1. End to End Illustrative
1) Data Warehousing?
- Moving some data from data source into single database
2) Data Cleansing?
- Correcting missing data, wrong data and non-standard data
3) Star Schema for Data warehouse
- Star schema : data warehouse에 사용되는 data modeling
- join, grouping, aggregation 등을 통해 없는 정보를 추가하고, 정제하고 등등하여 (tool을 사용) star schema 작성
=> legacy data로 부터 D/W를 만드는 것이 쉽지는 않음 (but, 중요한 concept)
① fact table (center) : 분석의 주제 테이블, only, 핵심 수치나 속성을 포함 (대량)
② dimension table : fact table에 추가 정보(세부 정보)를 제공하며, fact table의 외래키를 기본키로 가지고 있음 (주로 fact table보다 volume이 작음)
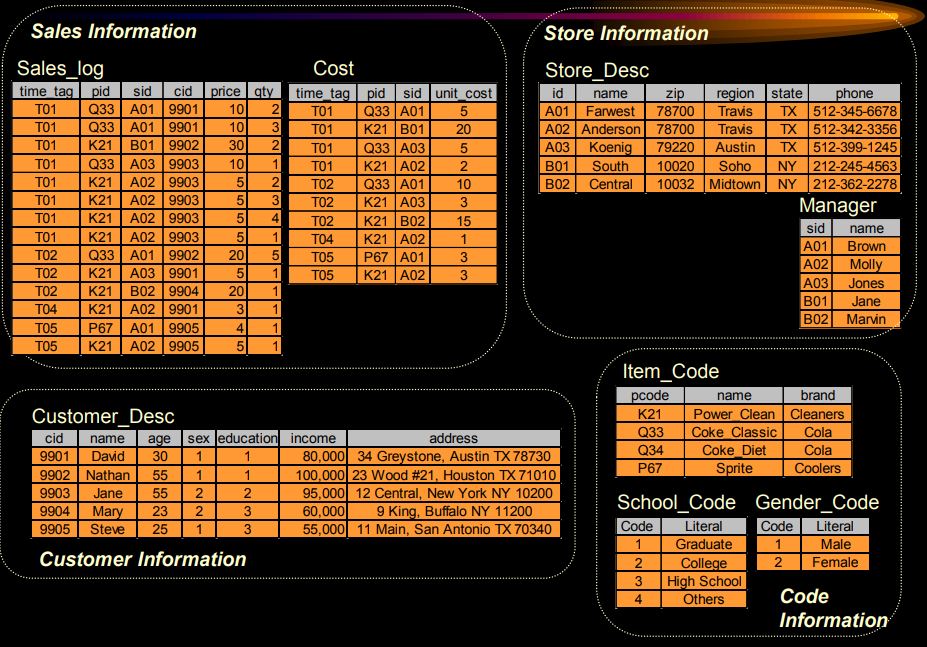
e.g. building sales table from sales_log & cost
- Data Sources (lots of dirty data)
- ETL (Extract-Transform-Load)
Sales_log테이블과 Cost테이블을 time_tag,pig,sid를 조인 속성으로 조인
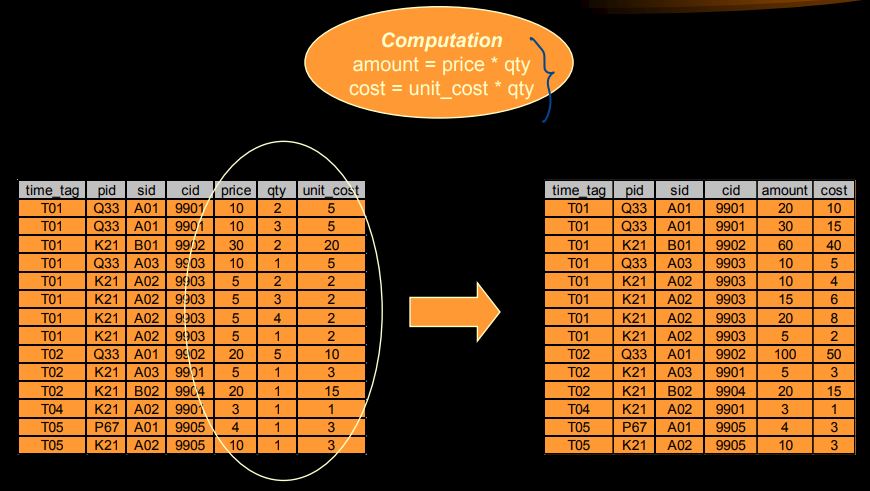
- ETL (Computation: amout = price qty, cost = unit_cost qty)
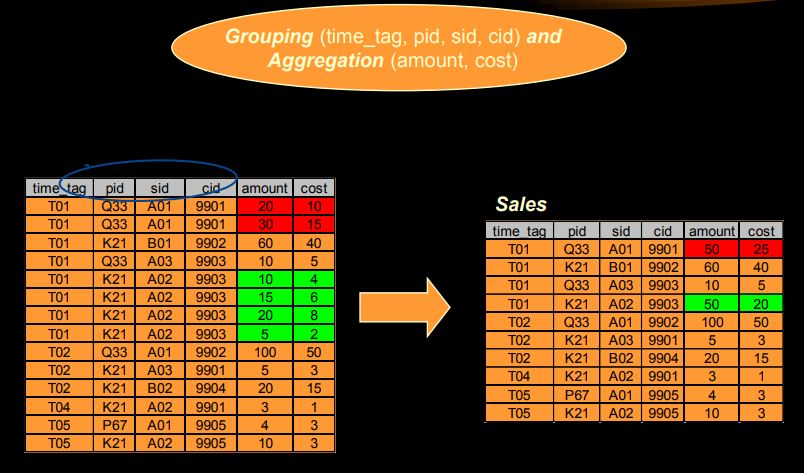
