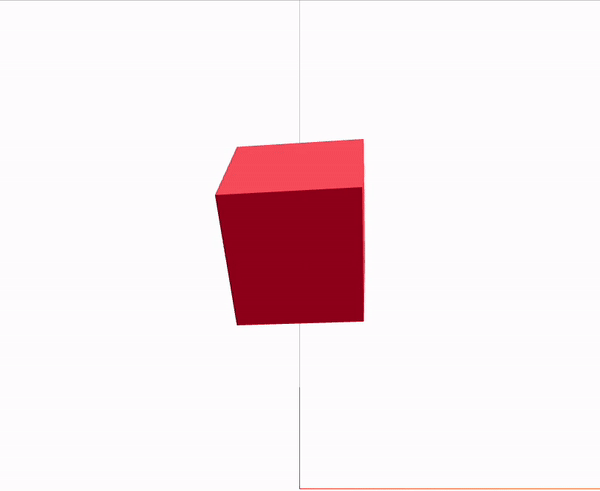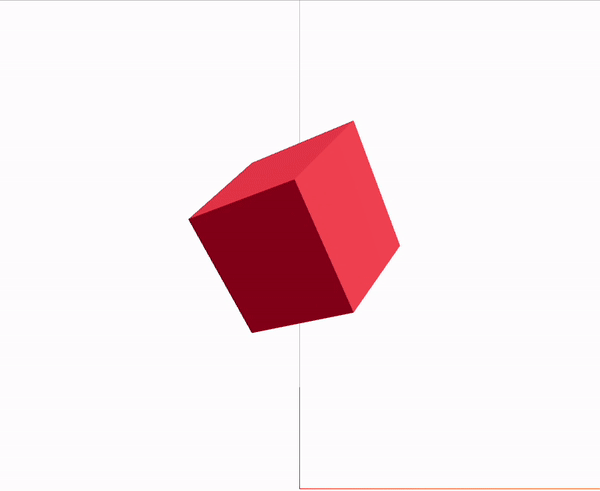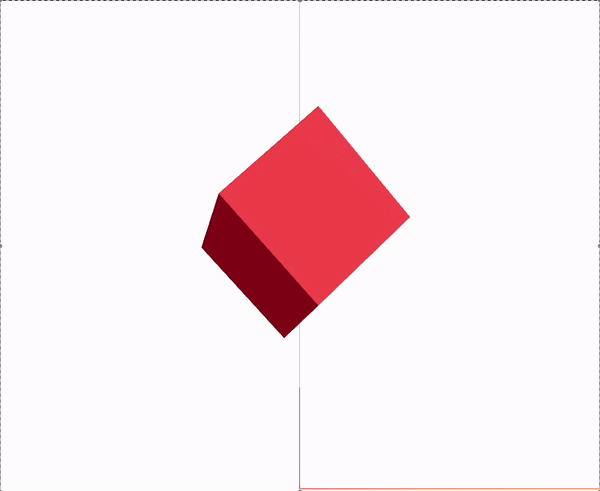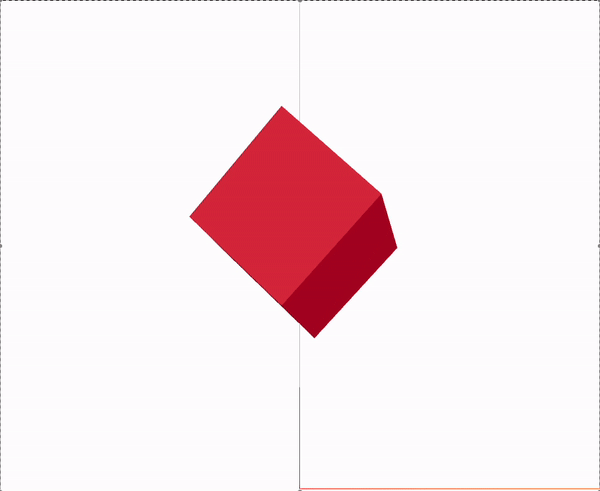
Canvas
R3F의 Canvas는 쉽게 말해 3D 공간이다.
따라서 3D 공간인 Canvas Element 자식에서 구현해야 한다.
<Canvas>
<mesh>
...
</mesh>
</Canvas>mesh
mesh에는 다양한 속성이 있다.
- position
- since
- rotate
mesh는 기본적으로 Geometry와 material 이 두 element의 부모가 되며 3D객체는 이 구가지 요소로 생성된다.
args는 x, y, z 축의 비율을 의미한다.
처음에는 조명이 없기 때문에 color 값을 주어도 검은색일것이다.
light도 다양한 조명이 있는데 다음에 설명하겠다.
light의 position도 x, y, z 값이다.
<Canvas>
<directionalLight position={[1, 1, 1]} /> // 조명
<mesh>
<boxGeometry args={[1, 1, 1]} />
<meshStandardMaterial color="red" />
</mesh>
</Canvas>이 속성들을 이용해 애니메이션을 구현할 수 있다. ( useFrame )
OrbitControls
이대로 따라왔다면 의문을 가질것이다. 왜 2D인데? 어떻게 해야 3D인거지?
이 코드를 추가하고 드래그 및 휠조작해보면 3D임을 확인할 수 있다.
import { OrbitControls } from "@react-three/drei";
<Canvas> // 3D 공간
<directionalLight position={[1, 1, 1]} /> // 조명
<OrbitControls /> // << 3D임을 확인
<mesh> // 3D 객체
<boxGeometry args={[1, 1, 1]} />
<meshStandardMaterial color="red" />
</mesh>
</Canvas>useFrame
3D Element가 렌더링 되기 직전에 실행되는 callback함수로 state, delta 등 다양한 속성이 있고 이 안에서 애니메이션을 구현한다.
useFrame((state, delta) => {
console.log(state);
console.log(delta);
});
useFrame은 Canvas 자식 Component에서 구현해야 에러가 나지 않는다. ( 동일한 컴포넌트에서 작업 ❌ )
App.tsx
function App() {
return (
<Canvas>
<Box />
</Canvas>
);Box.tsx
// ...
useFrame((state, delta) => {
if (boxRef.current) boxRef.current.rotation.y += delta;
});
return // ...애니메이션
const boxRef = useRef<HTMLMesh>(null);
useFrame((state, delta) => {
if (boxRef.current) boxRef.current.rotation.y += delta;
});
return (
<mesh ref={boxRef}>
<boxGeometry args={[1, 1, 1]} />
<meshStandardMaterial color="#cd2640" />
</mesh>
);