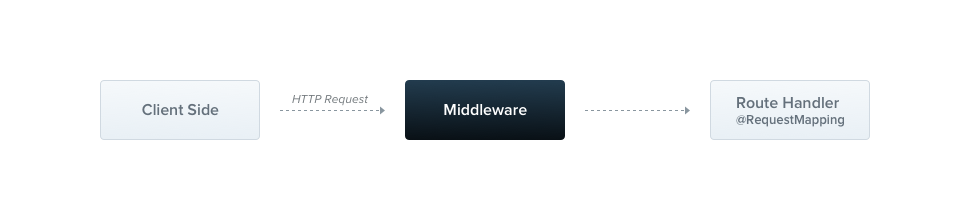
미들웨어 (Middleware)
미들웨어는 라우트 핸들러 보다 먼저 호출되는 함수입니다 . 미들웨어 함수는 요청 및 응답 객체에 접근할 수 있으며, next()애플리케이션의 요청-응답 주기에서 미들웨어 함수에 접근할 수 있습니다.
Nest 미들웨어는 기본적으로 Express 미들웨어와 동일합니다. Express 공식 문서의 다음 설명은 미들웨어의 기능을 설명합니다.
미들웨어 기능은 다음과 같은 작업을 수행할 수 있습니다.
- 모든 코드를 실행합니다.
- 요청 및 응답 객체를 변경합니다.
- 요청-응답 주기를 종료합니다.
- 스택의 다음 미들웨어 함수를 호출합니다.
- 미들웨어 함수가 요청-응답 주기를 종료하지 않으면 next()다음 미들웨어 함수로 제어권을 넘기기 위해 호출해야 합니다. 그렇지 않으면 요청은 중단 상태로 남게 됩니다.
import { Injectable, NestMiddleware } from '@nestjs/common';
import { Request, Response, NextFunction } from 'express';
@Injectable()
export class LoggerMiddleware implements NestMiddleware {
use(req: Request, res: Response, next: NextFunction) {
console.log('Request...');
next();
}
}
Spring 에서 Filter 코드
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@Component
public class LoggerInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Request...");
return true; // false 반환 시 요청 중단
}
}
종속성 주입
Nest 미들웨어는 의존성 주입을 완벽하게 지원합니다. 공급자와 컨트롤러와 마찬가지로, 동일한 모듈 내에서 사용 가능한 의존성을 주입 할 수 있습니다
미들웨어 적용
데코레이터 에는 미들웨어를 위한 공간이 없습니다 . 대신 모듈 클래스의 메서드를 @Module()사용하여 미들웨어를 설정합니다 . 미들웨어를 포함하는 모듈은 인터페이스를 구현해야 합니다. 해당 레벨에서 미들웨어를 설정해 보겠습니다
import { MiddlewareConsumer, Module, NestModule } from '@nestjs/common';
import { AppController } from './app.controller';
import { AppService } from './app.service';
import { CatsController } from './cats/cats.controller';
import { CatsModule } from './cats/cats.module';
import { LoggerMiddleware } from './logger/logger.middleware';
@Module({
imports: [CatsModule],
controllers: [AppController, CatsController],
providers: [AppService],
})
export class AppModule implements NestModule {
configure(consumer: MiddlewareConsumer) {
consumer.apply(LoggerMiddleware).forRoutes('cats');
}
}
특정 경로로 제한
...
.forRoutes({ path: 'cats', method: RequestMethod.GET });경로 와일드카드
패턴 기반 경로는 NestJS 미들웨어에서도 지원됩니다. 예를 들어, 명명된 와일드카드( )를 사용하여 경로의 모든 문자 조합을 일치시킬 수 있습니다. 다음 예제에서 미들웨어는 뒤에 오는 문자 수에 관계없이 *splat로 시작하는 모든 경로에 대해 실행됩니다 .
...
forRoutes({
path: 'abcd/*splat',
method: RequestMethod.ALL,
});경로 경로는 , , 등과 'abcd/*'일치합니다 . 하이픈( )과 마침표( )는 문자열 기반 경로에서 문자 그대로 해석됩니다. 그러나 추가 문자가 없으면 경로와 일치하지 않습니다. 이 경우 와일드카드를 중괄호로 묶어 선택 사항으로 만들어야 합니다.
...
forRoutes({
path: 'abcd/{*splat}',
method: RequestMethod.ALL,
});
경로 제외
때로는 특정 경로를 미들웨어 적용에서 제외exclude() 해야 할 수 있습니다. 이는 메서드를 사용하여 쉽게 구현할 수 있습니다. 이 메서드는 제외할 경로를 식별하기 위해 exclude()단일 문자열, 여러 문자열 또는 객체를 받습니다.
consumer
.apply(LoggerMiddleware)
.exclude(
{ path: 'cats', method: RequestMethod.GET },
{ path: 'cats', method: RequestMethod.POST },
'cats/{*splat}',
)
.forRoutes(CatsController);
위의 예제를 사용하면 메서드 에 전달된 세 개의 경로를 제외한LoggerMiddleware , 내부에 정의된 모든 경로에 바인딩됩니다
이 접근 방식은 특정 경로나 경로 패턴에 따라 미들웨어를 적용하거나 제외하는 데 있어 유연성을 제공합니다.
함수형 미들웨어
우리가 사용해 온 클래스 LoggerMiddleware는 매우 간단합니다. 멤버도, 추가 메서드도, 종속성도 없습니다. 왜 클래스 대신 간단한 함수로 정의할 수 없는 걸까요? 사실, 가능합니다. 이러한 유형의 미들웨어를 함수형 미들웨어 라고 합니다 . 차이점을 보여주기 위해 로거 미들웨어를 클래스 기반에서 함수형 미들웨어로 변환해 보겠습니다.
import { Request, Response, NextFunction } from 'express';
export function logger(req: Request, res: Response, next: NextFunction) {
console.log(`Request...`);
next();
};
다중 미들웨어
위에서 언급했듯이 순차적으로 실행되는 여러 미들웨어를 바인딩하려면 apply()메서드 내부에 쉼표로 구분된 목록을 제공하기만 하면 됩니다.
import { MiddlewareConsumer, Module, NestModule, RequestMethod } from '@nestjs/common';
import { AppController } from './app.controller';
import { AppService } from './app.service';
import { CatsController } from './cats/cats.controller';
import { CatsModule } from './cats/cats.module';
import { logger, LoggerMiddleware } from './logger/logger.middleware';
@Module({
imports: [CatsModule],
controllers: [AppController, CatsController],
providers: [AppService],
})
export class AppModule implements NestModule {
configure(consumer: MiddlewareConsumer) {
consumer
.apply(LoggerMiddleware,logger)
.exclude(
{ path: 'cats', method: RequestMethod.GET },
{ path: 'cats', method: RequestMethod.POST },
'cats/{*splat}',
)
.forRoutes(CatsController);
}
}
글로벌 미들웨어
등록된 모든 경로에 미들웨어를 한 번에 바인딩하려면 인스턴스 use()에서 제공하는 메서드를 사용할 수 있습니다.
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
app.use(logger);
await app.listen(process.env.PORT ?? 3000);