스레드(Thread)
프로세스와 스레드
- 프로세스 : 실행 중인 애플리케이션(데이터, 컴퓨터 자원, 스레드로 구성)
애플리케이션 실행 시, 운영체제로부터 실행에 필요한 메모리를 할당받아 프로세스가 된다. - 스레드 : 데이터와 애플리케이션이 확보한 자원을 활용하여 소스 코드를 실행
💡 스레드는 하나의 코드 실행 흐름
메인 스레드
- 자바 애플리케이션을 실행하면 가장 먼저 실행되는 메서드는
main 메서드이다.
이main 메서드를 실행 시켜주는 것이메인 스레드이다. - 싱글 스레드로 작성 되었다면 오직
메인 스레드만 가지는 싱글 스레드 프로세스이다.
멀티 스레드
- 하나의 프로세스에 여러 개의 스레드를 가지고 있는 것
- 여러 스레드가 동시에 작업을 수행한다. -> 멀티 스레딩
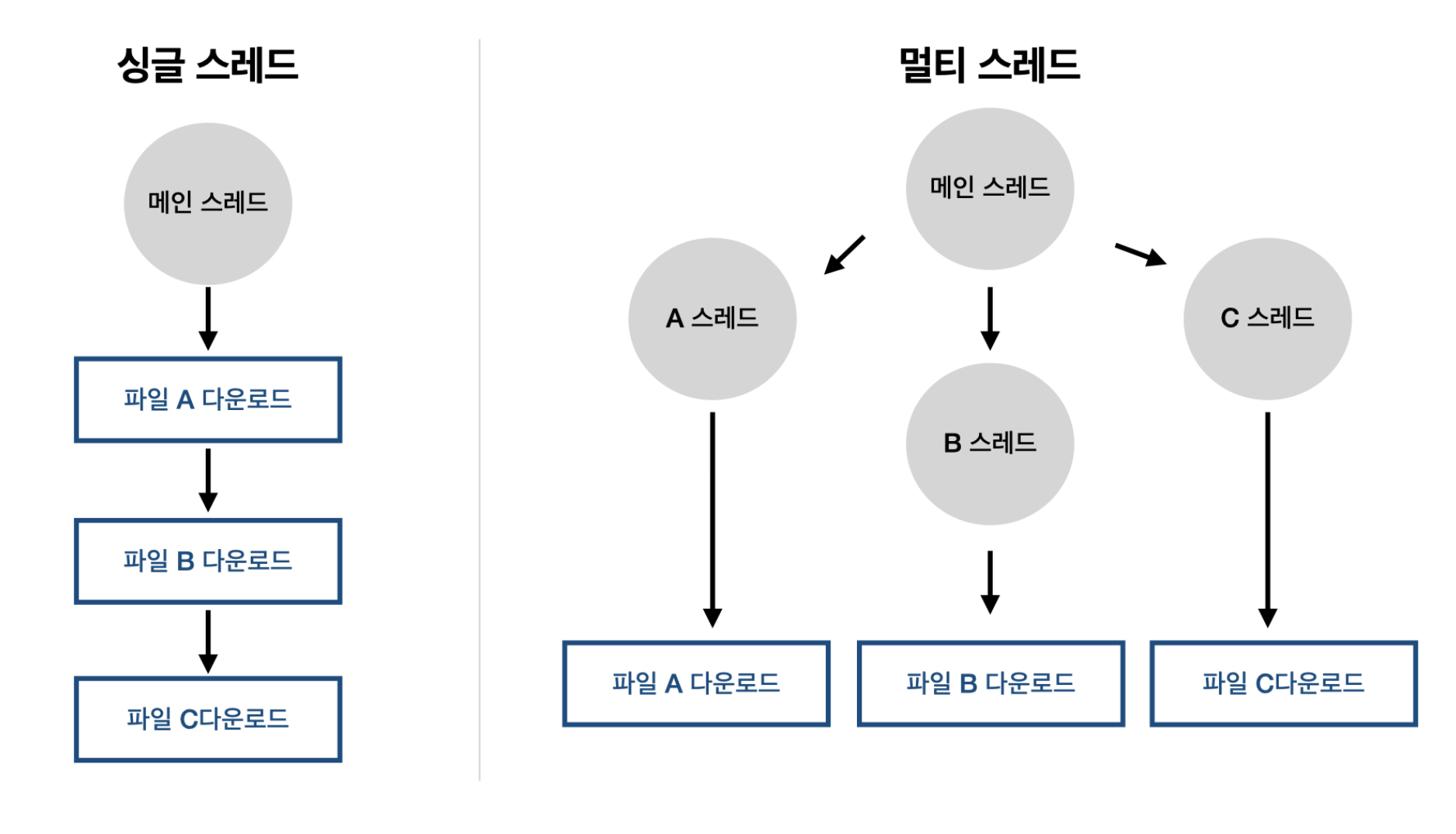
스레드의 생성과 실행
작업 스레드 생성과 실행
Runnable 인터페이스를 구현한 객체에서run()을 구현하여 스레드를 생성하고 실행하는 방법
public class ThreadExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Runnable 인터페이스를 구현한 객체 생성
Runnable task1 = new ThreadTask1();
// Runnable 구현 객체를 인자로 전달하면서 Thread 클래스를 인스턴스화하여 스레드를 생성
Thread thread1 = new Thread(task1);
// 위에 두줄의 코드는 Thread thread1 = new Thread(new ThreadTask1()); 로 쓸 수 있음
// 작업 스레드를 실행시켜, run() 내부의 코드를 처리하도록 합니다.
