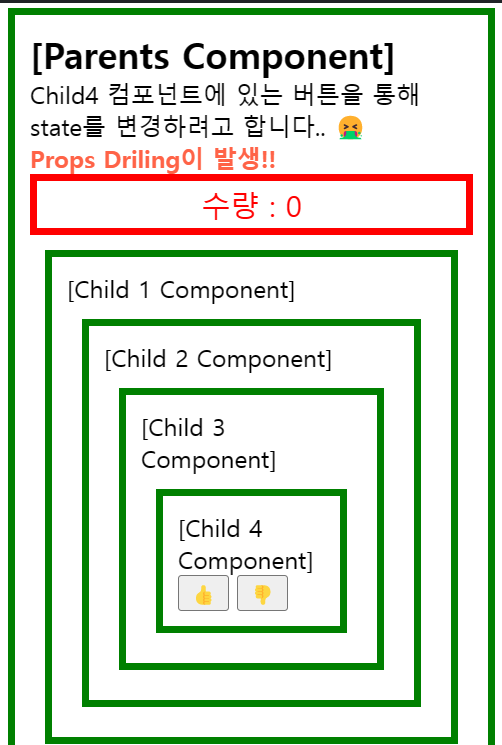
props drilling 예시1
아래의 예시는 props를 제일 깊은 컴포넌트까지 내려주어야 제대로 작동합니다.
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import styled from 'styled-components';
const Container = styled.div`
border: 5px solid green;
padding: 10px;
margin: 10px;
position: relative;
`;
const Quantity = styled.div`
text-align: center;
color: red;
border: 5px solid red;
padding: 3px;
font-size: 1.2rem;
`;
const Button = styled.button`
margin-right: 5px;
`;
const Text = styled.div`
color: ${(props) => (props.color ? props.color : 'black')};
font-size: ${(props) => (props.size ? props.size : '1rem')};
font-weight: ${(props) => (props.weight ? '700' : 'inherit')};
`;
export default function App() {
const [number, setNumber] = useState(1);
const plusNum = () => {
setNumber(number + 1);
};
const minusNum = () => {
setNumber(number - 1);
};
console.log('Parents');
return (
<Container>
<Text weight size="1.5rem">
[Parents Component]
</Text>
<Text>
Child4 컴포넌트에 있는 버튼을 통해
<br /> state를 변경하려고 합니다.. 🤮
</Text>
<Text weight color="tomato">
Props Driling이 발생!!
</Text>
<Quantity>{`수량 : ${number}`}</Quantity>
<Child1 plusNum={plusNum} minusNum={minusNum} />
</Container>
);
}
function Child1({
/* props로 전달받은 plusNum, minusNum를 가져오세요 */
plusNum,
minusNum,
}) {
console.log('Child1');
return (
<Container>
<Text>[Child 1 Component]</Text>
{/* plusNum, minusNum 함수를 props로 전달해주세요! */}
<Child2 plusNum={plusNum} minusNum={minusNum} />
</Container>
);
}
function Child2({
plusNum,
minusNum,
/* props로 전달받은 plusNum, minusNum를 가져오세요 */
}) {
console.log('Child2');
return (
<Container>
<Text>[Child 2 Component]</Text>
{/* plusNum, minusNum 함수를 props로 전달해주세요! */}
<Child3 plusNum={plusNum} minusNum={minusNum} />
</Container>
);
}
function Child3({
plusNum,
minusNum,
/* props로 전달받은 plusNum, minusNum를 가져오세요 */
}) {
console.log('Child3');
return (
<Container>
<Text>[Child 3 Component]</Text>
{/* plusNum, minusNum 함수를 props로 전달해주세요! */}
<Child4 plusNum={plusNum} minusNum={minusNum} />
</Container>
);
}
function Child4({ plusNum, minusNum }) {
console.log('Child4');
return (
<Container>
<Text>[Child 4 Component]</Text>
<Button onClick={plusNum}>👍</Button>
<Button onClick={minusNum}>👎</Button>
</Container>
);
}Props Drilling 예시1 - 해결방법
이 현상을 해결할 수 있는 방법 중 하나는 상태관리 라이브러리를 사용하는 것입니다. 아래의 예시는 상태관리 라이브러리 중 Redux를 활용한 예시입니다.
