1. 문제 개요
N행xM열 미로가 주어진다. 이 미로는 좌상단이 (1,1), 우하단이(N,M)인 좌표로 표현된다.
이때 미로 위의 값이 '1'인 경우 이동할 수 있는 칸이며, '0'인 경우 이동할 수 없는 칸이 된다.
(1,1)에서 시작하여 (N,M)에 도달하기 위한 최소 칸의 수를 출력하고자 한다.
BFS 알고리즘을 통해 최소 칸의 수를 탐색할 수 있다.
@ DFS가 아닌 BFS가 최소 도달 거리(최소 탐색 칸의 수)를 보장하는 이유는?
DFS가 최소 도달 거리를 보장하지 않는 가장 큰 이유는 "백트래킹" 때문이다.
DFS는 도달할 수 있는 최대 깊이의 정점까지 도달한 후 백트래킹하여 다시 그 다음 정점을 탐색한다. 이로 인해 최소 도달 거리를 보장할 수 없다.
2. 입출력 및 제한 사항
1) 입출력
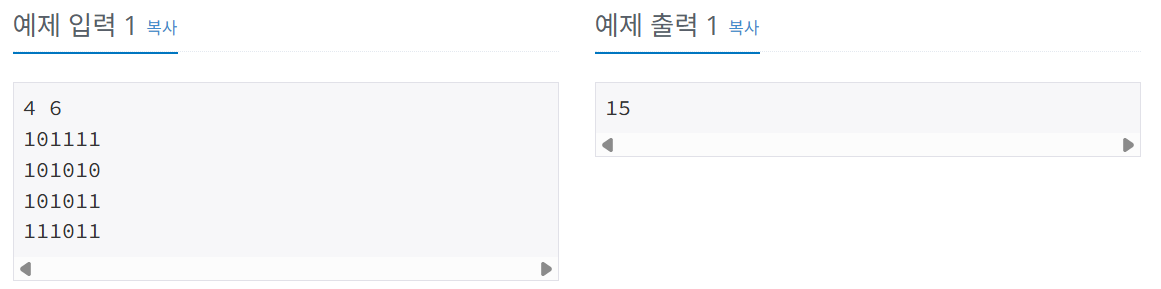
- 첫 째 줄에 두 정 수 N,M (2<=N,M<=100)이 주어진다.
- 다음 N개의 줄에서는 M개의 정수로 미로 정보가 주어진다.
- 이때 각 정수는 붙어서 입력된다.
즉, N행M열의 미로 정보가 주어진다.
3. 알고리즘 개요
(1,1) : 좌상단 -> (N,M) : 우하단 최소 도달 거리 탐색을 위해 BFS를 구현한다.
이때 미로의 2차원 배열 정보를 저장하는 변수 : mp
경로 상 정점의 방문 여부를 저장하는 변수 : v
다음으로 탐색할 방향을 결정하는 방향 변수 : dx, dy
4. Solution I.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int n,m;
int count=0;
vector <vector<int>> mp;
vector <vector<bool>> v;
vector <vector<int>> dis;
int dx[4]= {0,0,1,-1};
int dy[4]= {1,-1,0,0};
int main()
{
cin>> n>>m;
mp = vector<vector<int>> (n+1,vector<int>(m+1));
v = vector<vector<int>>(n+1, vector<int>(m+1,false));
dis = vector<vector<int>>(n+1,vector<int>(m+1,0));
for (int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
int val;
for (int j=0;j<m;j++)
{
cin>>val;
mp[i+1][j+1]=val;
}
}
// BFS 수행
count =1;
queue<pair<int,in>>q;
q.push({1,1});
v[1][1]=true;
dis[1][1]=1;
while(!q.empty())
{
int cx = q.front().first;
int cy = q.front().second;
if(cx==n&&ny==m) break;
// 다음 방향 탐색
for(int k=0;<4;k++)
{
int nx = cx+dx[k];
int ny = cy+dy[k];
if(nx<=0 || nx>=n||ny<0||ny>=m)continue;
if(v[nx][ny]==false && mp[nx][ny]==1)
{
q.push({nx,ny});
v[nx][ny]=true;
dis[nx][ny] = dis[cx][cy]+1;
}
}
}
count = dis[n][m];
// 최소 방문 칸의 수 출력
cout<<count<<endl;
return 0;
}※ 수행 결과

5. Solution II.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int n, m;
int cnt = 0;
vector <vector<int>> mp;
vector <vector<bool>> v;
vector <vector<int>> dis;
int dx[4] = { 0,0,1,-1 };
int dy[4] = { 1,-1,0,0 };
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
mp = vector<vector<int>>(n + 1, vector<int>(m + 1));
v = vector<vector<bool>>(n + 1, vector<bool>(m + 1, false));
dis = vector<vector<int>>(n + 1, vector<int>(m + 1, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
string row;
cin >> row;
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
// 숫자가 공백없이 주어짐을 체크해야함
// 101111 로주어지면 이 값을 하나의 val에 담게되므로 시간 초과 발생
//cin >> val;
mp[i + 1][j + 1] = row[j]-'0';
}
}
// BFS 수행
cnt = 1;
queue<pair<int, int>>q;
q.push({ 1,1 });
v[1][1] = true;
dis[1][1] = 1;
while (!q.empty())
{
int cx = q.front().first;
int cy = q.front().second;
if (cx == n && cy == m) break;
q.pop();
// 다음 방향 탐색
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int nx = cx + dx[k];
int ny = cy + dy[k];
if (nx <= 0 || nx > n || ny <= 0 || ny > m)continue;
if (v[nx][ny] == false && mp[nx][ny] == 1)
{
q.push({ nx,ny });
v[nx][ny] = true;
dis[nx][ny] = dis[cx][cy] + 1;
}
}
}
cnt = dis[n][m];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
cout << dis[i][j];
cout << endl;
}
// 최소 방문 칸의 수 출력
cout << cnt<< endl;
return 0;
}
수정 사항
- 미로 배열 입력 시 '공백 없이' 숫자 문자열이 제공되므로 string으로 입력받은 후 1자리 씩 int로 변환하여 저장
- 다음 정점 탐색 시 nx와 ny의 값이 n보다 크고, m보다 큰 경우에만 continue 하도록 수정
(각각 n과 m인 경우에는 정상적인 정점으로 봐야함. 최초 배열 선언 시 n+1행 m+1열로 선언되었으므로)