thread1.start();
}
}
class ThreadTask1 implements Runnable {
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.print("#");
}
}
}Thread 클래스를 상속 받은 하위 클래스에서run()을 구현하여 스레드를 생성하고 실행하는 방법
public class ThreadExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadTask2 thread2 = new ThreadTask2();
// 작업 스레드를 실행시켜, run() 내부의 코드를 처리하도록 합니다.
thread2.start();
}
}
class ThreadTask2 extends Thread {
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.print("#");
}
}
}익명 객체를 사용하여 스레드를 생성하고 실행하기
- Runnable 익명 구현 객체를 활용한 스레드 생성 및 실행
public class ThreadExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 익명 Runnable 구현 객체를 활용하여 스레드 생성
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.print("#");
}
}
});
thread1.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.print("@");
}
}
}- Thread 익명 하위 객체를 활용한 스레드 생성 및 실행
public class ThreadExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 익명 Thread 하위 객체를 활용한 스레드 생성
Thread thread2 = new Thread() {
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.print("#");
}
}
};
thread2.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.print("@");
}
}
}스레드의 이름
: 스레드는 기본적으로 이름이 가지고 있다.
main 스레드 -> main
그 외 추가적으로 생성된 스레드 -> Thread-n
스레드의 이름 조회하기
- getName() : 스레드의 참조값을 이용하여 스레드의 이름을 조회할 수 있다.
스레드의 이름 설정하기
- setName() : 스레드의 참조값을 이용하여 스레드의 이름을 변경할 수 있다.
스레드 인스턴스의 주소값 가져오기
- currentThread() : 실행 중인 스레드의 주소값을 얻는다.
// 실행중인 스레드의 이름을 알아야 할 때
Thread.currentThread().getName();
// 결과값
main스레드의 동기화
멀티 스레드의 경우 두 스레드가 동일한 데이터를 공유하게 되어 문제가 발생할 수 있다. 이를 방지하기 위해 임계영역과 락을 사용한다.
임계영역(Critical section)
: 오로지 하나의 스레드만 코드를 실행할 수 있는 코드 영역
락(Lock)
: 임계 영역을 포함하고 있는 객체에 접근할 수 있는 권한
임계영역을 설정하는 방법
- 기본적으로
synchronized키워드를 사용하여 영역을 지정하는데 2가지 방법이 존재한다.
- 메서드 전체를 임계 영역으로 지정하는 방법
: 메서드의 반환 타입 좌측에synchronized키워드를 작성한다.
public synchronized boolean withdraw(int money) {...}- 특정한 영역을 임계영역으로 지정하는 방법
:synchronized(해당영역이 포함된 객체의 참조) {코드}
public boolean withdraw(int money) {
synchronized (this) {
if (balance >= money) {
try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (Exception error) {}
balance -= money;
return true;
}
return false;
}
}스레드 상태와 실행 제어
스레드 실행 메서드
- start() : 스레드의 상태를
실행 대기 상태로 만들어주는 메서드
스레드 실행 제어 메서드
- sleep(long milliSecond) : milliSecond 동안 스레드를 잠시 멈춥니다.
Thread 클래스의 메서드이므로Thread.sleep();로 호출하는 것을 권장💡 sleep() 메서드를 사용하여 스레드가 일시 정지 상태가 되었다. 다시 실행 대기 상태로 바꾸는 방법은?
1. 인자로 전달한 시간 만큼의 시간이 경과한 경우 실행 대기 상태로 바뀐다.
2.interrupt()를 호출한 경우 - 주의 사항
interrupt()를 호출하면 기본적으로 예외가 발생한다.
따라서sleep()를 사용할 때는try-catch문을 사용해야 한다.try { Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (Exception e) {} - interrupt() : 일시 중지 상태인 스레드를 실행 대기 상태로 복귀시키는 메서드
- yield() : 다른 스레드에게 실행을 양보하느 메서드
- join() : 다른 스레드의 작업이 끝날 때까지 기다리는 메서드
- wait(), notify() : 스레드 간 협업에 사용되는 메서드