- ETL (GROUP BY time_tag, pid, sid ,cid) AND AGGREGATION(amount, cost)
3. OLAP
Viewing summary data from different perspectives
Data를 3차원으로 보는 것 (즉 동일한 데이터를 다른 측면에서 보는 것)
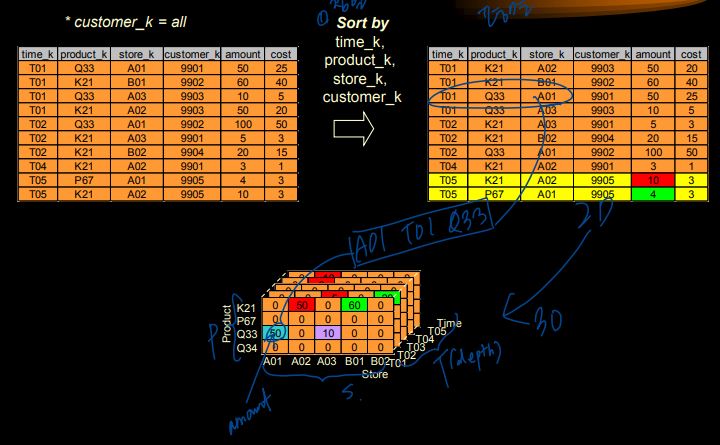
1) Building Cubes(3D)
e.g. Building Cubes from SALES table
- X축(store_k), Y축(product_k), Depth(time_k)
2) OLAP & DW
① Roll-up and Drill-down
: based on Hierarchy of Dimension
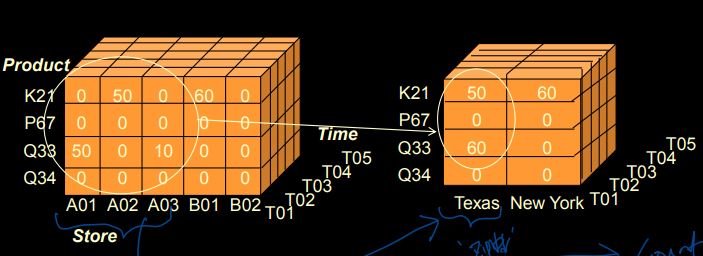
- A01,A02,A03 store "Texas"로 묶어서 'roll-up'
② Slicing
: 특정 값을 기준으로 '단면'으로 slicing
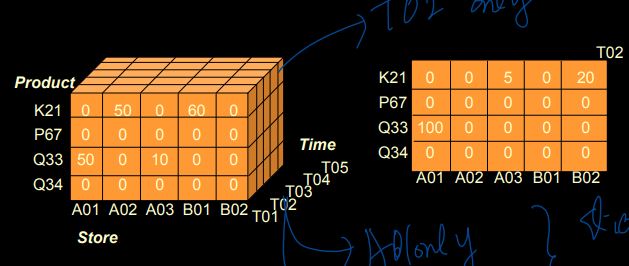
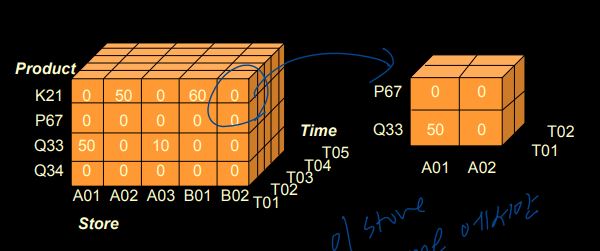
③ Dicing
: 특정 범위를 기준으로 'smaller cube'로 dicing
④ Pivoting
: cube를 회전하여 축을 변경
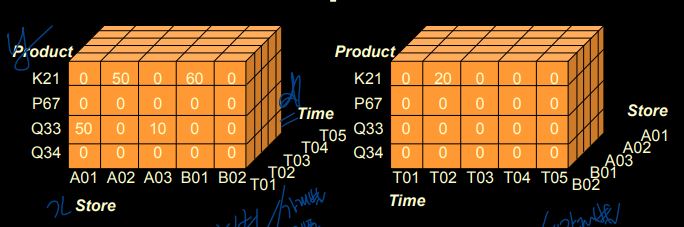
왼쪽 : Time 기준 / 오른쪽 : 가게 기준
=> 분석의 기준 축을 변경할 수 있음
=> Data Analysing in OLAP!
4. Decision Tree
1) Data Mining using Decesion Tree
Data Mining - Priori Algorithm 에서는 Priori 알고리즘을 사용한 Data Mining을 다룬다. 또 다른 Data Mining 방식으로는 Decision Tree가 있다.
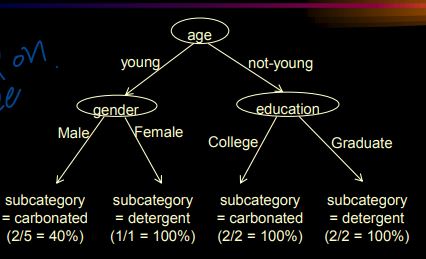
e.g.
- Young Male customers are likely to buy 'carbonated' (40%)
- Young Female customers are likely to buy 'detergent' (100%)
- Not-Young college customers are likely to buy 'carbonated' (100%)
- Not-Young Graduate customers are likely to buty 'detergent' (100%)
Those are interesting rules extracted from decision tree
which can lead to follwoing marketing
ⓐ advertise 'carbonated' to young male & not-young college customers
ⓑ advertise 'detergent' to young female & not-young graduate customers


Thanks for sharing your insights on the relationships between databases, data warehouses, and OLAP. Your concise explanation provides a clear understanding of their interplay. For those interested in delving deeper into the realm of enterprise data warehouses, I recommend checking out this informative article: https://www.cleveroad.com/blog/enterprise-data-warehouse/.