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import styled from 'styled-components';
import { useSelector, useDispatch } from 'react-redux';
const Container = styled.div`
border: 5px solid green;
padding: 10px;
margin: 10px;
position: relative;
`;
const Quantity = styled.div`
text-align: center;
color: red;
border: 5px solid red;
padding: 3px;
font-size: 1.2rem;
`;
const Button = styled.button`
margin-right: 5px;
`;
const Text = styled.div`
color: ${(props) => (props.color ? props.color : 'black')};
font-size: ${(props) => (props.size ? props.size : '1rem')};
font-weight: ${(props) => (props.weight ? '700' : 'inherit')};
`;
export default function App() {
const number = useSelector((state) => state);
console.log('Parents');
return (
<Container>
<Text weight size="1.5rem">
[Parents Component]
</Text>
<Text>
Child4 컴포넌트에 있는 버튼을 통해 <br /> state를 변경하려고 합니다. ☺️
</Text>
<Text weight color="tomato">
(Redux를 사용하는 경우)
</Text>
<Quantity>{`수량 : ${number}`}</Quantity>
<Child1 />
</Container>
);
}
function Child1() {
console.log('Child1');
return (
<Container>
<Text>[Child 1 Component]</Text>
<Child2 />
</Container>
);
}
function Child2() {
console.log('Child2');
return (
<Container>
<Text>[Child 2 Component]</Text>
<Child3 />
</Container>
);
}
function Child3() {
console.log('Child3');
return (
<Container>
<Text>[Child 3 Component]</Text>
<Child4 />
</Container>
);
}
function Child4() {
const dispatch = useDispatch();
const plusNum = () => {
dispatch({ type: 'Plus' });
};
const minusNum = () => {
dispatch({ type: 'Minus' });
};
console.log('Child4');
return (
<Container>
<Text>[Child 4 Component]</Text>
<Button onClick={plusNum}>👍</Button>
<Button onClick={minusNum}>👎</Button>
</Container>
);
}Props Drilling 예시2
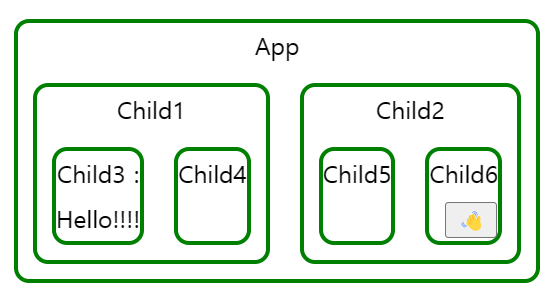
아래 예시는 Child6 에 있는 👋 버튼을 누르면 Child3에 느낌표가 하나씩 추가되는 간단한 애플리케이션입니다. 이 때, Child3, Child6이 하나의 상태를 공유하기 때문에 최상위 컴포넌트인 App에서 상태를 관리해야 합니다. 이 때문에 상태를 변경할 때마다 App 컴포넌트가 리렌더링 되면서 모든 컴포넌트가 리렌더링 됩니다. 변경되는 상태와 연관이 없는 컴포넌트까지 불필요하게 리렌더링 됩니다.
import * as React from 'react';
import './style.css';
import styled from 'styled-components';
import { useState } from 'react';
const Component = styled.div`
border: 3px solid green;
border-radius: 10px;
flex-grow: 1;
line-height: 30px;
text-align: center;
margin: 10px;
>button{
margin-left: 10px;
}
`;
const Container = styled.div`
display: flex;
width: 100%;
justify-contents: center;
`;
export default function App() {
const [greeting, setGreeting] = useState('Hello');
console.log('App');
return (
<Container>
<Component>
App
<Container>
<Child1 greeting={greeting} setGreeting={setGreeting} />
<Child2 greeting={greeting} setGreeting={setGreeting} />
</Container>
</Component>
</Container>
);
}
function Child1({ greeting, setGreeting }) {
console.log('Child1');
return (
<Component>
Child1
<Container>
<Child3 greeting={greeting} setGreeting={setGreeting} />
<Child4 />
</Container>
</Component>
);
}
function Child2({ greeting, setGreeting }) {
console.log('Child2');
return (
<Component>
Child2
<Container>
<Child5 />
<Child6 greeting={greeting} setGreeting={setGreeting} />
</Container>
</Component>
);
}
function Child3({ greeting, setGreeting }) {
console.log('Child3');
return <Component>Child3 : {greeting} </Component>;
}
function Child4() {
console.log('Child4');
return <Component>Child4</Component>;
}
function Child5() {
console.log('Child5');
return <Component>Child5</Component>;
}
function Child6({ greeting, setGreeting }) {
console.log('Child6');
return (
<Component>
Child6
<button onClick={() => setGreeting(greeting + '!')}>👋</button>
</Component>
);
}Props Drilling 예시2 - 해결방법
위 예시 애플리케이션에서 Redux를 활용하여 전역 상태 관리를 할 수 있게 만들어주었습니다. 상태의 영향을 받아 화면을 변경해야하는 컴포넌트만 리렌더링 되는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
import * as React from 'react';
import './style.css';
import styled from 'styled-components';
import { useSelector, useDispatch } from 'react-redux';
const Component = styled.div`
border: 3px solid green;
border-radius: 10px;
flex-grow: 1;
line-height: 30px;
text-align: center;
margin: 10px;
>button{
margin-left: 10px;
}
`;
const Container = styled.div`
display: flex;
width: 100%;
justify-contents: center;
`;
export default function App() {
console.log('App');
return (
<Container>
<Component>
App
<Container>
<Child1 />
<Child2 />
</Container>
</Component>
</Container>
);
}
function Child1() {
console.log('Child1');
return (
<Component>
Child1
<Container>
<Child3 />
<Child4 />
</Container>
</Component>
);
}
function Child2() {
console.log('Child2');
return (
<Component>
Child2
<Container>
<Child5 />
<Child6 />
</Container>
</Component>
);
}
function Child3() {
const greeting = useSelector((state) => state);
console.log('Child3');
return <Component>Child3 : {greeting} </Component>;
}
function Child4() {
console.log('Child4');
return <Component>Child4</Component>;
}
function Child5() {
console.log('Child5');
return <Component>Child5</Component>;
}
function Child6() {
console.log('Child6');
const dispatch = useDispatch();
const addBang = () => {
dispatch({ type: 'AddBang' });
};
return (
<Component>
Child6
<button onClick={addBang}>👋</button>
</Component>
);
}
